![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A flat, elongated organ dark in color. This pair lies in the sub-vertebral lymph sac dorsal to the pleuroperitoneal cavity. |
Kidney |
|
|
A pair of white tubes that run along the cloaca. Lateral to the mesonephric duct is a vessel, the renal portal vein. The male mesonephric duct is bigger than the female. |
Wolffian ducts |
|
|
A large bilobed membaranosus sac attached and opened to the ventral surface of the cloaca. The mesonephric duct conducts the urine from the kidney to the cloaca. |
Urinary bladder |
|
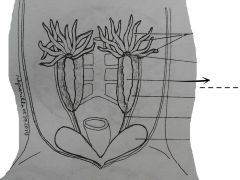
A pair of oval or elongated cylindrical yellowish bodies lying on the ventral surfaces of the kidneys. |
Testes |
|
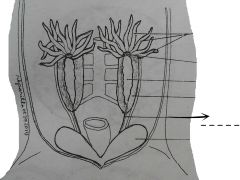
Delicate minute tubules conducting the sperm cells to the kidney. |
Vasa efferentia |
|
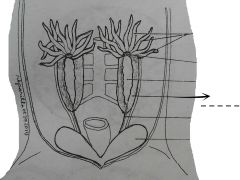
Each testis is attached to the kidney then to the dorsal body by a mesentery known as the ______ |
Mesorchium |
|
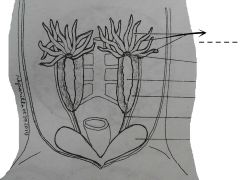
Yellowish fat finger-like bodies on top of the testes. |
Corpora adiposa |
|
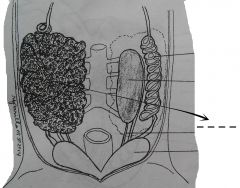
Varies greatly in size at different seasons of the year. When these are filled wtih eggs, they greatly distend the body walls. These are dark organs attached to the ventral surface of the kidneys then to the dorsal body by a mesentery, the mesovarium. |
Ovary |
|
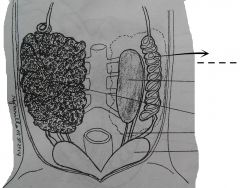
Paired white coiled tubes lying lateral to the kidneys. They vary in size at different seasons, like the ovaries. When ovaries are filled with eggs, the oviducts become dilated and very conspicuous. This serves as the passage of eggs released from the ovary to the ovisac. |
Oviducts |
|
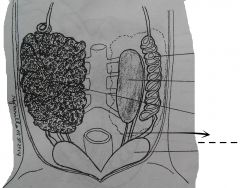
The openings of the oviducts into the pleuroperitoneal cavity located at the anterior ends of the oviducts and situated close to the anterior ends of the left and right lobes of the liver. |
Ostia |
|
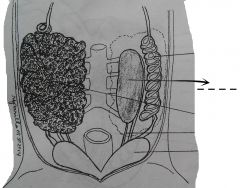
Thin-wall expanded posterior portions of the oviducts which open into the cloaca. |
Ovisacs |
|
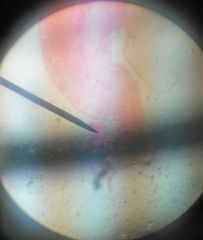
A space at the lateral border of the kidney lined by a thin simple squamous epilethium or endolethium and usually filled up with blood cells. |
Renal portal vein |
|
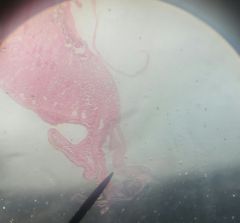
A smaller space located inner to the renal portal vein, and also at the lateral border. |
Mesonephric duct |
|
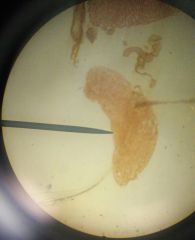
A small mass of epilethial cells on the median ventral surface of the kidney. This is an endocrine gland which secretes several hormones. |
Adrenal gland |
|
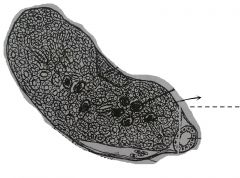
Empty structures of varied forms and lined by simple cuboidal epilethium. These are so numerous in one section, and form the bulk of the kidney structures. The tubules are for the passage of urine in the kidney and for males, also serve as the passage of sperm cells. |
Uniferous tubules |
|
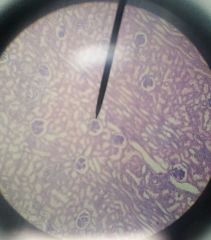
These are few solid masses of rounded bodies that appear very different from the uriniferous tubules. Each corpuscle is composed of a glomerulus and bowman's capsule. |
Malpighian bodies |
|
|
