![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is a biological tourniquet?
|
when tension is exerted in limb wounds
|
|
|
what are halsteads principles? (7)
|
strict aseptic technique
gentle tissue healing meticulous hemostasis preservation of blood supply obliteration of dead space accurate apposition of tissue planes minimization of tension on tissues |
|
|
what happens to skin as dogs age?
|
becomes thinner and less well perfused as it ages, making geriatric skin more susceptible to ischemia and stress
|
|
|
do you close wounds parallel or perpendicular to the lines of tension?
|
parallel
|
|
|
what techniques are recommended for wounds of various sizes?
|
<5cm: direct closure or tension relieving technique
5-10cm: tension relieving technique, skin flap <10cm:tension relieving technique, skin flaps, staged procedures, partial closure, second intention healing. |
|
|
where are shear forces very important to consider?
|
axilla
inguinal jaw/lips joints tail base foot pads |
|
|
name techniques for relieving tension
|
undermine
tension relieving sutures skin stretching techniques pretensioning sutures and presuturing relaxing incisions walking sutures chronic skin expansion |
|
|
in what layer should undermining be performed?
|
in areas with panniculus, undermine deep to that layer
in areas without panniculus undermine down to fascia of musculature, or even take some fascia. |
|
|
what are the most common tension relieving sutures?
|
strong subcutaneous sutures
stent sutures far near, near far far far, near near mattress |
|
|
stent sutures
|
approximately 2 cm away from wound edge
tied after closure of primary line left in for 3-4 days use of buttons is not recommended because they don't distribute the tension as well |
|
|
far near, near far
far far, near near |
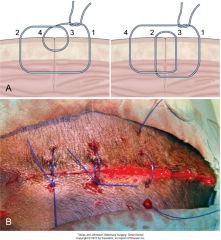
fnnf: about 1cm from wound edge
ffnn: about 5mm from wound edge good for minor tension or cyclic tension equally effective, surgeon's preference keep fairly loose often interspersed with simple interrupted |
|
|
where should knots be placed for tension releiving sutures?
|
NOT over the incision but off to the side
|
|
|
horizontal mattress.
|
genrally not recommended for SA reconstruction because horizontal part can compromis blood supply
|
|
|
vertical mattress.
|
causes eversion of wound edges
fnnf more functional? |
|
|
what are some skin stretching techniques?
|
pretensioning sutures
|
|
|
pretensioning sutures
|
take advantage of mechanical creep and stress relaxation (viscoelasticity)
|
|
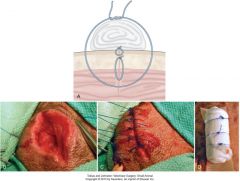
|
stent suture
|
|
|
stent
|
|
|
define pretensioning and presuturing
|
pretensioning:sutures placed to influence an existing wound
presuturing:sutures placed to influence an area planned for excision work well in hock/carpus/trunk, proximal limb |
|
|
4 ways of doing presuturing/pretensioning
|
1.insertion of simple continuous line through skin of wound edges
2.continuous horizontal intradermal running pattern secured through a button at either end 3.externally applied stretching device with velcro (cn also be used postop 4.lemberts (24 hours before sx) 4. |
|
pre
|
simple continuous pretensioning
|
|

|
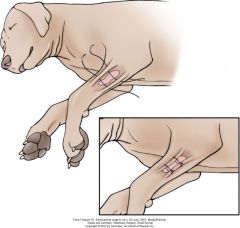
pretensioning velcro
|
|
|
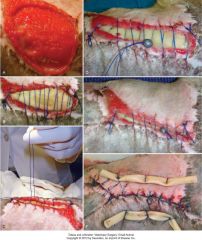
pretensioning vertical mattress
|
|
|
pretensioning sutures in wound on cat dorsum
gradually tightened over several days, then closed |
|
|
axute intraop skin stretching
|
skin hooks, towel clamps, etc.
must tension for 30-45minutes may not provide much benefit over simply undermining |
|
|
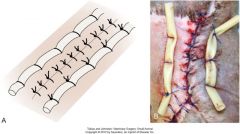
walking sutures
|
staggered rows of interrupted sutured through dermis to underlying fascia
skin appears dimpled must not penetrate epidermis (risk of deep infection) |
|
|
what are some cautions for walking sutures?
