![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
General ways of detecting pregnancy
|
-palpation of the reproductive tract (trans-rectal or abdominal)
-imaging of the reproductive tract (radiograph/US) -measurement of hormone concentrations in blood or other fluids |
|
|
Beef Cattle herds
-controlled breeding season length |
-60-90 days
|
|
|
Goal of pregnancy detection in beef cattle herds
|
-get a lot of cows pregnant and a lot of cows pregnant in the first 20 days of breeding
|
|
|
Pregnancy detection in beef herds
-reasons to detect |
-determine success of proceeding breeding season
-provide diagnostic information -identify open cows for alternate management |
|
|
Dairy herd
-controlled breeding season length |
-some dairies are seasonal (60 day breeding season)
but -most dairies are bred year round |
|
|
Why are most daires bred year round?
|
-for a steady milk supply
|
|
|
Pregnancy detection in dairy herds
-reasons to detect in individual cows |
-determine dry off date
-determine if cow should continue breeding pool -assess herd breeding program |
|
|
Dairy
-when should the dry-off begin |
-40-60 days prior to lactation
|
|
|
Milk Pregnancy Tests
-types |
-Milk or blood progesterone assay
-Pregnancy Sepcific Protein B (PSPB) -Early conception factor (ECF) -Detection of Estrus -US -Uterine palpation per rectum |
|
|
Milk progesterone values correlate with:
|
-blood values
|
|
|
Milk or Blood progesterone assay
-why is it important to know the breeding date? |
Test needs to be completed at a specific time after the breeding date (21-24 days post breeding)
-if progesterone is low----> not pregnant -if progesterone is high -----> either pregnant or in diestrus *can't do test randomly in the herd |
|
|
Pregnancy Specific Protein B
-produced by |
-conceptus
|
|
|
PSPB
-benefit |
-can be detected by 25 days of gestation
|
|
|
PSPB
-disadvantage |
0remains in blood for up to 3 months after parturition, overlapping with rebreeding
|
|
|
PSPB
-interpretation of a positive test on a cow with a calf-at-side 35 days after the start of the breeding season -interpretation of a positive test on a heifer 35 days after the start of the breeding season |
-cow with calf-at-side: don't know if she's pregnant
-heifer: should be pregnant |
|
|
Early Conception Factor
-produced by |
-embryo
|
|
|
Early Conception factor
-present in |
-serum
-milk -whole blood -urine |
|
|
Early Conception Factor
-can be detected as early as |
-6 days of gestation
|
|
|
Early conception factor
-disadvantage |
-unacceptable accuracy for use
*SHOULDN'T USE |
|
|
Detection of estrus
-why not just detect estrus and assume that cows not detected in estrus are pregnant? |
It gets inaccurate because we get bust
-they are only in heat for a short time, and if we that period, we may think they are pregnant |
|
|
Ultrasound
-accurate as early as |
-28 days
|
|
|
Ultrasound
-can determine sex of fetus when |
-55-65 days up to 75 days
-difficult past 90 days as the fetus gets too large |
|
|
Ultrasound
-time of fetal heartbeat detection |
-21 days
|
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-accurate by: |
-35 days gestation
|
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-advantages |
-accurate estimate of age of gestation
-low-cost |
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-disadvantages |
-repetitive strain injury
-less information than ultrasound (ovarian structures, fetal sex, fetal viability) |
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-rectal wall tear in bovine vs. equine |
Bovine
-not a big deal -pretty thick, cow should be fine Equine -uh oh! |
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-landmarks |
-pelvis - bony
-cervix - hard (cartilaginous) |
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-ovary location |
-lateral to or tucked under the uterus
|
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum
-uterine tube palpation |
-shouldn't be bale to palpate
-if felt, probably inflamed |
|
|
Uterine palpation
-reason to do a post-breeding season reproductive exam |
-estimate the age of the fetus
& -use that information to evaluate the breeding program and diagnose problems |
|
|
If you're comfortable determining fetal age via palpation from 35-100 days of gestation and you have a herd with a desired 60 day calving season, when can you palpate the herd after the start of the breeding season
