![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bronchiolitis |
RSV coryza Nasal flare WHEEZE difficulty feeding Bibasal crepts Rx Humidified Oxygen Admission for observation |
|
|
Anaphylaxis serum tryptase |
Elevated Upto 12 hours |
|
|
Radio femoral delay seen in |
COA |
|
|
Acute epiglottitis organism |
Hemophilus influenza B Stridor Drooling of saliva Dysphagia Thumb sign lateral x-ray Rx- intubate |
|
|
Croup |
Parainfluenza virus
Barking cough Resonant chest Steeple sign on x-ray
Rx
Single dose DEXAMETHASONE 0.15mg/kg to All
High flow oxygen+ nebs with adrenaline
Prognosis - natural resolution
|
|
|
Dysgraphia rx |
Refer to education psychologist |
|
|
ADHD rx |
Children- Methylphenidate (first line), ADHD-focused group parent-training programme
• Adults- Lisdexamfetamine or Methylphenidate first line in adults, CBT
• With Insomnia?- First line- Sleep hygiene, Second line- Melatonin |
|
|
Whooping cough/ pertussis |
Bordatella pertussis Bouts of cough Posttussive vomiting Cyanosis after cough Notifiable disease Unvaccinated child ( 2,3,4 months and 3-5 years) Pregnancy 20-32 weeks Ix PerNasal swab culture of bordatella PCR and serology Rx Macrolides |
|
|
LP contraindication |
LP Contraindications
Increased ICP Bulging, tense fontanelle Ongoing seizure GCS<9 or a drop of > 3 Unequal, dilated, unresponsive pupils Papilloedema |
|
|
When is g6pd enzyme activity checked |
6 weeks after the hemolytic attack |
|
|
Conjugated and unconjugated B stools |
Conjugated pale stools Unconjugated yellow stools |
|
|
Heinz bodies and bite cells in |
G6pd |
|
|
Biliary atresia ix |
Percutaneous biospy |
|
|
Painless vision loss |
Amourosis fugax Crao Crvo Retinal detachment |
|
|
D shaped pupil |
Iridodialysis |
|
|
Myopia is a RF for |
Cataract Open angle glaucoma Retinal detachment Retinitis pigmentosa |
|
|
Hypermetropia is a RF for |
Angle closure glaucoma |
|
|
RAPD |
optic neuritis ( monocular visual field loss) Crao Retinal detachment |
|
|
Central scotoma |
Optic neuritis Macular degeneration |
|
|
Tunnel vision nasal scotoma |
Retinitis pigmentosa Open angle glaucoma |
|
|
Floaters in |
Proliferative Diabetic retinopathy Retinal detachment CMV retinitis |
|
|
Ankylosis spondolytis seen in which eye disease |
Iritis / ant uveitis |
|
|
RA seen in which eye disease |
Scleritis/ episcleritis Sjogerns Steroid induced cataract |
|
|
Eye nerves |
LR6 SO4 O3 |
|
|
Acute iritis Sx Ix Rx |
Inflammation of iris and ciliary body Painful red eye Marked photophobia Irregular pupil, constricted and sluggish Hypopyon Assoc with Ankylosing spondolytis Reactive arthritis IBD RX Urgent opthalmology review cyclopentolate Atropine Steroids prednisolone Recurrent - cyclosporine |
|
|
Angle closure glaucoma Sx Ix Rx |
Shallow ant chamber Hard globe on palpation Fixed semi dilated pupil Coloured halos Hazy cornea
Rfx Hypermetropia Dark room SSRI / TCA
Ix High IOP ( Tonometry)
RX urgent referral Acetazolamide
BB, steroids
Pilocarpine BB, steroids Peripheral iridotomy Surgical "" Peripheral iridotomy Surgical ""
|
|
|
Open angle glaucoma |
Closed trabecular meshwork Tunnel vision Disc cupping Gradual visual field loss Painless Rx First line- prostaglandin analogue - Latanoprost topical BB topical Acetazolamide Trabeculoplasty |
|
|
