![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
295 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Purpose of business operations |
- To produce goods - To provide services |
|
|
Name 3 production processes |
- JOB - BATCH - FLOW |
|
|
Define Job production And give 3 examples |
- Making a one off product to meet specific customer needs Tailoring, Ironwork, Construction |
|
|
Define Batch production 3 examples |
- When groups/batches of similar items are produced together - Bread - Paints - Tyres |
|
|
Define Flow/mass production 2 examples |
- Large numbers of identical products - Cars - Electrical products |
|
|
3 advantages for Job production And 3 disadvantages for job production |
+ - Tends to have highest level of employee motivation - Products made to exact requirements - Staff are highly skilled so high quality _ - Most expensive as most labour intensive - Slow production (customer waits long time to receive product) - Machinery may be used frequently increasing risk of overuse and frequent replacement |
|
|
3 advantages and 3 disadvantages for Batch production |
+ - Has flexibility to produce different products in different groups - Can produce more in same time as Job production - Bulk buying raw materials will give lower unit costs than Job _ - Time needs to be adjusted between batches - Regular clean of machinery to avoid cross contamination - Work less skilled so staff may become demotivated |
|
|
What are the 5 stages of the sales process and define the meaning for each |
- Product knowledge: Customers expect staff to answer questions about product - Speed & efficiency of service: Customers should be treated politely, served quickly - Customer engagement: Communication should be concise, accurate, professional - Response to customer feedback: Ignoring feedback likely to lead customers ignoring businesses - Post sales service: Dealing with complaints, returns, repairs |
|
|
What are the things that could happen if the sales process is poor 3 marks then explain |
- Sale could be lost - Reputation could be damaged - Loss of repeat customers
Leading to... - Complaints - Sales in decline - Profit in decline |
|
|
Importance of good customer service to a business 5 marks |
- Likely to result with satisfied customers - Likely for them to return or make a purchase - This generate sales in the long run - Can be a USP for advantage over competitors - Maintain or bring about good reputation |
|
|
Biggest cause of problems in customer service for a business is 1 mark |
They over promise and can't deliver |
|
|
Formula for Gross profit |
Sales revenue - ( variable costs)
Profit is all revenue - all costs Gross profit: only sales revenue - only the variable costs |
|
|
Formula for Gross profit margin |
Gross profit/sales revenue x 100 |
|
|
Formula for Net profit |
Gross profit - operating expenses and interest |
|
|
Formula for Net profit margin |
Net profit/sales revenue x100 |
|
|
Formula for average rate of return |
Average annual profit (total profit/number of years) / cost of investment X 100 |
|
|
What is the difference between Gross profit and net profit |
Gross profit: - The revenue left over after deducting the costs of making a product or providing a service
Net profit: - The revenue left after all costs have been deducted from gross profit |
|
|
What is the average rate of return |
The measurement of profibility of investments on the basis of financial statements across the years |
|
|
What is another term for average rate of return |
ARR: Accounting rate of return |
|
|
What 2 things does gross profit tells a business |
- Whether it is worth producing a good or service - Does it cost more to make than they actually sell for |
|
|
State another term for Net profit and what does it tell a business |
"The bottom line" Tells a business how much money they have made after selling goods and services |
|
|
What is the difference between net profit and profit |
You need to calculate sales revenue not all revenue and then - it off all possible costs for Net profit |
|
|
What 3 calculations can a business use to measure their performance |
Gross profit margin Net profit margin ARR |
|
|
What does the ARR calculate |
The expected rate of return on an investment to see if it is worth the money or not |
|
|
Is it good for a business if the 3 calculations that measure performance are high or low |
HIGH GPM HIGH NPM HIGH ARR |
|
|
What does the GPM tell a business and what does it mean if a business has a GPM of 50% |
How much gross profit is made for each pound of sales revenue received Every £1 of goods sold, a business makes 50p gross profit |
|
|
What does the NPM tell a business and what does it mean for a business if their NPM is 30% last month |
- How much net profit is made for each pound of sales revenue received For every £1 of goods sold, the business makes 30p net profit |
|
|
What is the ARR often compared to.. |
The interest rate If the ARR is lower than the interest rate then it is a bad investment |
|
|
How do you calculate the average annual profit |
Total profit/number of years |
|
|
Do you add or subtract any cost of investments to average annual profit |
Subtract |
|
|
Calculate the ARR in question COST of car: £20,000 Additional income in year 1: £9,000 Additional income in year 2: £9,000 Additional income in year 3: £12,000 Additional income in year 4: £12,000 4 MARKS |
Total additional income: £40,000 £40,000 - Cost of car (£20,000) = £20,000 ( Total profit ) Average annual profit = £20,000 / 4 years = £5,000 ARR = £5000/ £20,000 (cost of investment or car) ARR = 25% |
|
|
What are the 3 sources of data that a business may have |
Financial data Marketing data Market data |
|
|
What do the quality of decisions depend on |
Reliability of data Ability to interpret data accurately |
|
|
Name types of financial data that a business can use to assess their performance |
Gross and net profit margins Gross and net profit Costs and revenue ARR (average/accounting rate of return) Break even point Cash flow forecasts |
|
|
