![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
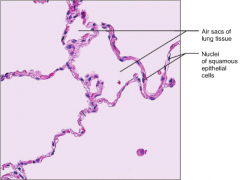
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
S: Single Layer
F: Allows diffusion & filtration were protection is not important. L: Kidney glomeruli; air sacs of the lungs |
|
|
|
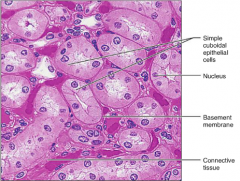
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
S: Single layer
F: Secretion & Absorption L: Kidney tubules; Ducts and secretory portions of small glands |
|
|
|
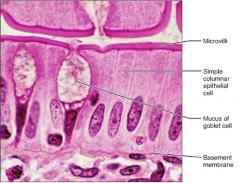
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
S: Single layer
F: Absorption; Secretion of mucus L: Gallbladder |
|
|
|
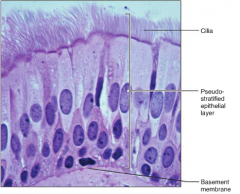
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
S: Single Layer of cells with different heights
F: Secretes substances, mostly mucus L: Trachea, and most of the upper respiratory tract |
|
|
|
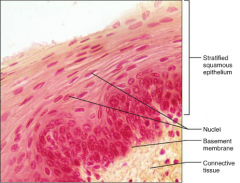
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
S: Thick membrane composed of several cell layers
F: Protects underlying tissues L: Esophagus, Mouth & Vagina |
|
|
|
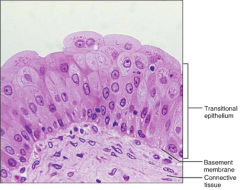
Transitional Epithelium
|
S: Resembles Stratified squamous and Stratified cuboidal
F: Stretches, permits storage of urine L: Lines of the Ureters, Bladder, and part of Urethra |
|
|
|
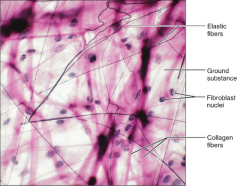
Loose Connective Tissue - (Areolar)
|
S: Gel-like matrix w/all 3 fiber types
F: Wraps & Cushions organs L: Distributed under Epithelia; forms Lamina propria of mucus |
|
|
|
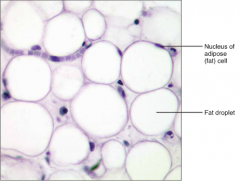
Loose Connective Tissue - (Adipose)
|
S: Matrix like (Areolar), But very sparse
F: Provides reserve food fuel; insulates L: around Kidneys; in Breasts |
|
|
|
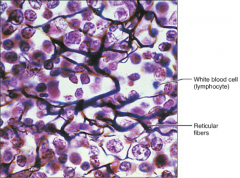
Loose Connective Tissue - (Reticular)
|
S: Network in a loose ground substance
F: Fibers form a Stroma, supporting other cell types L: Lymph Nodes, Bone Marrow, Spleen |
|
|
|
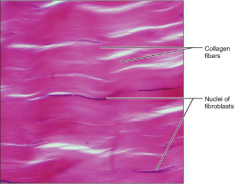
Dense Connective Tissue - (Regular)
|
S: Primarily parallel collagen fibers
F: Attaches muscle to bone or muscle (one directional pull) L: Tendons, and most Ligaments |
|
|
|
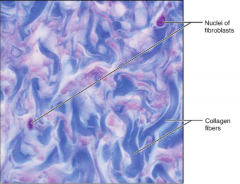
Dense Connective Tissue - (Irregular)
|
S: Irregularly arranged collagen fibers
F: W/stands tension exerted in MANY directions L: Fibrous capsules of Organ and Joints |
|
|
|
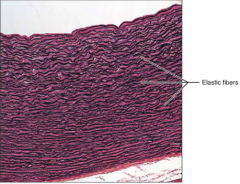
Dense Connective Tissue - (Elastic)
|
S: Contains a high portion of elastic fibers
F: Allows tissues to recoil after stretching L: Wall of large Arteries; W/in walls of the Bronchial tubes |
|
|
|
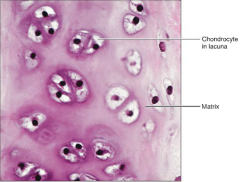
Cartilage - (Hyaline)
|
S: Firm matrix
F: Supports & Reinforces L: Forms most of the embryonic skeleton; Nose; Trachea; Larynx |
|
|
|
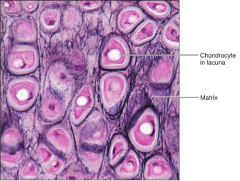
Cartilage - (Elastic)
|
S: Similar to hyaline; but more elastic
F: Maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexability L: External Ear; Epiglottis |
|
|
|
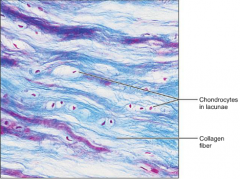
Cartilage - (Firbrocartilage)
|
S: Less firm than in Hyaline
F: Absorbs Compressive Shocks L: Intervertebral discs; Pubic symphysis |
|
|
|
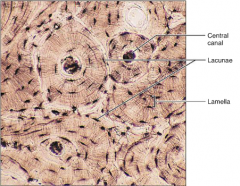
Bone Tissue - (Osseous)
|
S: Hard; Calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers
F: Supports & Protects L: Bones |
|
|
|
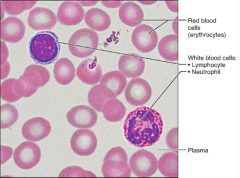
Connective Tissue - (Blood)
|
S: Red & White blood cells in the fluid matrix
F: Transport respiratory gasses, nutrients, wastes L: IN Blood Vessels |
|
|
|
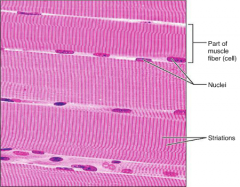
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
|
S: Long; Cylindrical
F: (Voluntary) facial expressions L: In Skeletal muscles attached to bones |
|
|
|
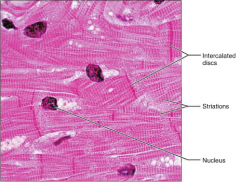
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
S: Branching; Straited
F: (Involuntary) As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation L: The walls of the Heart |
|
|
|
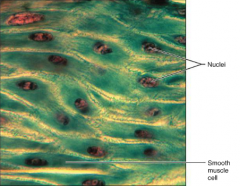
Smooth Muscle Tissue
|
S: Spindle-shaped cells w/in central nuclei
F: (Involuntary) Propels substances along internal passageways L: Walls of Hollow Organs |
|
|
|
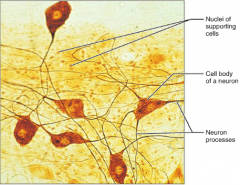
Nervous Tissue
|
S: Neurons are branching cells
F: Transmit electrical signals L: Brain; Spinal cord; Nerves |
|