Retinal detachment Sx Ix Rx |
Sx 4F Flashes Floaters Field loss Fall in acuity Painless + curtain falling down RAPD positive Ix Direct ophthalmoscopy - grey wrinkled retina balloons forward Rx Scleral buckling |
|
|
Retinitis pigmentosa |
Family Hx Night blindness Tunnel vision Black bone spicule pigmentation Mottling Routine referral |
|
|
Impaired red colour vision in which eye disease |
Optic neuritis |
|
|
Optic neuritis |
Assoc with Multiple sclerosis Triad: Pain on movement Central scotoma Impaired colour vision (red first) If RAPD positive then - monocular visual field loss Swollen pale optic disc Rx same as MS Acute - methylphenidate oral or IV long term - glatiramer acetate or interferon beta |
|
|
Bacterial conjunctivitis Rx |
<7 days Hygiene with cotton wool >7 days First line - topical chloramphenicol Pregnancy - fucidic acid |
|
|
When to give acyclovir in herpes zoster opthalmicus |
Hutchinson sign positive . immunocompromised IBD |
|
|
Ophthalmia Neonatorum organism |
Chlamydia > gonorrhea |
|
|
Congenital cataract organism |
Rubella |
|
|
Cataract |
Old Age + High Myopia + Eye Trauma + Hx of Steroids (Asthma, COPD, RA) + DM + UV (Australia)
Glare especially at night Dazzling Haloes Absent Red Reflex
• Fundoscopy- Dense opacities (lens becomes cloudy)
Rx- Extracapsular lens extraction f/ b intraocular lens implantation |
|
|
Von Graefe sign |
Failure of upper eyelid to follow promptly and smoothly with downward movement of the eye secondary to thyroid disease |
|
|
When to give finasteride in BPH |
Lower UTI Sx + prostate enlargement >30g +/- high PSA > 1.4Finasteride is 5 alpha reductase inhibitor |
|
|
Anti smooth muscle ab |
Autoimmune hepatitis |
|
|
Anti-mitochondrial ab |
Primary biliary cirrhosis |
|
|
TSH receptor ab |
Graves |
|
|
Polymyositis Ix Rx |
Raised CK, LDH And aldolase AntiJo ab Definitive test - muscle biopsy Rx steroids |
|
|
Dermatomyositis |
Features of polymyositis + Skin problems Helicotrope rash Gottrons papules Shawl sign Raised CK, LDH, Aldolase ANA muscle biopsy Rx Steroids Sun block |
|
|
Polymyalgia rheumatica |
Pain but no weakness in proximal muscles >50 year-old Shoulder, neck and pelvic girdle affected Assoc with giant cell arteritis Normal CK Raised ESR/ CRP Rx steroids |
|
|
Temporal / giant cell arteritis |
Headache, scalp tenderness, jaw claudication, vision loss Ix Initial - ESR definitive - temporal artery biopsy
Rx High dose prednisolone Low dose aspirin
Treat asap. Don't wait for result of biopsy |
|
|
Systemic sclerosis /scleroderma Features Ix |
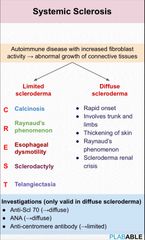
|
|
|
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies |
Conditions • Behcet's disease • Ankylosing spondylitis • Reiter's syndrome • Psoriatic arthritis |
|
|
Behcets disease |
Presentation • Recurrent oral ulcers • Recurrent genital ulcers • Anterior or posterior uveitis • Pathergy - Exaggerated skin injury after minor trauma Treatment • Topical corticosteroids |
|
|
Behcets disease |
Presentation • Recurrent oral ulcers • Recurrent genital ulcers • Anterior or posterior uveitis • Pathergy - Exaggerated skin injury after minor trauma Treatment • Topical corticosteroids |
|
|
Ankylosing spondolytis |