What type of data is marketing data and give some examples |
Qualitative data obtained from marketing activities: - Customer loyalty - Business reputation - Secondary and primary research - Market share |
|
|
What does market data refer to and give examples |
Activity outside a business that might concern the business Annual reportsof competing businesses Economic data Industry data and reports or trends Official government stats |
|
|
Explain what financial data essentially is and what it can do to decisions made by a business |
Quantatitive data: Can inform, support and justify decisions made by a business |
|
|
Name 3 types of quanatative data used to support, inform or justify business decisions |
Information from graphs and charts Financial data Marketing data |
|
|
What are the limitations of financial information/data |
- Data may be out of date: unreliable effecting business performance negatively - Data may be interpreted/reported inaccurately - There may be insufficient data to inform correct decisions |
|
|
What is the difference between hierarchical and flat structure |
Hierarchical: there are many layers of management
Flat: Few layers of management |
|
|
What is the difference between a centralised structure and a decentralised structure |
Centralised: Key decisions are made by a small number of senior staff Decentralised: Junior managers are given authority to make important decisions |
|
|
State the 4 types of organisational structures |
Flat structure Hierarchical structure Centralised structure Decentralised structure |
|
|
Why is it important for a business to be well structured |
SO THAT STAFF KNOW: - What there role is - Who they answer to - Who they are responsible for |
|
|
Define an organisatiomal structure |
A formal way of outlining the way that authority, responsibility and information will flow in a business |
|
|
What might a business plan use to Illustrate how they are structured |
Organisation chart |
|
|
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of hierarchical structures |
A: - employees can be closely supervised - Good promotion prospects for staff - There is a clear management structure showing authority and responsibility D: - Employees may feel restricted - Requires a number of middle mangers which is costly - Decisions will take longer to make |
|
|
What scale organisation would hierarchical structure and flat structure be used on |
(Large) big businesses (Small) smaller businesses |
|
|
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of flat structures |
A: - Promote better communication with staff - Decision making can be more effective - Removes expensive layer of middle managers D: - Fewer opportunities for staff to gain promotion - Roles and responsibilities may become blurred - May make it difficult for a business to grow/expand |
|
|
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of centralised structures |
A: - Senior management has more control - Standard procedure across all branches allow cost savings D: - Branch managers have limited responsibilities - May be fewer promotion opportunities within branches - Workers may feel they are not involved in decisions |
|
|
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of decentralised structures |
A: -Workers are empowered to make decisions - As a result workers tend to be more motivated - Branches can individually respond quickly to change
D: - Senior managers no insight in major decisions made - More managers with the high skill for decisions are needed (expensive) |
|
|
Why is structure important in a business |
- Maximise efficiency - Retain order and authority - Promote flexibility - Encourage creativity and motivation |
|
|
What happens if a business chooses the wrong structure 3 marks |
- Can hinder success of business and or growth Could lead to... - Poor communication - Slow decision making |
|
|
What are the 3 types of communication |
Writtten Visual Verbal |
|
|
What does the type of communication depend on |
The audience/stakeholder |
|
|
What is the result of effective communication 3 marks |
- Increase chance of business success - Employee motivation - Employee retention - Productivity ... Increases In turn could lead to - Lower costs and increase in profits |
|
|
Why might a business make less mistakes with effective communication |
- All employees are clear of aims and objectives - Better decision making |
|
|
What is the impact of excessive communication |
Employees may feel: - Stressed - Demotivated - Overwhelmed Or error-prone as important messages may be lost |
|
|
Explain the impact of too little communication on a business 3 marks |
Employees may feel: - Confused - Isolated - Demotivated Could lead to... - mistakes... - increase in costs.. - Increase in staff absence |
|
|
State the barriers to effective communication |
- Language barriers (jargon) - Unable to hear - Lack of interest - Assumptions |
|
|
Define use of jargon |
Special words used in a specific occupation or profession |
|
|
State the 3 different ways of working |
- Amount of hours of work - Type of employment (contract) - Technology |
|
|
What are the 3 types of hours of work an employee may have and describe each briefly |
Full time: 35 hours or more a week Part time: Less than 35 hours a week Flexible: Working hours can change |
|
|
What are the 3 types of employment an employee may have and describe each briefly |
Permanent: A job with no set end date and can be ended by giving an agreed amount of notice in advance Temporary: Ends on a specific date and is usually for a couple of days or weeks Freelance: Self employed person who will take on short term contracts working for others |
|
|
Explain how technology could allow a business to work more efficiently and not efficiently |
Efficiently: - Reduce need for large offices - Reduce need for travel for meetings (Saves alot of money) - Communicate and make decisions faster virtually - Increase flexibility
Not efficiently: - Staff may misuse remote working - Less work could get done/deadlines may not be met - Employee isolation/demotivation |