A network of arterial capillaries located at the center. |
Glomerulus |
|
|
A thin cup-shaped double membrane structure that encloses the glomerulus. |
Bowman's capsule |
|
The thin outermost covering of the testis and is lined by simple squamous epilethium. |
Visceral peritoneum |
|
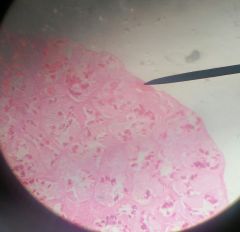
Small cavities located in the connective tissue spaces between the seminiferous tubules in the testes. These may be filled up with blood cells which may appear pinkish in color due to stain. |
Blood vessels |
|
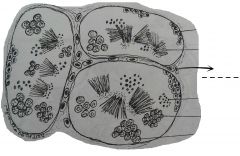
Oval or rounded cells; found outside the blood vessels and are embedded in the interstitial connective tissue. These are endocrime cells that excrete testosterone. |
Interstitial cells of Leydig |
|
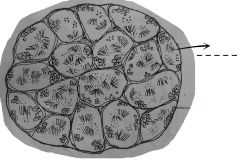
Compartent-like structures which fill up the interior of the organ. This sites of spermatogenesis and contains spermatozoa and spermatocytes. |
Seminiferous tubules |
|
A group of small rounded cells with compact dark nuclei located at the center of the cells. They are usually located next to the wall of the seminiferous tubules. These cells can undergo mitotic cell division. |
Spermatozoa |
|
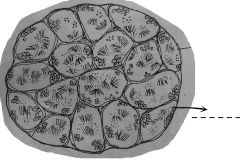
A group of cells with granular nuclei. The cells are of two kinds found separately: primary and secondary. |
Spermatocytes |
|
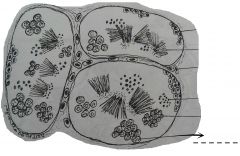
Big cells in the seminiferous tubules. |
Primary spermatocytes |
|
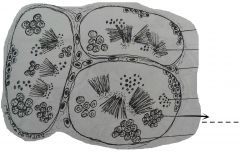
Small cells whose nuclei are similar to those of the primary spermatocytes. These cells undergo second meiosis and give rise to spermatids. |
Secondary spermatocytes |
|
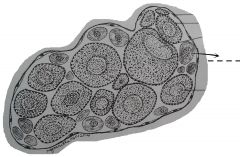
A small, dark blue in color, with a relatively large nucleus and adhere to the inner surface of the ovary wall. In the nucleus are several small dark staining bodies, the nucleoli. The nucleus of the egg is termed the germinal muscle. The cytoplasm is smooth and contains no yolk. |
Oogonium |
|
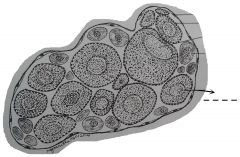
Bigger and less dark in color than the oogonium. The nucleus of each cell is centrally located. At the peripheral region of the young oocyte are smaller rounded spaces. The yolk sphereules in the cytoplasm are few and indistinct. They begin to move away from the ovary wall. |
Young oocyte |
|
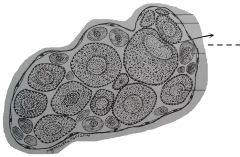
A very large cell with usually stained purple. The nucleus is located in one side of the egg above the center. The part with a dark surface and nucleus is the animal pole. The light surface is the vegetal pole. |
Old oocyte |
|
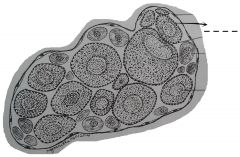
Small spherical or ovoid globules that are embedded in the cytoplasm of the oocytes. |
Yolk materials or yolk spherules |
|
|
A very thin non-cellular layer immediately around the young and old oocytes. |
Vitelline membrane |
|
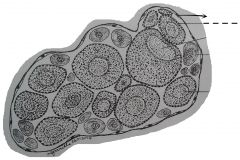
Found as a single later of flattened cells with elongated or oval nuclei adhering to the outer surface of the vitelline membrane. The gradual increase in size of the developing eggs in the ovary is attained by the synthesis as accumulation of yolk materials which are used as food reserve for the embryo. |
Follicular or nurse cells |

