![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thyroid Gland: Originates from the? Has a follicles that are surrounded with? What cells line the follicles? The lumen is filled with? What other cells surround follicles? If the thryoid gland is absent in the fetus, what develops? |
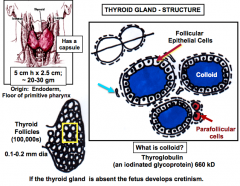
Endoderm CT from the capsule -has many blood vessels Follicular epithelial cells -cuboidal Thryoglobulin -Iodinated glycoprotein that give rise to T3 and T4 Parafollicular cells Cretinism (deficiency of T3 and T4) |
|
What functions do the vessels serve? |
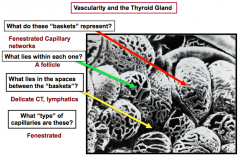
Vessels carry T3 and T4 to the rest of the body |
|
|
Thyroid follicular cell carries what 2 processes simultaneously? This cell is polarized |
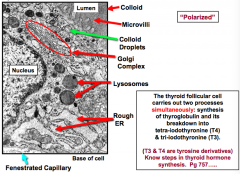
1. synthesizes thyroglobulin and stores it in the lumen (colloid) 2. reabsorbs thryoglobulin and the lysosome in the cell breaks it down into tri-iodothyronine (T3) and tetra-iodothyronine (T4) -T3 and T4 are tyrosine derivatives -Regulatebasal metabolism, heat production, growth and development |
|
|
1. __ is synthesized in rough ER 2. Terminal sugars are added to it in the Golgi 3. Thyroglobulin is released into the __ 4. __ of thyroglobulin occurs in the colloid 5. Uptake of colloid by __ 6. __ fuses with colloid droplet and thyroglobulin is degraded to T3 and T4 7. They diffuse out of the cell 8. Enter the capillary lumen |
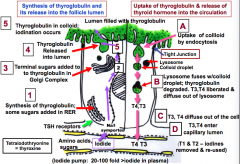
1. Thyroglobulin -made from a.a, sugars, and eventually iodide 3. Lumen 4. Iodination 5. Endocytosis 6. Lysosomes |
|
|
Parafollicular cells (C cells) have dense granules that contain? What does it act on? What does it do? |
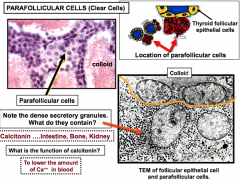
Calcitonin Acts on intestine, bone, and kidney Lowers Ca++ in blood |
|
|
Ways Calcitonin lowers blood Ca++ levels: 1. Inhibits Ca++ absorption in the? 2. Inhibits __ activity in bones 3. Inhibits __ allowing it to be secreted in the urine 4.Protects against calcium loss from skeleton during periods of calcium mobilization (such as pregnancy and lactation) 5. Does the opposite of parathyroid hormone, but electrolyte reabsorption in the kidneys is the same. What does it inhibit? |
1. Intestine 2. Osteoclast (breakdown bone) 3. Renal tubular cell resorption of Ca++ 5. Phosphate reabsorption by kidney tubules |
|
|
ReadClinical Correlation on Abnormal Thyroid Function on page 585-587
|
- |
|
|
Where are the parathyroid glands located and how many parathyroid glands are present? |
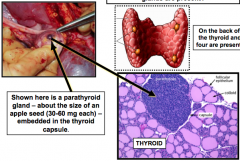
On the back of the Thyroid 4 are present (size of an apple seed) |
|
|
What tissue makes up the capsule of the parathyroid gland? Parathyroid gland has what 2 cells? |
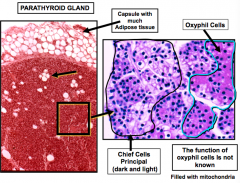
Adipose tissue 1. Chief cells (mainly) = dark and light -Make parathyroid hormone -has abundant RER, golgi, and secretory granules 2. Oxyphil cells = eosinophilic and filled with mitochondria |
|
|
Regulation of parathyroid hormone
1. PTH brings about the breakdown of bone, which results in? 2. It acts in the kidney to? 3. Acts on gut to increase absorption of Ca++ 4. PTH also increases excretion of __ by kidney tubules which does what to the urine and blood? What turns off PTH release? |
1. Release of Ca++ thereby increasing level of Ca++ in the circulating blood 2. Increase reabsorption of calcium from the urine in proximal convoluted tubule 4. Phosphate! -raises phosphate in the urine which leads to decrease of phosphate in blood Increase of Ca++ in the blood inhibits release of PTH by chief cells |
|
|
Whatwould happen if these glands were removed during a thyroidectomy?