|
|
State 5 factors to consider with advantages and disadvantages to the different ways of working |
- Motivation - High/low skill/knowledge level in certain areas - Commitment - Flexibility - Communication |
|
|
What does more motivation lead to... |
Higher levels of productivity |
|
|
State the all the different job roles in a business |
- Directors - Senior manager - Supervisors/team leaders - Operational staff - Support staff |
|
|
State the job roles of a director and give an example |
MD: Managing director - Leads and supervises a business - making strategic decisions to reach firms aims and objectives |
|
|
Put in order of highest rank to lowest in terms of who reports to who in a business: - Board of directors - Managing directors - CEO - managers |
Managing directors (lead the board of directors) Board of directors CEO Managers |
|
|
State the roles of a senior manager and give an example |
CEO: chief executive officer Top senior manager in business
- Communicating with board of directors - Managing overall operations and resources of a business - Managing and leading senior team |
|
|
What is the difference between a CEO and a manager or lower senior manger |
Senior/manager: - Put strategy into practice - Plans work that needs to be done in specific area - Leading staff in area - Organsing resources in area |
|
|
What are the roles of a superviser/team leader |
Oversees work of operatives - Solving routine daily problems - Organising and directing staff they are responsible for - Adhering polices made by managers |
|
|
What is the role of support staff and give 4 examples |
To make sure day to day running of business goes smoothly: - Maintenance staff - Catering staff - Cleaning staff - IT staff |
|
|
State the roles of operational staff |
- Those employees that directly produce the goods and services - They meet targets set by supervisers - They do not supervise others |
|
|
What is a job description and what should it contain |
- Document written by a business to outline a job role - Job title - Responsibilities of job - Place of hierarchy - Working conditions |
|
|
State what is information can be found in the hierarchy and working conditions section of a job description |
Place of hierarchy: - Who you are responsible for - Who you report to Working conditions: - Pay - Hours - Location |
|
|
Suggest 4 reasons why job vacancies may arise |
Increased sales Staff leaving Staff promotions Temporary absence due to injuries |
|
|
What does the person specification describe, State the requirements and rules with a person specification |
- Personal qualities needed for the job Outline requirements in terms of: - Educational qualifications - Professional qualifications - Previous experience - General skills (IT skills etc) - Should not discriminate against any particular group |
|
|
State the 3 documents a business needs in the recruitment process |
- Job description - Person description - Application form (CV) |
|
|
What does the application form ask a potential employee |
- Name - address - contact details - language skills - Educational and professional qualifications |
|
|
Suggest what candidate may be asked to do in a interview 3 marks |
Tests: IQ Role play: stimulate work they will do Activities: see how well they work together |
|
|
What 2 ways can a business recruit to meet specific needs |
- Internally: advertise vacancy within a business - externally: advertise vacancy outside business |
|
|
Discuss the possible advantages and disadvantages of internal recruitment |
A: - Cheaper than external - Candidate will know the business, so they can settle quickly - It motivates other employees as they see promotion opportunities
D: - No fresh ideas brought into the business - Other employees may feel resentful if they don't get the job (demotivating) |
|
|
Discuss the possible advantages and disadvantages of External recruitment |
A: - New ideas and skills brought to business D: - More expensive than internal - May demotivate existing staff as they feel lack of promotion opportunities - Tends to be longer method of recruitment |
|
|
What is....... Focused on - training - development |
Training: - Teaching knowledge and skills for a specific job - Improving current job performance Development: - Long term improvement of skills and experience |
|
|
Reasons why employees should be trained or undergo development |
- Improve motivation - Improve retention - Improve/update skills - Make efficient use of technology |
|
|
Explain how improving employees skills benefits a business 3 marks |
- Likely to improve performance - Increased productivity or - Improved customer service in turn.... - Improve profitability of business |
|
|
Why might updating skills be useful to a business |
To make effective and efficient use of new technology |
|
|
Explain how motivation can benefit a business 3 marks |
- Makes employees feel valued - Therefore they will work harder - Improving a business reputation or production - Which improves the performance of a business |
|
|
Explain how training can lead to increase in employee retention and saves money for a business |
- Training makes an employee feel valued - More likely to remain loyal to a business and less likely to leave - Which avoids expensive recruitment process which would be needed if they left |
|
|
Define formal and informal training and give an example for each |
Formal: - Structured, organised programme - May lead to formal qualification For example: Paid courses Informal: - No formal goals or tests - Take place a convient time of learning - No formal recognition For example: Observing a colleague |
|
|
Give advantages and disadvantages of formal training |
A - Recognised achievements - Official training
D: - May be harder to apply to workplace - Likely to be more expensive |
|
|
Give advantages and disadvantages of informal training |
A: - May be more realistic to workplace making it easier to apply - Less expensive than formal training D: - Limited learning and may not be effective training as it is unofficial - training may not be reliable - Limited access to experienced colleagues maybe |
