![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Worsted yarns vs. Woolen yarns |
Worsted: smooth, compact, sleek Woolen: fluffy, soft, bulky, weak |
|
|
The difference between: Blend Mixture Combination |
Blend: intimate mixture, think of a blender Mixture: when the warp and weft have different yarn types Combination: when the separate plies have different fiber types |
|
|
Direct System measurements |
Denier (weight of 9,000 meters) Tex (weight of 1,000 meters) Decitex (weight of 10,000 meters) Length is defined, weight is the variable SMALLER NUMBER = SMALLER YARN |
|
|
Indirect System measurements |
English counting system Used for cotton, worsted, woolen However many "hanks" it takes to make 1 lb Weight is defined, length is the variable SMALLER NUMBER = BIGGER YARN |
|

|
Boucle yarn |
|

|
Gimp yarn |
|
|
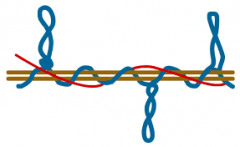
Snarl/spike yarn |
|

|
Spiral/corkscrew yarn |
|

|
Slub yarn |
|

|
Chenille Yarn |
|

|
Ratine yarn |
|

|
Flake/fleck/flock yarn |
|
|
Most common types of texturizing? |
1. False twist - twist inserted and heat set 2. Air-jet - flung around in a hot air |
|
|
Types of yarn twist |
Low twist Nap twist Average twist Voile twist Crepe twist |
|
|
Spun yarns |
fuzzy, comfortable, bulky, more likely to pill yarn strength is NOT related to fiber strength higher twist = higher strength |
|
|
Continuous filament yarns |
smooth, no pilling, compact, no bulk, shiny yarn strength IS related to fiber strength |
|
|
What does texturizing do? |
Increases bulk and stretch |

