![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
150 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tissue |
group of cells working together to perform common function |
|
|
Four Types of Tissue |
Epithelial Nervous Connective Muscle
|
|
|
Where do we find Epithelial Tissue? |
Lines inner and outer body surfaces Glands |
|
|
What are the 5 functions of Epithelial tissue? |
Filtration Absorption Sensation secretion Protection
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Epithelial tissues? |
Cells are tightly together Avascular One apical surface Basal (Basement) surface High regeneration capacity
|
|
|
How do we classify Epithelial tissue? |
Number of layers Shape
|
|
|
One layer of Epithelial tissue |
Simple
|
|
|
More than one layer of Epithelial |
Stratified |
|
|
Appears to be more than one layer of Epithelial cells but only one layer |
Pseudostratified |
|
|
Squamous |
Flattened |
|
|
Cuboidal |
Cubed shaped, Same width and height, nucleus in center; round nucleus |
|
|
Columnar |
Tall column shaped cells, more cytoplasm above nucleus than below (often oval shaped nucleus) |
|
|
Simple Squamous |
One layer of flat cells
Diffusion and secretion
Lines body cavity (mesothelium) Forms walls of aveoli in lungs Capillaries (endothelium)
|
|
|
Where would you find simple squamous? |
capillaries (endothelium) Forms walls of aveoli in lungs lines body cavities (mesothelium)
|
|
|
What is the function of simple squamous? |
secretion and diffusion |
|
|
Simple Cuboidal |
One layer, cubed shape cells
Secretion and absorption
Ducts of glands Kidney tubes covering the ovaries
|
|
|
What is the function of simple cuboidal? |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
Where would you find Simple cuboidal? |
Kidney tubes duct of glands covering ovaries
|
|
|
Simple Columnar |
One layer, column shaped, often goblet cells
Absorption and secretion
Lines digestive tract, gallbladder, uterine tubes
|
|
|
Where would you find simple Columnar? |
Digestive tract Uterine tubes Gallbladder
|
|
|
What is the function of simple columnar? |
Absorption and secretion
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous |
Many layers of flat cells
protect underlying skin or tissue from abrasion
skin, mouth, esophagus, rectum, vagina |
|
|
Where would you find stratified squamous? |
Mouth esophagus rectum vagina skin |
|
|
What is the function of stratified squamous? |
protect underlying skin or tissue from abrasion |
|
|
Stratified Cuboidal |
Many layers, cubed shape, round nucleus
secretion
lines sweat glands |
|
|
Where would you find stratified cuboidal? |
Lining of sweat glands |
|
|
What is the function of Stratified cuboidal? |
Secretion
|
|
|
Stratified Columnar |
Apical cells are columnar, cells underneath vary
Secretion
Large duct of glands (salivary gland) |
|
|
Where would you find Stratified Columnar? |
Large duct of glands (salivary glands) |
|
|
What is the function of Stratified Columnar? |
secretion |
|
|
Pseudostratified |
Single layer, but appears to be more, jumbled nucleus ; May contain goblet cells
secretion, propel substances (mucus) across cell surface
upper respiratory tract, male urethra
|
|
|
Where would you find Pseudostratified? |
upper respiratory male urethra
|
|
|
What is the function of pseudostratified? |
to move substances (mucus) across surface |
|
|
Transitional |
Numerous layers, basal cell appears cuboidal, apical cells are dome or balloon shape
Stretches to permit distension of urinary organs
Lines ureter, bladder, renal pelvis
|
|
|
Gland |
one or more cells that produce secretions |
|
|
What are the two types of glands? |
Endocrine
Exocrine |
|
|
Endocrine Gland |