|
|
Define ongoing training |
- Personalised training - That is perfecting the skills regularly with employees - Compulsory on certain issues or changes |
|
|
Give advantages and disadvantages of Ongoing for employees |
A: - Can increase an employees efficiency overtime - Helps businesses keep up to date with technological and legal change - May increase work satisfaction and definitely value and retention D: - Increase business costs (likely) |
|
|
Explain self learning training |
When employees teach themselves about their job in a business |
|
|
In most 3 markers for Business studies theme 2 what 4 factors do you relate to (positive and negative) |
Improve/ decrease or missout on improving: - De/motivation Lead to productivity + or - - staff retention - Staff value - Skills Leads to Less/ more mistakes More costly to a business
Ultimately improves decreases a businesses and the employees - performance as a whole and - Profitability |
|
|
Why is target setting and performance reviews important to a business |
Target setting: - ensures targets are met - Employees have goals to meet so the business is moving forward Performance reviews: - Leads to employees feeling valued as they are getting feedback on what to improve on - This leads to development of skills and less mistakes - Further benefiting the businesses performance |
|
|
State what is meant by the term fringe benefits and give 5 examples |
- When an employee receives a reward apart from actual money - It can be fixed as part of employees contract or incentives such as: - company car - holidays - Life insurance - Pension contributions - Private healthcare |
|
|
What is autonomy |
When an employee is given the independence and power to make decisions in the workplace |
|
|
What does increasing motivation in a workplace do to a businesses performance |
Improves performance |
|
|
Give 5 things that employees may be motivated by |
- Earning money - Gaining status - Working with others - Avoiding boredom - Satisfying ambitions |
|
|
State the importance of motivation in the workplace Or WHY motivation is important |
- To retain staff - Improve productivity - Attract employees |
|
|
Happy staff are usually..... Staff |
Motivated |
|
|
State the financial methods of motivation and explain how each costs the business money |
- Commission: Recieve a % of value of products they sell - Fringe benefits: Additional benefits that is not actual money - Promotion: Staff will get higher pay or salary - Bonuses: Additional payment as reward of good performance - Remuneration: Payment for work |
|
|
Explain how remuneration works and give 2 examples |
Refers to the payment for working for the business This can be in: - Wage - Salary |
|
|
State the differences with wage and salary |
Wage: - Paid weekly - Based on how much work is done - Overtime available
Salary: - Quoted annually (fixed) - Paid in monthly installments - Not related to how much work - No overtime |
|
|
State possible drawbacks for financial methods of increasing motivation (Not money related) |
Remuneration: If they have a salary it may not motivate employees that much
Bonuses: Some staff may cut corners if they rely on bonuses
Commission: Can lead to staff putting pressure on customers to buy
Promotion: Some staff may be demotivated if they don't get the promotion
Fringe benefits: Demotivate those who don’t get fringe benefits as incentives |
|
|
State the non-financial methods of increasing motivation |
- Job rotation - Job enrichment - Autonomy |
|
|
Describe Job rotation and 2 advantage and 1 disadvantage |
Improves motivation through creativity: - Workers changing activity/work on a regular basis
Advantages: - Relives boredom from repetitive tasks - Helpful when covering staff absences
Disadvantages: - Does require staff to have additional training can be costly |
|
|
State the difference between job enrichment and a promotion |
Job enrichment: Workers are provided with more responsibility by providing them with more tasks or more complicated tasks with no increase in pay
Promotion: Same as above but with more pay |
|
|
State a possible drawback to have more Autonomy |
They have the freedom to make more decisions so they are likely to be held accountable for poor decisions they make |
|
|
What does training likely do to all employees |
Improve performance |
|
|
Define economies of scale |
The cost advantages of expanding As the cost per unit/product decreases as the firm or business increases |
|
|
Describe internal and external growth |
Organic: Growth that occurs from inside/within the business without external influences
Inorganic: When growth comes with the aid of external sources |
|
|
Define a merger |
When 2 or more firms agree to join together to make 1 new business |
|
|
Define a takeover |
This is where 1 business buys control (at least 51%) of another business |
|
|
What is another term for takeover |
Acquisition |
|
|
State 5 ways of organic growth (6 marker) |
- New products (innovation, research and development)
- New markets (through changing the marketing mix, expanding overseas, taking advantage of technology) |
|
|
State 3 ways of growth through new markets |
Through: - changing the marketing mix - expanding overseas -taking advantage of technology |
|
|
State 2 ways of growth through new products |
- Innovation - Research and development |
|
|
State the 2 ways a firm can grow Inorganically |
- Mergers - Takeovers |
|
|
State 2 issues that may come up if a firm grows to quickly |
- May not be able to react to changes in the market quick enough: slow to meet customer needs
- Communication must be difficult |
|
|
State 2 issues that may come up if a firm grows to quickly |
- May not be able to react to changes in the market quick enough: slow to meet customer needs
- Communication must be difficult |
|
|
What is the biggest type of private businesses in UK |
PLC: public limited companies |
|
|
State 1 initial disadvantage to a PLC business |