|
-95-100 days
|
|
|
Uterine fluid volume
-day of gestation: 40, 60, 90, 120 |
-40 days: 75 mL
-60 days: 300 mL -90 days: 1000 mL -120 days: 3000 mL |
|
|
35 days
-uterine characteristics |
-slight accumulation of fluid
-able to "slip" fetal membranes -placenta starts to occupy non-pregnant horn |
|
|
40 days
=uterine characteritics |
-slightly more fluid
-uterine wall is thinning -size disparity between pregnant and non-pregnant horn |
|
|
60 days
-uterine characteristics |
-pregnant uterine horn is about the size of a banana
-still able to hold the entire uterine tract in your hand |
|
|
90 Days
-uterus characteristics |
-can barely still reach around the entire uterus (about the last time you can retract the uterus)
-routinely bump the calf -begin to feel small placentomes |
|
|
120 days
-uterine characteristics |
-can't reach around entire tract
-prominent placentomes (nickled sized, but larger or smaller depending on relation to uterus) -fremitus in mid-uterine artery on the pregnant side |
|
|
150 days
-uterine characteristics |
-placentomes about the size of a quarter
|
|
|
6.5 months
-uterine characteristics |
-mid-uterine artery on pregnant side has grown to the size of your little finger
-mid-uterine artery on the non-pregnant side is beginning to fremitus |
|
|
Reasons uterine tract may not be felt
|
-6-8 months pregnant
-adhesion holding tract to the abdominal floor -infection or malignancy that makes the uterus heavy |
|
|
Structures possibly confused with pregnancy
|
-bladder
-back of rumen -left kidney -gas bubble in intestine -pyometra -lymphoma -uterine involution (post calving) |
|
|
Urinary bladder
-reason why confused |
-thin walled and fluid filled
but will usually be emptied by the animal when being worked, so won't feel |
|
|
Back of rumen
-reason why confused |
-thick and doughy kind of like a large fetus
but won't lead to cervix |
|
|
Left kidney
-reason why confused |
-can feel like fetal head
|
|
|
Gas bubble in intestine
-reason why confused |
-feels like a vesicle
but bubble should be gone if re-examined in 5 mins |
|
|
Pyometra
-reason why confused |
-large fluid-filled uterus
but, thick walled with a doughy consistency |
|
|
Lymphoma
-reason why confused |
-large open feeling uterine tract
but wall will thicken and other masses can be found |
|
|
Uterine involution
-reason why confused |
-feels a lot like a pregnant cow
but, walls are thickened |
|
|
Ultrasound
-equipment |
-linear array, real time B-mode scanner
|
|
|
Ultrasound
-disadvantages |
-just a snap-shot
-can't determine if structures are getting bigger or smaller |
|
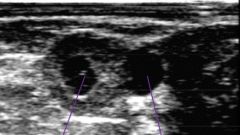
Label the structures
|
-left = CL
=right = follicle |
|
|
Ultrasound
-uses |
Pregnancy diagnosis
-earlier preg diagnosis (@ 25 days) -assess fetal viability -determine sex Embryo transfer -Identify recipients with CL -follow follicular dynamics of donor cow Early non-pregnancy determination coupled with resynchronization protocol for dairies -couple with timed insemination for optimized labor use -reduce days open |
|
|
Ultrasound
-disadvantage |
-slower than palpation
-does not increase accuracy of preg detection past 45 days -early pregnancy diagnosis may reveal higher risk of pregnancy loss than pregnancy diagnosis past 56 days |
|
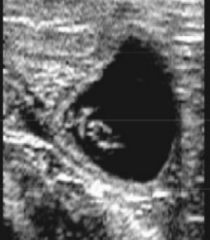
Approximately how far into pregnancy is this animal
|
-35 days
|
|
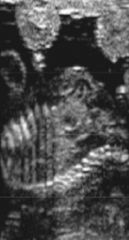
Approximately how far into pregnancy is this animal
|
90 days
|
|
|
US
-sex determination |
genital tubercle is in a different position by 55 days gestation
-caudal to umbilicus in male -ventral to tail in female |
|
|
US
-when does it get difficult to determine sex |
-past 70 days
|
|
|
Integrated reproductive program
-purpose |
Use US for synchronization/resynchronization strategy
-allows manager, employees, and vet to focus on reproduction 2 days per week -ultrasounds (w/ injections) on Tuesdays -breeding on Thursdays |
|
|
Integrated reproduction program
-time between AI service for cows still open |
-35 days
|
|
|
Integrated reproductive program
-flaws |
-not the best synchronization protocol
-need to be good at ultrasound |
|
|
Given that bovine are essentially non-seasonal breeders, which of the following of you think is the current recommended breeding season length for beef cattle?
