![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Simple squamous epithelium |

Allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration |
Air sacs of lungs |
|
|
Simple cubodial epithlium |
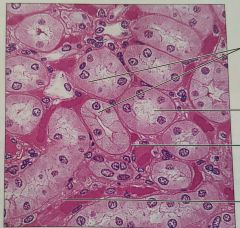
Secretion and absorption |
Kidney tubules |
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium |
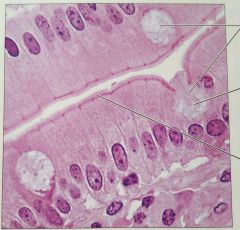
Absorption and secretion |
Digestive tract; stomach and rectum |
|
|
Pseuodostratified columnar epithelium |
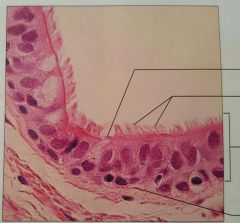
Secretes substances, particularly mucus |
Ciliated variety lines trachea, noncilliated in male's sperm-carrying ducts |
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium |
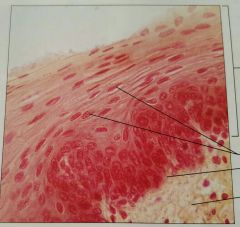
Protects underlying tissues |
Nonkeratinized forms moist lining of esophagus and vagina. Karetinized forms epidermis |
|
|
Stratified cubodial epithlium |
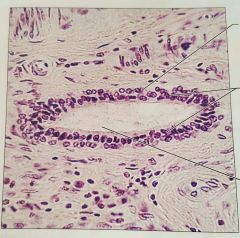
Protection |
Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands. |
|
|
Stratified columnar epithelium |
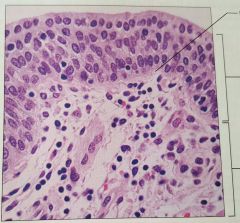
Protection, secretion |
Rare; male urethra, large ducts in some glands |
|
|
Transitional epithelium |
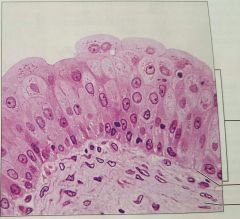
Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organs |
Urinary bladder |
|
|
Embriotic connective tissue: mesenchyme |
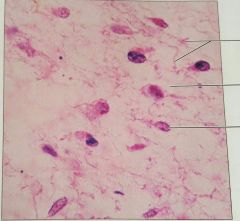
Gives rise to all other connective tissue types |
In embryo |
|
|
CTP: loose connective tissue, areolar |
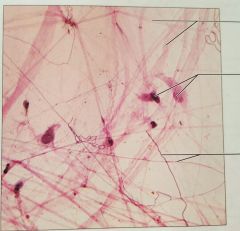
Wraps and cushions organs, important role in inflammation |
Papillary layer of dermis |
|
|
CTP: loose connective tissue, adipose |

Insulates against heat loss |
Found in hypodermic layer, in breast |
|
|
CTP: loose connective tissue, reticular |

Fibers form soft internal skeleton supports other cell types: ie: white blood cells |
Lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen |
|
|
CTP: dense regular connective tissue |
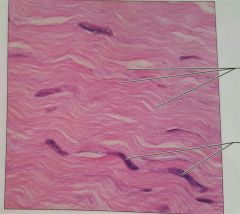
Attaches muscle to bone or other muscle, bone to bone, withstands great tendile stress |
Tendons, most ligaments |
|
|
CTP: elastic connective tissue |

Allows recoild following stretching |
Walls of large arteries, certain ligaments with vertebral column, bronchial tubes |
|
|
CTP: dense irregular connective tissue |
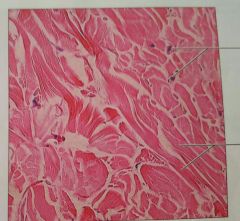
Withstand tension exerted in many directions |
Fibrous capsules of organs, reticular sub-layer of dermis |
|
|
Cartilage: hyaline |

Supports and reinforces, resists compressive stress |
Costal cartilage (ribs), nose, trachea, larynx |
|
|
Cartilage: elastic |
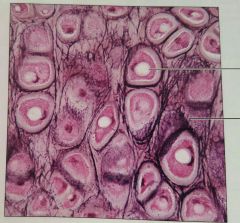
Maintains shape while allowing flexibility |
External ear, epiglottis |
|
|
Cartilage: fibrocartilage |

Tensile strength ability to absorb shock |
Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, knee joint |
|
|
Bones (osseous tissue) |

supports and protects |
Bone |
|
|
Blood |
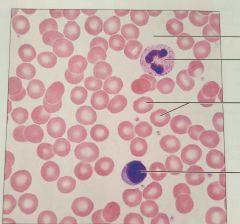
Transports respiratory gases |
Within blood vessels |
|
|
Nervous tissue |

Electrical signals |
Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
|
|
Skeletal muscle |

Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression |
Attached to bone or skin |
|
|
Cardiac muscle |

Propels blood into circulation |
Walls of heart |
|
|
Smooth muscle |
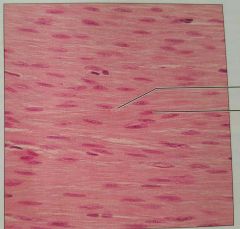
Propels substances or baby along passageways, involuntary |
Walls of hollow organs |