High initial start up capital needed: Minimum 50k |
|
|
State 2 sources of internal sources of finance |
- Retained profit - Selling assets |
|
|
State 1 form of finance that a PLC specifically can gain and where |
- Sell shares - On the stock market
Called Stock market floatation |
|
|
What is stock market flotation: - Internal source of finance - external source of finance |
External source of finance |
|
|
State the forms generally of external sources of finance 3 marks |
- Loan capital - Share capital - Stock market flotation |
|
|
Explain 1 disadvantage to internal growth 3 marks |
- Growth may be too slow - Market share may fall as other businesses expand - Leading to a small customer base and low profits |
|
|
State 5 reasons why businesses aims and objectives change as they evolve |
Market conditions Technology Performance Legislation Internal reasons |
|
|
Expalin why with 2 examples perfomance and internal reasons are reasons why a businesses aims might change |
- If a business is doing well and making low profits its performing bad which may be due to its aims
- The business is making a loss which is a interal reason why they might change their aims |
|
|
State 2 internal reason why a business aims or objectives might change |
Business performance
Changes in management |
|
|
If business has high capital: And conditions are as below - Low competition - High demand - Variety markets available - Small workforce What 4 aims should u make to maximise profits and why |
Aim to: - Grow and expand: Low competition - Increase production High demand - Grow workforce: Support demand - Enter more markets Large variety & plenty of capital |
|
|
Define Globalisation 2 marks |
-The process by which the world is becoming more interconnected - through trade and culture |
|
|
State 2 reasons why Globalisation has increased over the years |
- Better communication with tech - More international agreements |
|
|
State the 4 main impacts of Globalisation on businesses |
- Imports - Exports - Location of Businesses - Multinationals |
|
|
Domestic meaning |
A relation to a certain home or country or place |
|
|
Domestic products meaning 1 mark |
A product made inside the country or city in question |
|
|
How will an increase in imports impact businesses |
- Less spending on domestic products - Increased competition from foreign businesses |
|
|
State 2 advantage to increase in Exports |
- Operating on a international basis: Title - Opportunities to access new markets and new customers |
|
|
How has an increase in Globalisation had an impact on the locations of branches of businesses 1 marks |
Its allows businesses to situate stores more easily in other countries |
|
|
State 4 challenges of operating overseas |
- More costs - Certain equipment needed may not be available - Not skilled workers - Communication issues |
|
|
Explain 4 factors of increase in costs overseas |
- Land and building - Labour - Technology - Transport |
|
|
State 2 ways how communication could be a issue for businesses when operating overseas |
- Different languages - Time differences |
|
|
Define Multinationals 1 mark |
A business that operates in more than 1 country |
|
|
State what MNC means |
Multinational corporations |
|
|
Explain 2 positive impacts of Multinationals 2 marks |
- Prices may be low to manufacture meaning inflation stays low - May Create Jobs for locals in many places |
|
|
State 2 negative impacts of Multinationals |
- Difficult for smaller businesses to complete - Increase global warming |
|
|
State the 2 barriers to international trade |
- Tariffs - Trade blocs |
|
|
State the 2 barriers to international trade |
- Tariffs - Trade blocs |
|
|
If there was no barriers to international trade state 3 impacts of this on a country |
- Job losses - Business closures - Money leaving domestic economy |
|
|
Define a tariff 1 mark |
A tax on imports or Exports |
|
|
What are tariffs designed to do: Explain your answer 3 marks |
- Make foreign imports more expensive - Make domestic products cheaper - Therefore more domestic consumers would buy the cheaper option |
|
|
What is a trade bloc 2 mark |
- An agreement between states or countries - To reduce or remove tarde barriers between them |
|
|
State the 2 ways a business can compete internationally |
- Using the Internet through ecommerce - Changing the marketing mix |
|
|
State 4 risks of competing internationally |
- Ethical risks - Shipping risks - Legislation risks - Political risks |
|
|
State some potential changes to the marketing mix when competing internationally 4 marks |
- Change name on product - Adapt price to local market and currency - Buy facilities or improve websites for international use - Promote isong different languages and media more suited to area |
|
|
5 reasons why Businesses should be ethical |
- Loyal and motivated staff through respect - Good public reputation - Strengthen trust with investors and suppliers - Additional sales through good publicity - May gain rewards promoting business |
|
|
Explain 1 reason why a business may not be ethical 3 marks |
- Increased costs due to ethical approach - Less competitive: Higher prices - Lower profits due to higher price |
|
|
Define sustainability 1 mark |
- Ensuring natural resources can be replaced or replenished |
|
|
State 2 ways a business may be more sustainable 2 marks |
- Using renewable energy - Using less fossil fuels |
|
|
State 1 way a business may use less fossil fuels |
Less plastic in packaging |
|
|
State 3 ways to reduce waste from a business |
- Better quality control: Getting things right the first time - Using resources efficiently - Improving design of products |
|
|
Reducing the carbon footprint of a business will allow which Stakeholder to not hate the business |
Pressure groups |
|
|
State 2 ways a business can benefit from recycling |
- Positive eco friendly image - Reduces landfill tax charges |
|
|
Define pressure groups 3 marks |
- An organised group of people - Who will try to influence business activity - To promote shared interest |
