![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the speed of light in air? |
186,000 mps |
|
|
Why does the speed of light travel faster through air than other substances? |
transparent substances offer more resistance |
|
|
What happens when light enters a medium at any angle other than 90 degrees? |
-the light is refracted/bent |
|
|
index of refraction |
a comparison/ration, of the speed of light in air, to the speed of light in another medium |
|
|
index of refraction for air |
1.00 |
|
|
index of refraction for water |
1.33 |
|
|
index of refraction for PMMA |
1.49 |
|
|
PMMA |
polymethylmethacrylate |
|
|
index of refraction for ophthalmic crown glass |
1.523 |
|
|
index of refraction for flint glass |
1.616 |
|
|
formula to calculate lens power in diopters |
D= 1m/focal length (m) |
|
|
focal length |
the distance from the lens to the point where the parallel light rays come to focus |
|
|
if diopter power is known, focal length can be calculated by: |
focal length= 1m/D |
|
|
The highter the _____ _____, the more the light rays will be bent; or the _____ _____ will be shorter. |
lens power |
|
|
What are the two basic types of ophthalmic lenses? |
plus and minus |
|
|
plus lenses |
-convex lenses |
|
|
minus lenses |
-concave lenses |
|
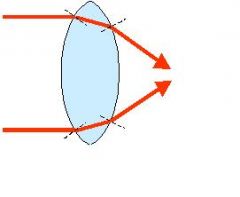
|
parallel light rays passing through a convex lens |
|
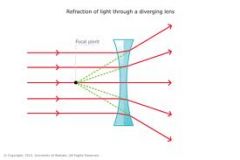
|
parallel light rays passing through a concave lens |
|
|
prism |
-thought of as a triangle |
|
|
prism power |
is measured by prism diopters |
|
|
the formula to calculate the power of a prism |
prism (D)=deviation of light ray (cm)/distance from prism (m) |
|
|
prism diopters |
1.00prismD will deviate a ray of light (or displace an image) 1 cm for every 1m of distance (measured on the tangent scale) |
|
|
What are the two basic lens forms used for ophthalmic prescriptions? |
spherical and cylindrical |
|
|
spherical lens |
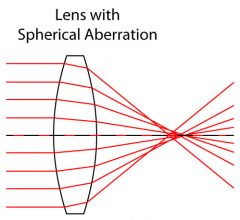
can be thought of as a portion of a round ball; deviates rays of light in the same direction |
|
|
What are the 5 types of spherical lenses? |
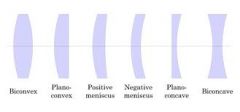
-biconvex |
|
|
biconvex spherical lens |
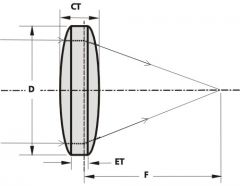
both of the lens surfaces are plus and converge light to one focal point |
|
|
plano convex spherical lens |
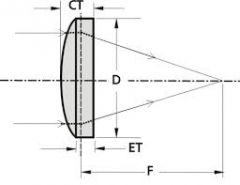
has one plus surface and one plano surface and acts to converge light to a single focal point |
|
|
biconcave spherical lens |
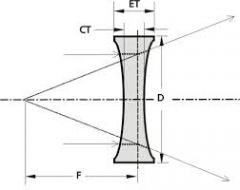
both lens surfaces are minus and diverge light rays as if the focus was in front of the lens |
|
|
plano concave spherical lens |
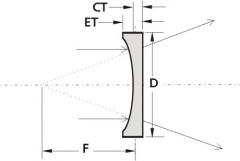
has one surface that is minus and another that is plano; diverges light rays as if the focal point were in front of the lens |
|
|
meniscus spherical lens |
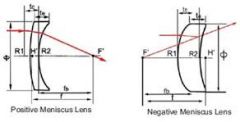
has one surface minus and another surface plus; it will either converge or diverge light rays, depending on which surface has more power |
|
|
cylindrical lens |
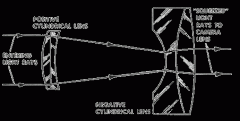
deviates light in different directions; front surface has one curved surface and one flat surface; light striking the curved surface will converge light rays, flat surface will not bring to focus (therefore has no power in one meridian and spherical plus power in the other) |
|
|
spherocylindrical lens |
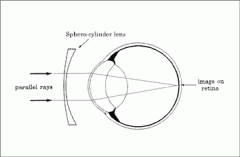
has power in one major meridian and a different power in the meridian 90 degrees away |
|
|
optical cross |
-is a diagram that denotes the dioptric power in the two principal meridians of a lens |
|
|
How far apart are the principal meridians? |
90 degrees |
|
|
total optical cross |
is a combination of the front surface power and the back surface power |
|
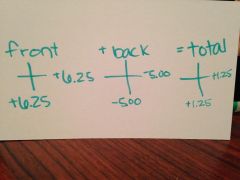
|
convex/plus optical cross |
|