|
need fairly think skin
can damage blood supply--not recommended in skin flaps careful of pocketing--not good in infected/contaminated wounds |
|
|
what is chronic skin expansion and when is it indicated
what is biologic creep? |
in treatment of large sefects
in chronic wounds (not for acutely traumatized wounds) utilizes biologic creep: biologic creep is the creation of new dermal and epidermal components after prolonged and constant loading an inflatable silicone device is placed surgically in sq. after initial healing period of few day, it is expanded 10-15% every 48 hours until final volume is reached. decreases sq and fat while expanding epidermis skin perfusion is enhances. best to give it a few days at final volume to improve skin quality |
|
|
name 5 types of relaxing incisions
|
mesh expansion
simple relaxing incision v-y plasty z-plasty m-plasty |
|
|
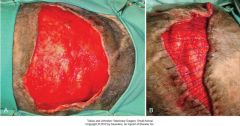
mesh expansion technique
|
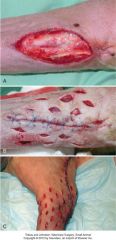
intially wound edges are undermined.
then 1cm stab incisions 1 cm from wound edge and 1 cm apart. rows should be staggered. can mesh circumferentially in a limb oclussive bandage placed until epithelialization skin can look bad for a few days but outcome is usually excellent. not recommended for flaps |
|
|
what is a simple relaxing incision?
what are the measurements? what should you not exceed |
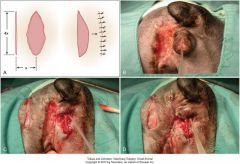
also called a bipedicle flap
great near orifices or important structures incision parallel to wound with length the same as wound and width of healthy skin bridge the same as width of wound length to width issue should not exceed 4:1 because vascular supply to wound bridge can be compromised |
|
|
v-y plasty
|
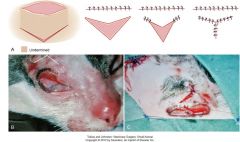
indicated for closing defects that are chronic and surrounded by inelastic skin and closing wounds in areas that could be easily distorted if under tension (near eye)
|
|
|
z plasty
when is it best |
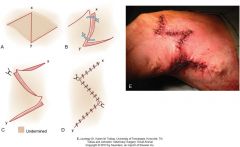
1.along a cicatrix (most commonly used technique for contracture bands in humans)
2.facilitate closure of nearby wounds only perform when sufficient laxity parallel to the wound create central arm perpendicular to the long axis of the wound, at least 3 cm away from wound edge. central limb is directed along lines of tension 3 limbs should be the same length the arms are angled back about 60 degrees (30-90) |
|
|
m-plasty
|
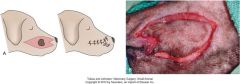
can be used at 1 or both ends of a fusiform incision
useful at sternal end of mastectomy closure |
|
|
m-plasty
|
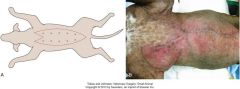
|
|
|
closing crescent shaped defects if disparity between edges less than 20%
|
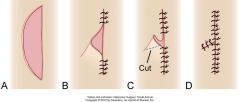
1. edges can be fudged
2.closing the wound from both ends and then cutting the central ear 3.closing the wound from the center and excising both dog ears on the ends |
|
|
fudging the edges to deal with length disparity
|
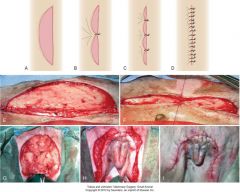
|
|
|
what techniques can you use when there are larger length discrepancies
|
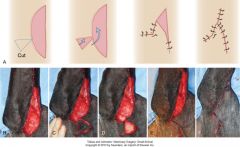
half bow tie technique
equilateral triangle is dissected from the skin of the longer wound edge |
|
|
triangular defects
|
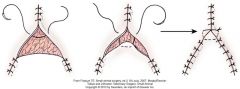
|
|
|
rectangular defects
|
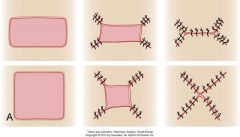
|
|
|
name 4 ways to close circular defects
|
1. close in a linear fashion with excision of dog ears
2.convert to fusiform 3. divide circle into 3 equal arcs. perform 3 point closure 4.combined v-plasty/O to S plasty |
|
|
closure of circular defect with 3 arcs
|
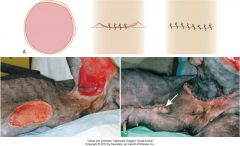
|
|
|
closure of circular defect with Vplasty/ O to S
|
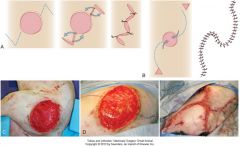
|