|
|
State 2 types of pressure groups |
- Promotional groups - Sectional groups |
|
|
3 ways pressure groups can influence business activity |
- Protests - Boycotts - Negative publicity |
|
|
Define trade-off 2 marks |
- Balancing out certain factors -to reap maximum benefits |
|
|
If a business gets rid of employees after a takeover, they may do it unethically or without reason. Explain the negative effect of this 3 marks |
- Decrease motivation - meaning it will decrease productivity - Meaning less products will be produced impacting profits |
|
|
Explain 1 way businesses face barriers to international trade (tariffs) 3 marks |
- May have to pay tariffs when importing. - Companies may charge higher prices to maintain high profits - Low levels of sales due to consumers more likely to buy cheaper, similar domestic products |
|
|
State 1 ethical consideration for employees. 1 mark |
Ensuring that staff are treated fairly and with respect / higher than MW |
|
|
State 3 ethical consideration for product development 3 mark |
- Dont do animal testing - Use non toxic materials - Less packaging for sustainability |
|
|
State the elements of the design mix 3 marks |
- Function - Aesthetics: Design - Cost |
|
|
Describe what happens in the development stage 2 marks |
- Research would have to happen on the product to see if its a opportunity - The product would then be developed |
|
|
State 3 words to describe Aesthetics |
- look - feel - smell |
|
|
State each stage of the product life cycle 6 marks |
- Research & development - Introduction - Growth - Maturity - Decline - Withdrawal |
|
|
Which stage of the product life cycle has the: - Highest sales |
- Growth |
|
|
Draw the average product life cycle |

|
|
|
Explain why a product may reach its Maturity stage quicker than usual 2 marks |
- More Competition - - - - > - Less popularity |
|
|
State 3 reasons why a business may try to extend their products life |
- Maintain reputation
- Next product may still take time until release
- Maximise profits due to costs
|
|
|
State which stage extension strategies will be put in place for products and why this stage 2 marks |
- Maturity stage - to prevent decline |
|
|
State 5 ways businesses van extend a products life cycle |
- Changing the price - Adding value - New packaging - Excessive Advertising - Explore new markets |
|
|
State 3 ways a business can add value to extend a products life |
- Adding new varieties or flavours - Adding new features such as prizes - Adding new pack sizes |
|
|
State 2 ways a business can explore new markets |
- Supplying regions where it was not previously sold - Create target markets with people who may of not already tried product |
|
|
Define product differentiation 2 marks |
- A way of making a product stand out - In order to be different from other products |
|
|
State 2 ways of making a product different |
- Branding (adding value) - Creating a USP |
|
|
State the long term pricing strategies 3 marks |
- Competitive pricing - Cost based/plus pricing - Psychological pricing |
|
|
State the short term pricing strategies 3 marks |
- Price skimming - Price penetration - Loss leader pricing |
|
|
State 1 advantage to competitive pricing |
Knowing that consumers are willing to pay that price |
|
|
Give an example of psychological pricing 1 mark |
£9.99 instead of 10 quid |
|
|
What happens if you overuse psychological pricing 1 mark |
It may become ineffective |
|
|
State and explain briefly the 2 types of psychological pricing |
Charm pricing: £9.99 Prestige pricing: Giving the impression of quality |
|
|
Describe what loss leader pricing is (2 marks) and why might businesses use this (1 mark) |
- Using very low prices - That lead to loss when purchased - Idea being that consumers would be other profitable items as well |
|
|
Describe price skimming 2 marks |
- Charge high inital price when first available - Later lowered price as product life cycle progresses |
|
|
Price penetration is opposite to which type of pricing strategy 1 mark |
Price skimming |
|
|
Describe price penetration 1 mark |
Charging a low price for a limited time to attract customers |
|
|
State the influences on pricing strategies 4 marks |
- Technology - Competition - Market segments - Product life cycle |
|
|
State 5 different forms of promotion |
- Advertising - Sponsorship - Product trials - Special offers - Branding |
|
|
Why is important to use the most suitable form of advertisement 1 mark |
So that the particular audience can view the advertising |
|
|
Define advertisement 1 mark |
Use of media to communicate with potential customers |
|
|
State 6 different forms of advertisement |
- Websites - Social media - Television - Newspapers - Magazine - Radio |
|
|
State 2 benefits and disadvantages for newspapers as promotion |
Pros: - Can be effective when reaching a local crowd - Can give detailed information Cons: - Can be expensive per reader if national - May be harder to gain attention due to many ads (may be ignored ) |
|
|
State 2 Pros & Cons of magazines as promotion |
Pros: - Can target specific groups - Reader can refer back (can be national) Cons: - Competition may also be advertised (less effective) - Needs to be booked in advanced (costs time due to planning |
|
|
Give 2 Cons to radio as promotion |
- Non visual (lose interest) - Message is short lived |
|
|
Define sponsorship 2 marks |
- Supporting an event financially - or by providing them your products/services |
|
|
2 Pros to Sponsorship |
- Builds relationships -Create positive/ high profile |
|
|
Define product trial 2 marks |
Providing expense free samples of the product to consumers |
|
|
Define special offers 1 mark |
Use of incentives to persuade consumers to make purchases |
|
|
State what BOGOF stands for |
Buy one get one free |
|
|
State 3 ways businesses can use technology to promote their products |
- Targeted online advertising - Viral marketing (social M) - E newsletters (signed up) |
|
|
Describe targeted online advertising in 2 words |
Personalised ads |
|
|
What do indirect distribution channels use |