expels secretion (hormones) directly into surrounding tissue , diffuses into bloodstream; ductless |
|
|
Examples of Endocrine Glands |
Thyroid Pituitary Adrenal |
|
|
Exocrine Gland |
expels secretions onto a surface through a duct |
|
|
Types of exocrine Glands |
Unicellular multicellular |
|
|
Describe a unicellular Exocrine Gland |
one cell scattered within epithelium
ie: Goblet cell |
|
|
Describe a multicellular Exocrine Gland |
Has a glandular portion and duct, forms by invagination of epithelium
ie: sweat and oil |
|
|
How do we classify Exocrine Glands? |
Branching of ducts Shape of secretory portion Mode of secretion |
|
|
Types of Ducts |
Compound Simple |
|
|
Compound duct |
Branching |
|
|
Simple duct |
single unbranched duct |
|
|
Shapes of secretory portion |
Acinar/ Alveolar tubular tubuloavealar |
|
|
Acinar/ Alveolar |
grape shaped, pockets or sacs
|
|
|
Tubular |
Tube shaped |
|
|
Tubuloalveolar |
Secretory portion with both tubular and acinar shapes |
|
|
Modes of Secretion |
merocrine apocrine holocrine |
|
|
Merocrine |
Secrete product by exocytosis
ie: Sweat, salivary, pancreas |
|
|
Apocrine |
pinching off of cytoplasm containing
ie: Mammary Gland |
|
|
Holocrine |
Rupture of cell to release secretion
ie: sebaceous (oil gland)
|
|
|
Where do you find Connective Tissue? |
Everywhere |
|
|
What are the 5 functions of Connective Tissue? |
Binds body tissues together Provides structure and support Protection Insulation Transportaion |
|
|
Mesothelium |
Simple squamous lining body cavities |
|
|
Endothelium |
Simple squamous lining capillaries |
|
|
Characteristics of Connective Tissue |
Arise form Mesenchyme Vascularity varies Contains extra cellular matrix Contains Special cells
|
|
|
Extracellular matrix |
Ground substances Fibers
|
|
|
Ground substances
|
Interstitial fluids and proteins various in viscosity ( liquid, gel, solid)
|
|
|
Fibers in Extracellular matrix |
Collagen Elastic Reticular
|
|
|
Characteristics of collagen fibers |
High tensile strength, resist stretch Pink Wavy
|
|
|
Characteristics of Elastic Fibers |
ability to stretch and recoil Thin branched
|
|
|
Characteristics of Reticular Fibers |
Branching network Supports organs Twigs, usually black
|
|
|
Mesenchyme |
Embryo Connective Tissue Star shape Very fine protein filaments between cells Gives rises to all other CT
|
|
|
Areolar Tissue
|
AKA Loose CT
|
|
|
What is the extra cellular matrix like in Areola tissue? |
Gel like
|
|
|
What fibers are in Areolar tissue? |
Elastic Collagen Reticular
|
|
|
Function of Areolar Tissue |
Cushion binds organs holds body fluids defends against infection
|
|
|
Specialized cells in Areolar Tissue |
Fibroblast Masts WBC Macrophages Defends against infection
|
|
|
Where do you find Areolar tissue? |
everywhere, under epithelium Around organs and blood vessels
|
|
|
Adipose Tissue |
Fat tissue
|
|
|
Function of Adipose cells |
Insulation Energy stores Cushioning |
|
|
What is the matrix of adipose tissue? |
Aveolar tissue |
|
|
What are the specialized cells of Adipose tissue? |
adipocytes |
|
|
How can you identify fat tissue? |
Light and airy cells with nuclei squished to top |
|
|
Where do we find adipose tissue? |
under skin around kidneys, abdomen breasts |
|
|
Reticular CT Description |
CT with reticular fibers that provide support for free blood cells, |
|
|
Reticular CT functions |
form soft supportive skeleton for organs and supports Free blood cells |
|
|
Location of Reticular CT |
found in organs with numerous blood cells, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver |
|
|
What is Dense Regular? |
CT that resists unidirectional stress |
|
|
Where do we find Dense regular?
