![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Negative feedback describes |
when a small change stops a bigger change from happening. conditions are maintained at an average level. |
|
|
What is the "master gland"? |
The pituitary (particularily the anterior pituitary). |
|
|
What is the function of the posterior pituitary? |
storage and secretion of hormones made by the hypothalamus (oxytocin & ADH) |
|
|
Explain the tropic effects of hGH |
it stimulates the liver to produce growth factors, which in term cause the growth of bones & muscles. |
|
|
What hormone is responsible for moving calcium into the bones?
What gland produces this hormone? |
Calcitonin.
the thyroid. |
|
|
The hormone that requires 4 iodine molecules for synthesis is...
This hormone is responsible for regulating... |
thyroxin.
metabolic rate. |
|
|
Calcitonin is antagonistic to the hormone |
parathyroid hormone. |
|
|
where exactly is the hormone glucagon produced? |
the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas |
|
|
what two ways does insulin perform it's function? |
causes excess glucose to be stored by the liver as glycogen
stimulates cells (ex. muscle) to take up and use glucose |
|
|
What conditions stimulate the production of glucagon? |
low blood sugar: ex. fasting, exercising |
|
|
Insulin injections are not usually as effective in patients with...
because... |
type 2 (late onset) diabetes
the target cells no longer respond to insulin. |
|
|
what is the difference between the Adrenal medulla and the adrenal cortex? |
the medulla is responsible for the immediate response to stress (triggered by nerve impulses)
the cortex is responsible for the long term response to stress (triggered by other hormones) |
|
|
Which two hormones are produced by the adrenal medulla? |
epinephrine and norepinephrine |
|
|
Give an example of a glucocorticouid, and describe it's main function |
cortisol
increases blood glucose levels |
|
|
Give an example of a mineralcorticoid, and describe it's main function |
aldosterone
increases blood pressure through sodium reabsorption. |
|
|
Thyroxin completes a negative feedback loop through the inhibition of |
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) |
|
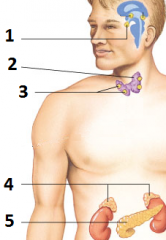
the glands labeled 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are called |
1: pituitary 2: thyroid 3: parathyroid 4: adrenal 5: pancreas |
|
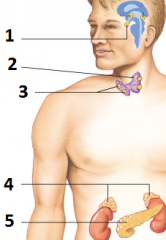
the structure labeled 1 does not directly stimulate the structure labeled... |
5 (the pancreas responds to changes in blood sugar, not nerve impulses) |

