![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
|
Thermal equilibrium is transitive.
|
It is number zero.
|
|
|
What is the first law of Thermodynamics?
|
The total energy of and isolated system is conserved.
|
|
|
|
How is the internal energy of a system defined?
|
dU = dW + dQ (Not exact diff)
|
|
|
|
What are the Clausius and Kelvin-Planck statements of the second law of Thermodynamics?
|

Heat cannot flow from cold to hot, and not all heat can be converted into work.
|
|
|
|
How does the second law of Thermodynamics affect entropy?
|
Entropy must increase in a spontaneous process.
|
|
|
|
What is the third law of Thermodynamics?
|
The entropy change associated with any condensed system undergoing a reversible isothermal process approaches zero as temperature approaches 0 K (where condensed system refers to liquids and solids). It is impossible to reach absolute zero.
|
|
|
|
What is Carnot's Theorem?
|
No engine operating between two reservoirs can be more efficient than a Carnot engine between the same two reservoirs.
|
|
|
|
What can be said about the efficiency of two different Carnot engines operating between the same two reservoirs?
|
They are the same, regardless of working substance.
|
|
|
|
Sketch a Carnot cycle on a P-V diagram.
|
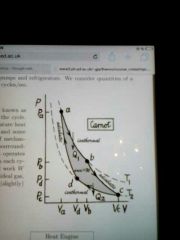
|
|