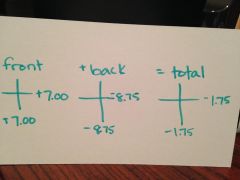
|
concave/minus optical cross |
|
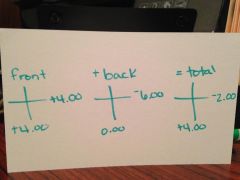
|
spherocylindrical optical cross |
|
|
the horizontal meridian is located at: |
180 degrees |
|
|
the vertical meridian is located at: |
90 degrees |
|
|
Obtaining a written prescription from an optical cross: |
-spherical power=most plus, or the least minus power |
|
|
transposing plus cylinder to minus cylinder |
-combine sphere + cylinder power =new sphere power |
|
|
transpose: |
+3.00 -1.00 x170 |
|
|
sphere equivalent of an ophthalmic prescription: |
is used for a patient's prescription when the doctor desires to prescribe less than a full cylinder of power |
|
|
formula to create spherical equivalent: |
divide cylinder power in half and combine it with the sphere power |
|
|
Why is a prism normally prescribed? |
when the two eyes don't align properly |
|
|
Abbreviations for base direction of a prism: |
BO - base out |
|
|
lens optical center for prism |
-spot in the lens with no induced prism power |
|
|
PD |
interpupillary distance |
|
|
Prentice's rule |
-used to calculate induced prism |
|
|
decentration |
may be utilized in order to avoid induced prism |
|
|
formula for calculating decentration |
frame PD (eye size+bridge size) - the patient's distance PD / 2 |
|
|
decentration is inward when: |
frame PD is LARGER than patient PD |
|
|
decentration is outward when: |
frame PD is SMALLER than patient PD |
|
|
To calculate proper multifocal power, the optometrist must: |
determine how much power the patient needs at distance and how much power the patient needs at near |
|
|
vertex distance |
the measurement from the corneal surface of the eye to the eyeglass correction |
|
|
What is the speed of light in air? |
186,000 mps |
|
|
Light waves produce vision in humans by stimulating the __________________. |
rods and cones |
|
|
The ratio of the speed of light in air to the speed of light in another medium is called the __________________. |
index of refraction |
|
|
The index of refraction 1.523 is for which of the following media? |
a |
|
|
What is the dioptric power of a lens whose focal length is 800mm? |
1.25D |
|
|
A _____________ lens will make objects appear larger. |
plus/convex |
|
|
A _______________ lens will make objects appear smaller. |
minus/concave |
|
|
Light rays passing through a prism will always be bent toward the _________ of the prism. |
base |
|
|
When looking through a prism, objects will appear to be displaced toward the _________ of the prism. |
apex |
|
|
When both of the lens surfaces are plus and converge light to one focal point, it is a ____________ lens. |
biconvex |
|
|
A __________________ lens has one surface that is flat, one surface that is plus, and it converges light to one single point. |
plano convex |
|
|
Most lenses used in ophthalmic prescriptions are ___________ lenses. |
meniscus |
|
|
A spherocylindrical lens has maximum power in one major meridian and a minimum power in the meridian _______ degrees away. |
90 |
|
|
Ophthalmic prescriptions written by ________________ will usually be in minus sylinder form. |
optometrists |
|
|
What is the minus cylinder form of the following prescription? |
OD +0.25 -5.00 x 123 |
|
|
What would be the best spherical equivalent substitute for a broken lens with a prescription of -4.25 -1.50 x 180? |
-5.00 sph |
|
|
If a patient's PD is 72 and the frame PD is 68, how much and in what direction will the laboratory need to decenter each lens in order to match the optical centers to the patient's PD? |
2mm, out |
|
|
The near correction in a multifocal lens is usually calculated for a working distance of __________ inches. |
16 |
|
|
Multifocal lenses that are used to correct three working distances are called _________________. |
trifocals |
|
|
When ordering a trifocal lens, the intermediate segment will be made ______ of the near add power unless stated otherwise. |
50% |