|
If the glands are removed in theirentirety the individual can die
-muscles of the respiratory system and thelarynx will go into stay contracted because of a drop in bloodcalcium -Acts at the level of bone, kidneyand gut |
|
|
The Adrenal gland is embedded in __ and is found? Its encapsulated with __ that extend into the parenchyma and has? |
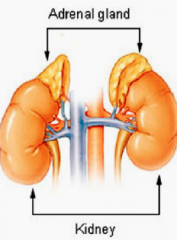
Embedded in Fat Sits on top of the kidney CT trabeculae -has blood vessels and nerve |
|
|
The __ accounts for 90% of the volume of the adrenal gland, and the __ is about 10% What do each of these produce? |
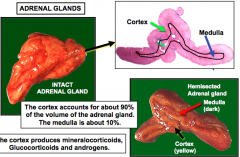
Cortex = 90% Medulla = 10% Cortex produces mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens Medulla produces catecholamines |
|
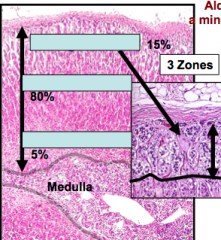
What are the 3 zones of the cortex in the adrenal gland? Which zone produces and stores aldosterone? |
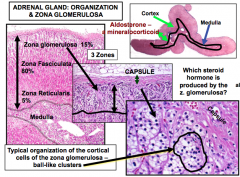
Zona glomerulosa Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis -Z. glomerulosa produces and stores aldosterone |
|
|
What 4 things does aldosterone act on? What 4 things does it stimulate? |
1. Distal tubules of the nephron in the kidney 2. Gastric mucosa 3. Salivary glands 4. Sweat glands 1. Conservation of sodium 2. Secretion of potassium 3. Water retention 4. Stabilizes blood pressure |
|
|
Renin-Antiogensin-Aldosterone review -Fluid and electrolyte balance 1. Decreased BP and decreased sodium in plasma causes juxtaglomerular cells to release? 2. This is released into the blood converting angiotensinogen to angiotensin I 3. Angiotensin I becomes angiotensin II by ACE in the? 4. This circulation causes cells of zona glomerulose of the adrenal gland to secrete? 5. This goes in the general circulation acting on distal convoluted tubule and collecting tubule 6.What does this cause? 7. This leads to increase in volume of fluid and sodium in BV, increasing BP and turns off renin secretion |
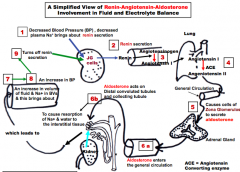
1. Renin 3. Lung 4. Aldosterone 6. Resorption of Na+ and water to the interstitial tissue |
|
|
What steroid hormone is made by the Zona fasciculata? What is this under the control of? Cells of this zone is arranged in? Also has capillaries between cords and CT that supports cords and capillaries |
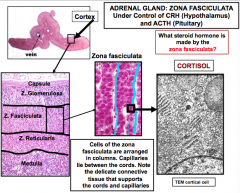
Cortisol -Hypothalamus- corticotropic releasing hormone (CRH) -Pituitary- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) columns |
|
|
Thecortical (adrenocortical) cells of all zones have abundant SER and many mitochondria. Why?
Thecortical cells of the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculataoften have a “spongy” look. Why? FUNCTIONS OF CORTISOL: -Promotes normal metabolism, especially carbohydrate. -Stimulates glycogen synthesis in liver. -Stimulates mobilization of fats -Suppresses inflammation -Also involved in resistance to stress. |
Because both organelles bear the enzymesthat are involved in synthesizing thesteroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex
Becausethecellscontainmanylipid droplets |
|
|
Adrenal Gland: Zona reticularis What steroid hormone is made here? What distinguishes this zone? This zone contains many? |
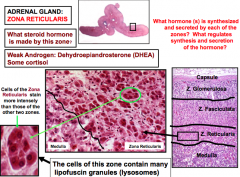
Androgen: Dehydroepiandosterone (DHEA_ and some cortisol Cells are dark red lipofuscin granules (lysosomes) |
|
|
Adrenal Medulla (center region): Chromaffin and Autonomic ganglion cells There are 2 types of chromaffin cells, what do each of them make? Autonomic ganglion cells are neurons with no known function What is one way to distinguish the Medulla? |
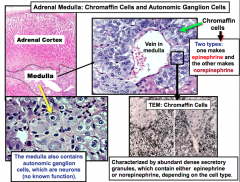
Chromaffin: - One makes epinephrine - One makes norepinephrine Has large thin walled veins in the medulla |
|
|
Chromaffin cell has secretory granules containing epinephrine or norepinephrine. 80% of the output of the medulla is the? There's an axon of preganglionic neuron (it's cell body is in the spinal cord), that signals chromaffin cell to release epinephrine an norepinephrine to the? These hormones result in vasoconstriction, increase glucose, re-routes blood flow to skeletal muscle, etc. |
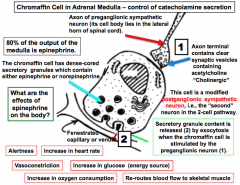
Epinephrine Fenestrated capillaries/venules by exocytosis |
|
|
Normally a cell would have a postsynaptic axon, but it does not. This cell is a?
Why does it not have a postsynaptic axon? |
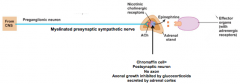
Modified postganglionic sympathetic neuron
Glucorticoid made in the cortex are brought down to the medulla by the blood vessels and inhibit axonal growth |
|
|
Pineal Gland Pine-cone like structure Develops from the neuroectoderm Located near the center of the brain It's a __ organ What else does it do? It has glial cells called? -Has calcified concentrations called brain sand (corpora aranacea) used to identify pineal gland |
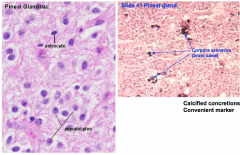
Photosensitive organ Time keeper of the body -regulator of day/night cycle = Circadian rhythm Pinealocytes |
|
|
Pineal gland: During daylight what happens? During night what happens? Stimulated at night Pinal gland and adrenal medulla do something similar, transduces a signal from the __ to a __ |
Daylight: Inhibition of Melatonin Night: Stimulation of Melatonin Transduce signal from sympathetic NS into a hormonal signal |
|
|
Besides adjusting to changes in day length and having a role in emotional response to change in length of day and temperature, it regulates reproductive function How does it do this? What does this result in? Tumors that destroy the pineal gland are associated with? |
Blocks production of GnRH from neurons in the hypothalamus Decreased GnRH results in decrease in release of FSH and LH from pituitary. Precocious puberty (early puberty) |

