![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give 4 functions of the skeleton |
1. Support 2. Movement 3. Protection 4. Production (red bone marrow - red blood cells, platelets and monocytes) |
|
|
Name the 2 parts of the skeleton |
Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton |
|
|
What passes through the central canal of the vertebrae? |
Spinal cord |
|
|
What does the axial skeleton consist of? |
The skull, vertebral column(spine), ribs and sternum |
|
|
Give the 5 regions of the vertebrae |
Cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacrum (5 fused), coccyx (tailbone, 4 fused) |
|
|
What substance is between each vertebra and what is its function? |
Discs of cartilage. Prevents friction |
|
|
The spinal vertebra |
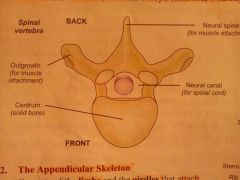
|
|
|
The spine |
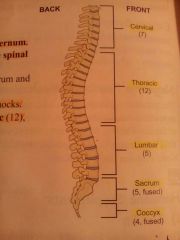
|
|
|
Name the two girdles |
The pectoral girdle The pelvic girdle |
|
|
What does the pectoral girdle consist of? |
The clavicle and the scapula |
|
|
What are attached to these? |
The bones of the arm - humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges |
|
|
Name the bones of the leg |
femur patella tibia fibula tarsals metatarsals and phalanges |
|
|
The human skeleton |

|
|
|
What is the pelvic girdle attached to? |
The sacrum of the vertebral column |
|
|
What does the appendicular skeleton consist of? |
The limbs and the girdles that attach them to the spine |
|
|
What is a joint? |
Where two bones meet |
|
|
Name the 3 different types of joints |
Immovable, slightly movable and free moving (synovial) |
|
|
A synovial joint |

|
|
|
Name two synovial joints |
Hinge joint - knee Ball and socket joint - shoulder |
|
|
What are antagonistic muscles? |
Muscles that work together in pairs to perform a particular action |
|
|
Give an example of a pair of antagonistic muscles |
Bisceps and triceps |
|
|
The biceps and triceps |

|
|
|
Name the 4 major components of the long bone |
Compact bone Spongy bone Articular cartilage Medullary cavity |
|
|
What is compact bone? |
Dense outer-layer of smooth, solid bone Strength and rigidity Contains living cells - osteoblasts |
|
|
What is spongy bone? |
Consists of honeycomb structure Strength and rigidity Lighter Spaces filled with either red or yellow bone marrow |
|
|
What is Articular Cartilage? |
Surrounds the end of bone and protects it from friction and shock |
|
|
What is the medullary cavity |
Central cavity bounded by compact bone tapering at ends to spongy bone. Filled with yellow bone marrow in adults and red bone marrow in children |
|
|
The long bone structure |
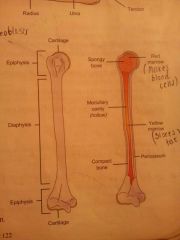
|
|
|
What is the skeleton of the human embryo made from? |
Cartilage |
|
|
At what week is the cartilage replaced by bone tissue? |
Week 8 |
|
|
How is bone made? |
Osteoblasts secrete a protein matrix which combines with calcium phosphate to form bone |
|
|
How are bones lengthened? |
At the growth plates |
|
|
What are growth plates made from ? |
Cartilage cells which divide to lengthen the bone and then change to bone by osteoblasts |
|
|
What happens to the plates when the bone is fully grown? |
They disappear - max height |
|
|
The growth plates of a bone |

|
|
|
What breaks down bone in adults? |
Osteoclasts |
|
|
How do osteoclasts work? |
Absorb broken-down bone cells and deposit calcium into the blood |
|
|
What is the calcium used for? |
Used by the osteoblasts to make calcium phosphate for new bone |
|
|
Name 4 hormones which regulate bone growth |
Thyroxine, growth hormone, oestrogen and testosterone |
|
|
Name a disorder in the human skeleton, the cause and treatment |
Disorder: arthritis Cause: joint cartilage degenerating through wear and tear and old age Treatment: asprin or replacement |
|
|
How can arthritis be prevented? |
Good diet, good footwear, avoiding excess stress on joints |
|
|
Ligaments join... |
Bone to bone |
|
|
Tendons join... |
Muscle to bone |