|
Tendon
Ligaments |
|
|
Tendon |
Attach muscle to bone |
|
|
Ligament |
Attach bone to bone |
|
|
Matrix of Dense irregular
|
parallel bundles of collagen fibers
|
|
|
What are the specialized cells of Dense regular? |
Fibroblast |
|
|
Fibroblast |
Makes collagen |
|
|
How do you recognize dense regular? |
Lots of Collagen bundles going same direction
|
|
|
Dense irregular |
CT resists multidirectional stress |
|
|
What is the matrix of dense irregular? |
Randomly arranged bundles of collagen |
|
|
What are the specialized cells of dense irregular? |
fibroblasts |
|
|
Where do you find Dense irregular? |
Dermis of skin Joint capsules
|
|
|
How can you recognize Dense irregular tissue? |
Randomly arranged bundles of collagen
|
|
|
What are the types of cartilage? |
Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage
|
|
|
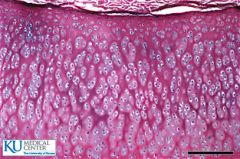
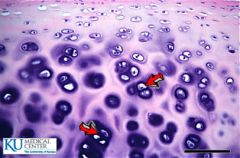
Hyaline cartilage
|
Collagen fibers in a rubbery matrix Chondrocytes appears glassy and uniform
|
|
|
Function of Hyaline Cartilage
|
provide structure yet flexible |
|
|
Where do you find hyaline cartilage? |
Nose, ends of bones, coastal cartilage, tracheal rings
|
|
|
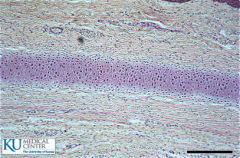
Elastic cartilage
|
Elastic fibers in Rubbery Matrix Chondrocytes
|
|
|
Function of Elastic Cartilage
|
Very flexible able to tolerate repeated bending and maintain shape |
|
|
Location of Elastic Cartilage |
External ear and epiglottis
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage |
Cartilage packed with collagen fibers chondrocytes
|
|
|
Function of Fibrocartilage
|
Withstand heavy pressure and highly compressible |
|
|
Location of fibrocartilage
|
intervertebral disc Pubic symphysis Menisci
|
|
|
Bone |
Matrix composed of hard calcium salts with collagen fibers Osteocytes
|
|
|
Specialized cells of bones |
Osteocytes |
|
|
Where do you find Bone CT |
Bones |
|
|
Function of Bone CT |
Structure for body and protection of organs
|
|
|
Blood |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets surrounded by plasma |
|
|
Where do you find Blood? |
Cardiovascular system |
|
|
Muscle Tissue |
produces movement |
|
|
Types of Muscle Tissue |
Cardiac Smooth Skeletal
|
|
|
Describe Skeletal Tissue |
Long parallel, cylindrical cells Multiple nuclei Striations |
|
|
Function of Skeletal Tissue |
