![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the smallest particle of matter |
ATOM |
|
|
has mass and takes up space |
MATTER |
|
|
who was the first who proposed the idea of an atom who believed that all things are made up of tiny, invisible particles |
LEUCIPPUS |
|
|
Student of leucippus |
DEMOCRITUS |
|
|
Atom comes from the greek word of |
ATOMOS |
|
|
What is the meaning of the greek word of atom? |
INVISIBLE |
|
|
What do you call to the people who supported the idea of the atom? |
ATOMISTS/LEUCIPPUS GF STAN |
|
|
Leucippus and Democritus theory that atoms were indivisible was strongly opposed by |
ARISTOTLE |
|
|
what are the four elements that all matter consisted that Aristotle claimed |
EARTH, FIRE, WATER AND AIR |
|
|
Who said that all elements of matter are composed of extremely small particles called atoms? |
JOHN DALTON |
|
|
states that the different samples if the same compound always contains constituent elements in the same proportion by mass |
LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS |
|
|
If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element is in ratios of the whole numbers |
LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS |
|
|
Involves only the seperation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms |
CHEMICAL REACTION |
|
|
States that matter can be neither created nor destroyed |
LAW OF CONSERVATIVE OF MASS |
|
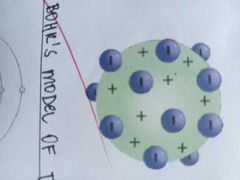
the atom is made up of something like a positively charged pudding-like material in which negatively charged electrons were scattered like plums in the pudding |
THOMSON'S PLUM PUDDING MODEL OF THE ATOM |
|

Atom is mostly an empty space that has a dense positively charged center that repelled the positively charged alpha particleswhich he used "bullets" in the experiment. This center of the atom was given the name "nucleus" by Rutherford. |
RUTHERFORD MODEL OF THE ATOM |
|

in his model, he placed each electron on a specific energy level. This electron move in different orbits around the nucles. |
BOHR'S MODEL OF THE ATOM |
|
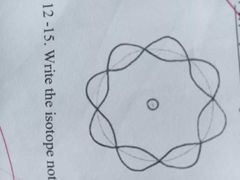
The theory of wave mechanics explains that the movement of electrons about an atom has no definite path. |
WAVE MODEL OF THE ATOM |
|
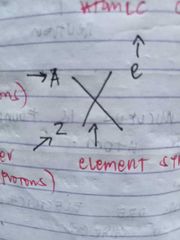
A- mass number (no. of protons and neutrons) Z- atomic number (no. of protons) X- element symbol e- atomic change |
ISOTOPE NOTATION |
|
|
Found at the center of the atom |
NUCLEUS |
|
|
Electrically neutral they have no charge |
NEUTRON |
|
|
Positively charged sub particle found in the nucleus of the atom |
PROTON |
|
|
Negative charged particle |
ELECTRON |
|
|
number of proton is equal to the number of electrons |
ATOMIC NUMBER OF THE ATOM |
|
|
Atomic mass is equal to the total number of protons and neutrons |
eurt |
|
|
Formed by chemical bonds. Composed of two or more elements |
COMPOUND MOLECULES |
|
|
when molecules tend to share electrons to complete the required electrons. (Occurs in between non metals) |
COVALENT BOND |
|
|
Electrons are transferred (occurs in between a metal and non metal) |
IONIC BOND |
|
|
The extend of sharing of electrons between atoms in a molecule is dependent of the electronegativity or the ability of each atom to attract electrons toward it |
tama |
|
|
All atom has its own electronegativity value (Ev) |
sigi |
|
|
Electronegativity unit |
∆EN |
|
|
Based of Linus Pauling's scale, () is the most electronegative element |
FLOURINE |
|
|
Least electronegativity element |
CESIUM & FRANCIUM |
|
|
∆EN ≥ 2.0 (2.0- UP) |
IONIC BOND |
|
|
0.5 < ∆EN < 2.0 (0.6-1.9) |
POLAR COVALENT BOND |
|
|
0 ≥ ∆EN ≤ 0.5 (0-0.5) |
NONPOLAR COVALENT BOND |

