![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cell |
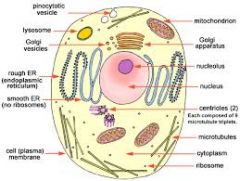
the basic unit/structure of all living things (Schwan and sheldon) |
|
|
who said "all living things come from pre-existing cells"? |
virchow |
|
|
cell size is limited by __ __ to __ __. |
surface are to volume ratio |
|
|
fluid mosaic model (FMM): |
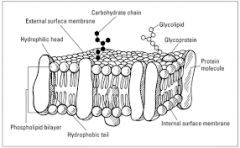
|
|
|
inclusion |
a misc. category not an organelle. a body or particle recognizably distinct from the substance in which it is embedded. |
|
|
organelles |
are found only in eukaryotic cells and are absent from the cells of prokaryotes such as bacteria.provides a variety of functions bound within eukaryotic cells |
|
|
mitochondria |
the site of aerobic cellular respiration contain cristae, which increase the surface area. has it's own DNA: important in the search for eve used in forensics such as 9/11 |
|
|
melas |
Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes syndrome, a rare form of dementia caused by mutations in the genetic material (DNA) in the mitochondria.a person has stroke-like symptoms and their lactic acid is up |
|
|
LHON |
a progressive disease in which you don't get enough energy to the eye. may go blind. |
|
|
ribosomes |
where your cell assembles proteins |
|
|
endoplasmic reticulum (ER) |
a network of tubular membranes within the cytoplasm of the cell smooth: lacks ribosomes rough: builds protein products |
|
|
golgi apparatus: |
has 40 known functions, some include: ceasing raw material puts together material stores material puts material out often referred to as "factory-like" or "the post office" also associated with the production of microbodies |
|
|
lysosomes |
an organelle in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells containing degradative enzymes enclosed in a membrane. |
|
|
tay sachs |
the most painful infantile death; an lysosome defection higher in people of Jewish decent tt homozygous recessive |
|
|
peroxisomes |
breaks down hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
adrenoleukodystrophy |
peroxisomal dysfunction can bring about nerve damage lethal infantile death |
|
|
cytoskeleton |
give the cell its shape contain microfilaments :made up of protein , actin, and myosin micro tubules: made up of tubulin intermediate filaments: made up of the protein keratin. makes cell tougher |
|
|
spherocytosis |
when cells lose their normal shape |
|
|
passive transfer |
type of transfer not involving ATP Ex: diffusion, osmossis |
|
|
diffusion |
the random movement of particles in a system from regions of greater to smaller concentration ex: perfume diffusion from a corner of a room to the whole room |
|
|
how to influence the diffusion rate |
1. increase temperature 2. increase pressure |
|
|
osmosis |
the moving of water in a system |
|
|
solute |
what is dissolved |
|
|
solvent |
what the solute is dissolved in |
|
|
hypertonic solution |
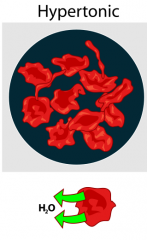
salinity |
|
|
hypotonic solution |
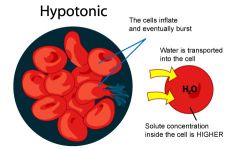
|
|
|
isotonic solution |

balancing the outside and the inside world. this happens in plasma. |
|
|
active transfer |
a type of transfer that uses ATP |
|
|
sodium potassium pump |
a type of pump that pumps sodium; potassium in cell
|
|
|
calcium pump |
a tpe of pump that brings calcium into the cell |
|
|
proton/hydrogen pump |
a type of pump that brings hydrogen into the cell helps maintain a constant pH |
|
|
cystic fibrosis (cf) |
an example of pump failure over 900 mutations; one including delta 508 (respiratory problems , rep. organs, and sweat glands) |
|
|
hyperkalemic period paralysis (HPP) |
A sodium potassium pump problem that effects your nervous system. brought about by stress |
|
|
long Q-T |
a sodium potassium pump error associated with deafness and heart problems Q on EKG is elongated |
|
|
cell cycle |
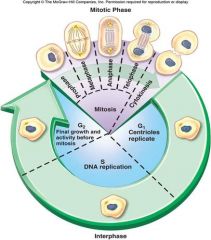
|
|
|
growth hormones |
regulate the cell clock |
|
|
acromegaly |
growth is normal at birth and in childhood they start hitting an unbelievable growth spurt |