Movement of bones and facial expressions involuntary
|
|
|
Location of Skeletal tissue |
attach to bones |
|
|
Describe smooth Muscle Tissue |
Fusiform shaped cells that interdigitate no visible striations single central nucei
|
|
|
Functions of smooth muscle |
Movement of substances through organs involuntarily
|
|
|
Location of smooth muscle |
surrounds hollow organs |
|
|
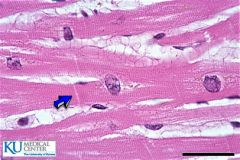
Describe Cardiac muscle |
Branching striated cells central round nuclei Intercalated disks
|
|
|
Function of Cardiac Muscle |
pump blood, involuntary |
|
|
Location of Cardiac Muscle |
Heart |
|
|
Nervous Tissue |
Consists of neurons and nuero glial cells |
|
|
Function of Nervous tissue |
transmit impulses throughout the body |
|
|
Location of nervous tissue |
Brain Spinal cord nerves
|
|

|
Simple squamous |
|
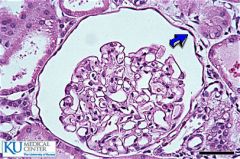
|
Simple squamous |
|
|
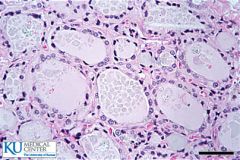
Simple cuboidal |
|
|
Simple Cuboidal |
|
|
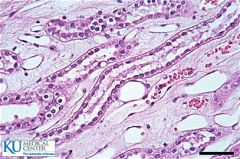
Simple columnar |
|
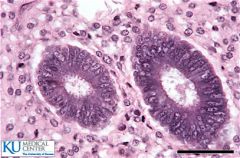
|
Simple columnar |
|
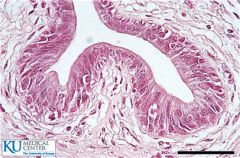
|
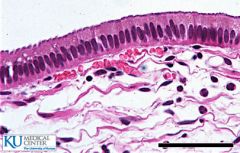
Pseudostratified |
|
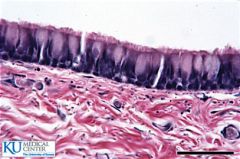
|
Ciliated Pseudostratified |
|
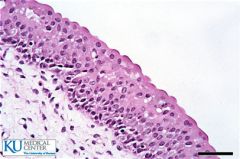
|
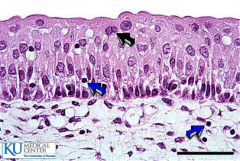
Transitional |
|
|
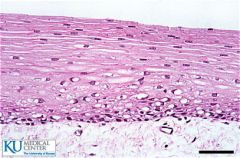
Transitional |
|
|
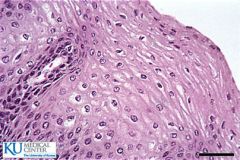
Stratified Squamous |
|
|
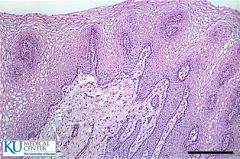
Stratified squamous |
|
|
Stratified squamous |
|
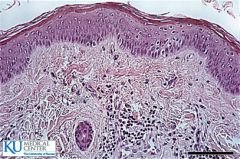
|
Keratanized Stratified squamous |
|
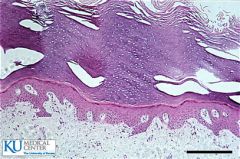
|
Keratanized Stratified squamous |
|
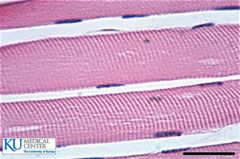
|
Skeletal Muscle |
|
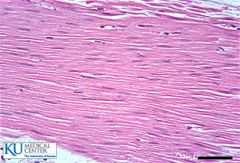
|
Smooth muscle |
|
|
Cardiac Muscle |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Chondrocytes Hyaline Cartilage |
|
|
Elastic cartilage |
|
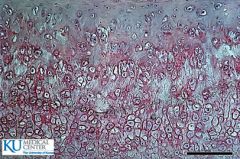
|
Elastic cartilage
Chondrocytes
|
|
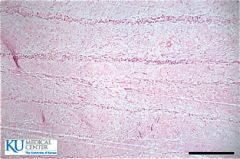
|
Fibrocartilage
|
|
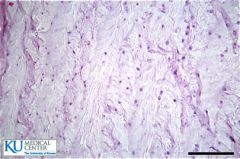
|
Fibrocartilage |
|
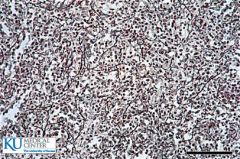
|
Reticular CT |
|
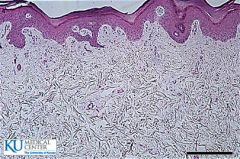
|
Dense Irregular |