Intermediaries: who act as a link |
|
|
Describe which type of people retailers sell to and who they don't sell to 2 marks |
- Consumers - Not salesman |
|
|
Who do wholesalers sell to and desribe the scale of quantity they sell it in 2 marks |
- To retailers - Large quantities |
|
|
State 3 common intermediaries |
Agents Wholesalers Retailers /e tailers |
|
|
State the 2 types of distribution channels and which is more complex |
Direct Indirect: complex |
|
|
Describe e tailers in terms of retailers |
They are retailers that operate online |
|
|
State the difference between ecommerce and e-tailers 4 marks |
Ecommerce refers to any online sale including to other businesses Whereas E tailers are a type of e commerce to customers only |
|
|
State which distribution channel includes no intermediaries |
Direct |
|
|
State which industry of businesses including scale would use direct distribution channels and give an example 3 marks |
- Small businesses - The consumable industry (local bakery) |
|
|
How can you change the marketing mix to gain a competitive advantage 4 marks |
Price: Low Promotion: As many audiences as possible Product: differentiation/ USP Place: Widely available or exclusive |
|
|
State the 2 factors that can can create a competitive price |
- High productivity - Low unit costs |
|
|
What does the advantage: Flexible production mean |
More product can be ready quickly for JIT purposes |
|
|
As you progress from Job to batch production what happens to prices and output 2 marks |
- Reduced prices - Increased Output |
|
|
State 3 advantages with flow production |
Lower unit costs (economies of scale)
Products have consistant quality
Usually automated so takes place continuously (24 hour) |
|
|
State 3 disadvantages for mass production |
Inflexible production
High inital costs for machinery
Breakdowns can halt production easily |
|
|
State 2 ways technology has affected production |
Productivity increase Quality is consistant usually |
|
|
Why might technology on production terms reduce prices: state 2 ways 2 marks |
- Less employees to manage production as now automated - Price per unit decreases in long run |
|
|
State 1 word to describe goods compared to services |
Tangible |
|
|
Businesses need to have a good relationship withsuppliers in order to avoid problems with: 3 marks |
- Quality
- Stockavailability
- Deliveries |
|
|
State the names of 4 different ways someone might refer to a substance as STOCK |
- Raw materials - Spares (in case machinery break down) - Work in progress items - Finished goods |
|
|
State the main reason why stock is important 1 mark |
- Needed to produce stock |
|
|
State 3 money issues with holding too much stock |
- bigger storage costs - Higher insurance - opportunity costs |
|
|
State 2 possible issues with too much inventory (except cash problems e.g cash flow issues) |
- Increase risk of shrinkage - Increase risk of wasting large amounts of products if consumable |
|
|
State 4 disadvantages of holding too little stock |
- Loss of sales (lead to customer loss)) - Damage reputation - Longer waiting times forloyal customers - Lead to loss of goodwill |
|
|
define shrinkage with an example 2 mark |
loss of inventory through illegal action such as robbery |
|
|
- Define goodwill 2 marks |
The price paid by the owner of the acquisition subtracted from the market price of the business |
|
|
How are managed stock presented 1 mark |
Through Bar-gate graph |
|
|
State another term for bar gate graph |
Stock control graph |
|
|
Which stage is most stock used up in a business |
Production |
|
|
State 3 assumptions made by Bar gate graphs with Stock |
- Deliveries are correctand on time - There are no faultystocks - stock is used up at production at aconstant rate |
|
|
- JIC - JIT - JIS
stands for 3 marks |
JIC: Just in case STOCK
JIT: Just in time
JIS: Just in sequence (opposite as JIT) |
|
|
OUTLINE 1 way a business choice of method of distribution may affect the way it is promoted if it sells to high street retailers 2 marks |
- Could promote product through posters or freestanding adverts in passageways - That way they nay be more persuaded to buy product after viewing promotion |
|
|
Explain why a business may decide to lower the priceof a product that is in the decline phase of its life cycle. 3 marks |
- Product will be losing sales due to decline stage - Lowering price attracts more customers - Which extends the life of the product and maintains reputation |
|
|
Explain 1 reason why a company will match the branding of a new product to the company's overall brand image
3 marks |
- In order to prevent confusion of ownership and present a strong image
- More easily recognised by customers
- increase likelihood of sales |
|
|
How does sponsorship of an event by a business work 2 marks |
- The business will give money towards event
- in exchange for business image/name being shown at event |
|
|
Discuss how a business may use technology to promote its products to specific market segments 6 marks State the 3 topics u would talk about |
- Social media (different marketing segments) - Targeted advertising: though search history and location - E newsletters for promotional materials |
|
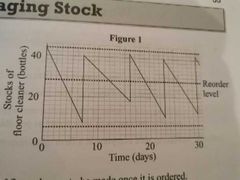
Work out lead time in days |
- Reorder = 3 days - Spike down = 7 days 7 days - 3 days = 4 days 4 days |
|
|
State the external reasons why aims and objectives change 3 marks |
- Changes In market conditions - Changes in technology - Changes in legislation |
|
|
State how JIT helps cash flow problems 1 mark |
- Less delay on buying from supplier and selling product |
|
|
Explain 1 disadvantage to JIT when managing stock 3 marks |
- Need for frequent deliveries - If there is a time issue on delivery or mistakes are made - Business may lose out on stock and sales |
|
|
State 3 disadvantages to JIT |
- Lose out on economies of scale due to low quantity buying
- Mistakes/ delay with delivery: Lose out on stock/ sales - If demand suddenly increases may not be able to supply |
|
|