Ankylosing Spondylitis • Back pain and morning stiffness • Pain improves with physical activity, not with rest • Tenderness of sacroiliac joint • Anterior uveitis • X-ray - Sacroiliitis • males < 30 years of age
Treatment • Physiotherapy • NSAIDs • Oral corticosteroids • Etanercept and adalimumab (severe cases) Complication: Fusion of the spine (bamboo spine) |
|
|
Reyters syndrome |
• Presents 2-4 weeks after a genitourinary or gastrointestinal infection • C. trachomatis and C. pneumoniae are most common cause • Also, known as reactive arthritis |
|
|
Gout rx |
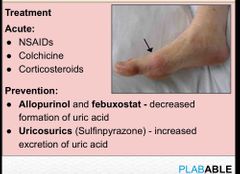
Back (Definition) |
|
|
RA |
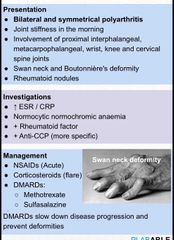
|
|
|
Sarcoidosis has which kind of granuloma |
Non caseating |
|
|
Syndrome with sarcoidosis |
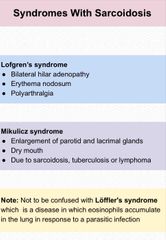
|
|
|
New onset dysphagia requires |
URGENT ENDOSCOPY |
|
|
Hemorrhoids grade |

|
|
|
Diverticulosis affects which part mainly |
Sigmoid colon |
|
|
Acute diverticulitis Rx |
Admit and give IV ABX |
|
|
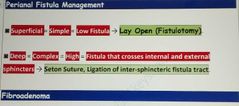
Perianal fistula management |
|
|
|
Patient had epidural analgesia. Catheter removed and unable to void. Urinary retention. What to do |
Bladder scan CheckS post residual volume. If greater than 500ml then reinsert the catheter |
|
|
When to offer prophylactic mastectomy |
1) Strong Family History of breast cancer. 2) Inherited Mutations in Breast Cancer Susceptibility genes (BRCA1 and/or BRCA2). These genes are Autosomal Dominant. 3) Previous breast cancer in one breast. 4) Biopsy that shows -> Lobular Carcinoma in Situ and/or atypical hyperplasia. |
|
|
Cancer of head of pancreas |
Raised ALP, Conjugated bilirubin Itching, pruritus, Jaundice Pale stool Dark urine Hyperglycemia Palpable GB IX Initial US IoC High resolution CT prognosis ca19-9 Rx Without metastasis - Whipple resection (pancreaticoduodenectomy) With metastasis - palliative ERCP with stent |
|
|
Ulcer on medial malleolus. Normal capillary refill. Hemosiderin deposits Shallow |
Venous ulcer |
|
|
Ulcer on lateral malleolus Very painful. Irregular deep necrotic Prolonged capillary refill time Weak pulses |
Arterial ulcer Rx ABPI PAD manage PADsurgical revascularization surgical revascularization |
|
|
PAD IX |
ABPI DUPLEX ULTRASOUND - first line MRA before any intervention |
|
|
PAD RF |
smoking **** Obesity |
|
|
AAA Ix |
Initial US Next CT SCAN |
|
|
Subclinical hypothyroidism |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
DVLA epilepsy |
Can drive if Seizure free for last year Or Seizure free for last 6 months if antiepileptic medications were changed. |
|
|
Alzheimer's dementia and DVLA |
Inform DVLA about diagnosis Can drive but notify DVLA |
|
|
DVLA OSAS |
If suspected - tell patient to stop driving until further investigation If confirmed moderate to severe OSAS or mild OSAS with daytime sleepiness not controlled within 3 months - inform DVLA |
|
|
DVLA TIA |
Stop driving for 1 month No need to inform DVLA if they had TIA and have recovered |
|
|
DVLA and stroke |
Stop driving for 1 month After 1 month if there is any neurological deficits then inform DVLA |
|
|
DVLA and pE |
No restrictions as long as patient did not lose consciousness and can move leg freely |
|
|
Doxycycline contraindicated in pregnancy |
Give amoxicillin |
|
|
Orbital cellulitis |
CT scan of orbit sinuses and brain |