|
-60-80 days
|
|
|
Which of the following methods of pregnancy diagnosis do you think will provide the most information?
|
-Uterine palpation per rectum
-trans-rectal US |
|
|
Equine Pregnancy Detection
-methods |
-eCG
-Estrogens -Estrone sulfate -Early pregnancy factor (EPF) -Cervical tone and appearance -uterine palpation per rectum and trans-rectal ultrasound -Ultrasound for fetal sexing |
|
|
Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin
-produced by -when |
-fetal chorionic tissue that invades endometrium and forms endometrial cups ---> secrete eCG
-36-38 days |
|
|
eCG
-function |
-luteinize the normal follicular waves that are occuring and results in the formation of secondary CLs
-inc. progesterone levels |
|
|
eCG
-time of peak |
-60-80 days (2-3 months)
|
|
|
eCG
-best for use in |
-mini horses (difficult to palpate)
|
|
|
eCG
-problem |
-remains elevated if pregnancy is lost
|
|
|
Estrogens
-test used |
-Cuboni test
-fluorescence of urine due to estrogen |
|
|
Estrogens
-detect pregnancy when |
-accurate by 100-150 days gestation
*easy to palpate pregnancy per rectum at this time |
|
|
Estrogen sulfate
-present where |
-serum
-urine -feces |
|
|
Estrogen sulfate
-benefit |
-good for assessing wild equine reproduction
-associated with fetal viability after day 44 |
|
|
Early pregnancy factor
-what is it |
-immunosuppressive protein secreted by early embryo
|
|
|
Early pregnancy factor
-when to detect |
-24-72 hrs after mating
-elevated through 2nd trimester |
|
|
Early pregnancy factor
-problem |
-poor accuracy
|
|
|
Equine cervical tone and appearance
-function |
-high levels of progesterone cause the cervix and uterus to have exaggerated tone
|
|
|
Equine
-progesterone peak |
-80-90 days
|
|
|
Equine cervical tone appearance
|
-cervix is elongated and firm
-uterus has increased tone |
|
|
Equine cervical tone
-when noticed |
-day 16 to end
|
|
|
Equine cervical tone
-problem |
-looks like diestrus
|
|
|
Uterine palpation per rectum (equine)
-when palpable |
-days 18-day 60/70
|
|
|
Trans-Rectal US (equine)
-when detectable |
-day 10
|
|
|
Equine day 10-18 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum -characteristics via trans rectal ultrasound |
Palpation
-not palpable US -spherical fluid-filled vesicle |
|
|
Equine day 28 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum -characteristics via trans rectal ultrasound |
Palpation
-size of small egg US -embryo visible in middle of vesicle |
|
|
Equine day 35 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum -characteristics via trans rectal ultrasound |
Palpation
-size of lemon US -embryo near the top of the vesicle and the yolk sac is nearly gone |
|
|
Equine day 42 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum -characteristics via trans rectal ultrasound |
Palpation
-size of orange US -embryo visible in middle of vesicle and umbilicus is visible |
|
|
Equine day 49 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum |
-size of grapefruit
|
|
|
Equine day 56 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum |
-size of cantaloupe
|
|
|
Equine day 90 gestation
-characteristics palpable per rectum |
-cranial margin out-of-reach
|
|
|
US for fetal sexing (equine)
-when |
-day 59-68
*earlier can't visualize genital tubercle *later can't position probe |