State the aim of a JIT system 1 mark |
Keep stock levels to bare minimum |
|
|
State 4 benefits of JIT system |
- Reduced cash flow issues
- reduced risk of Shrinkage
- Less storage costs/ insurance
- Stock less likely to go out of date
|
|
|
Define logistics 2 marks |
- Getting goods or services from - 1 part of the supply chain to the another |
|
|
Define Procurement 2 marks |
- Finding and buying things that a firm needs from suppliers - Outside of the firm |
|
|
Explain why a business should have good procurement and logistics systems in place 3 marks |
- Improves efficiency of the business - Allows supplies to arrive at correct times - There will no breakdowns in production and consistency |
|
|
Explain 1 advantage of effective procurement and logistics systems 3 marks |
- Improve efficiency.... - Reduces overall costs - As unit costs should be lower - Allowing high profits |
|
|
State the 6 factors a business must consider when choosing a supplier |
- Delivery: near/far - Quality of stock - Price of stock - Availability of stock - Reliability of stock: On time and damagable - Trustworthiness |
|
|
How can high quality be an benefit 4 marks |
- Competitive advantage - (USP) - Improves brand image - Less costs more control |
|
|
State 2 ways that high quality products control costs |
- Reduced customer service costs: due to less complaints
- Less refunds due to fit for purpose |
|
|
Describe the process of quality control 4 marks |
- Checks raw materials from suppliers - Random samples to check quality of work in progress - Random samples of finsihed goods ( If bad they are scrapped) |
|
|
Define quality control 2 mark |
- Maintaining quality - Checking for faults at certain parts production |
|
|
Define quality assurance 2 mark |
- Maintaining quality - Checking faults at all stages Making sure faults dont happen (stop errors) |
|
|
State the 2 systems a business can use for high quality products
2 marks |
- Quality Control
- Quality assurance |
|
|
How might a business offering services use quality control 1 mark . . .,.,2 |
Use secret shoppers |
|
|
Explain how awards and certificates may help a business 3 marks |
- Reassures customers of high quality business
- More likely to buy due to competative advantage
- Increase profits and revenue |
|
|
Why might quality control be more expensive than quality assurance 1 mark |
- Products may have to be scrapped due to low quality
- Better than having dissatified customers |
|
|
State 1 disadvantage except from decrease in sales with poor customer service 1 mark |
Lower market share |
|
|
State 2 ways that good customer service can be costly 2 marks |
- More staffing costs - After sales care |
|
|
State 3 forms businesses can offer post sales services |
- User training on how the product works - Help line for phoning on issues - Servicing the product with tuning (watch links) |
|
|
State the steps of the sales process 6 marks |
- Finding customers - Approaching customers - Assessing customer needs - Presenting product to customer - Get customer to buy - Follow up with post sales help |
|
|
Explain 1 way quality assurance can help a firm to control its costs. 3 marks |
- No errors are made meaning it will save on not wasting materials - Due to it being quality checked at each stage - This in turn will control costs due to high efficency |
|
|
State 4 things bad quality can lead to (eventually causing loss of sales) |
- Poor reputation ( Lack of trust in business) - Compensation/ refunds - Lose competitive advantage - Complaints (expense on customer services) |
|
|
Explain how a better customer service can result in increase in revenue |
- Good customer service makes them feel valued - Increasing loyalty & better chance of recommendation - Therefore increase in revenue due to larger customer base |
|
|
Define net profit 1 mark |
- The profit a firm makes when all expenses are taken into account |
|
|
If you want to find gross or net profit margin what do you divide by. 1 mark |
Sales revenue |
|
|
Is insurance an operating expense Yes or No |
Yes |
|
|
A company calculates gross profit margin to be 25% & its net profit margin to be paid 4% Why would the company decide to find cheaper insurance 2 marks |
- Low net profit margin due to gross profit margin - It will increase net profit margin due to lower operating costs |
|
|
Will cheaper insurance impact gross profit margin Yes or No |
NO |
|
|
Explain the impact of the gross profit margin when increasing prices with the costs staying the same 3 marks |
- Customers will pay higher prices: increasing revenue - Cost stay same: Less percentage of profit going to production costs - Meaning Gross profit margin is higher |
|
|
Investing 140k Y1: Y2: Y3: 170k 130k 150k Work out ARR 4 marks |
Net profit: 160 + 130 + 150 - 140 = 300k Average Annual profit: 300/ 3 years = 100k ARR = AAP/ start investment ARR = 100k / 140k (x 100) = 71. 43% |
|
|
State 3 disadvantages to special offers as a promotional strategy |
- Gain less/no profit than usual - May decrease high status of brand (losing interest if certain market segments) - Customers may not pay normal price (future sale loss) |
|
|
Define a e-tailer 1 mark |
A company thats sells online |
|
|
Define a retailer 1 mark |
A business that sells products to customers |
|
|
State 1 advantage to high street retailers rather than selling online |
Likely to have: - Better customer service |
|
|
State 1 reason why e tailers are able to sell at at lower price than retailers
1 mark |
- No running premises costs |
|
|
Bespoke meaning and association with which type of production 2 marks |
- Selling a unique product - Job production |
|
|
TQM stands for |
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
What do u call a series of workers, working on products in flow production 1 mark |
Assembly line |
|
|
Which type of quality check would most likely be associated with TQM |
Quality assurance |
|
|
Define TQM 2 marks |
Top quality standards - Focus on max customer satisfaction - With zero defects with production and execution of sales |