|
|
Canine pregnancy detection
-methods |
-abdominal palpation
-transabdominal US -radiograph -relaxin |
|
|
Canine abdominal palpation
-how |
-start at dorsal abdomen and move down
-feel uterus slip between thumb and fingers |
|
|
Canine palpation
-when to palpate |
-day 21-31: small, firm, round vesicles (walnuts)
-day 31-50: vesicles not detectable -day 51-end: puppies palpable (2 wks from whelping) |
|
|
Canine abdominal palpation
-drawbacks |
-accurate fetus counting not possible
-can't determine fetal viability -difficult in large dogs, dogs that tense their abdomen, dogs with mammary gland development |
|
|
Canine trans-abdominal US
-when useful |
-day 18-20 after LH peak: fetal vesicles visible (round, black sacs)
-day 23-25 after LH peak: fetal heartbeat -day 34-36 after LH peak: fetal movement |
|
|
Canine trans-abdominal US
-drawback |
-difficult to count fetuses
|
|
|
Fetal stress
-heart rate |
> 200 bpm
|
|
|
Canine Radiographs
-when useful |
-days 42-52 (after breeding) 44-47 (after LH peak): fetal skeletons first seen
-day 50-end: can count skeletons |
|
|
Relaxin (canine)
-sample needed to measure |
-blood
|
|
|
Relaxin
-detected when |
-day 20-30 after LH peak
*still present after birth, but not big deal because we're not breeding again right away |
|
|
Relaxin (canine)
-benefit |
-commercial kit
-allows differentiation between pregnancy and pseudopregnancy because relaxin is only formed by the placenta |
|
|
Porcine Pregnancy Detection
-methods |
-detection of return to estrus
-A-mode ultrasound -doppler ultrasound -real-time ultrasound |
|
|
Non-pregnant sow should return to estrus how long after breeding
|
-17-24 days
|
|
|
Detection of return to estrus (sow)
-how |
-detect behavior in presence of boar
|
|
|
Detection of return to estrus (sow)
-problem |
-false positives are common
-if mounting is missed, we assume pregnant |
|
|
A-mode ultrasound
-how it works |
-use US waves to detect a fluid filled uterus
-either uses sound or lights |
|
|
A-mode ultrasound
-time of highest accuracy |
-35-75 days
|
|
|
A-mode ultrasound (sow)
-problems |
-number of false negatives increases after day 75 due to a decreased percentage of fluid present (can't differentiate between animal and fetus)
-bladder is a fluid filled sac ---> false positives |
|
|
Doppler ultrasound (sow)
-when to use |
-30-34 days
|
|
|
Doppler US (sow)
-function |
-detects fetal heart
-pulsing umbilical/uterine arteries |
|
|
Doppler US (sow)
-drawbacks |
-risk of false positives during proestrus or diestrus due to some fluid being present in a muscular uterus
|
|
|
Real-time ultrasound (sow)
-advantages |
-not owned on many small farms (need you)
-can detect pregnancy sooner than A-mode US or doppler (23 days) |
|
|
Real-time ultrasound (sow)
-disadvantages |
-able to detect pregnancy sooner
-better reproductive performance of a farm, the less advantage to using US |
|
|
Ovine and Caprine pregnancy detection
-methods |
-Real-time ultrasound
-pregnancy-specific protein B |
|
|
Real-Time US (caprine, ovine)
-advantages |
-detect pregnancy
-assess fetal numbers |
|
|
Real-time US (ovine, caprine)
-when to start using |
-as early as 25 days
|
|
|
Pregnancy-specific protein B (ovine, caprine)
-when to start detecting |
-as early as 20 days
|

