![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In 1953 model of the shape of DNA was published in part due to work of Watson, Crick, Wilkins and Franklin. The shape of DNA was described as a. linear single strand b. a linear double strand c. double helix d. a ring |
c. double helix |
|
|
The monomers that help build DNA and RNA are nucelotides. A nucleotide includes a. an amino acid, a sugar and nitrogen base b. an amino acid and a sugar c. a polysaccharide and fat d. a polysaccharide, sugar and nitrogen base e. a sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base |
e. a sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base |
|
|
A sample of DNA contains 13% Guanine. Without mutations, we would expect a. 13% uracil in the sample b. 13% adenine in the sample c. 13% thymine in the sample d. 13% cytosine in the sample |
d. 13% cytosine in the sample |
|
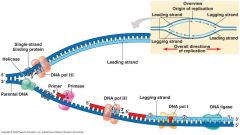
The process shown below allows the chromosomes to be copied and is called a. protein synthesis b. DNA replication c. meiosis d. mitosis |
b. DNA replication |
|
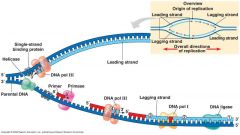
If letter D indicates an enzyme that seals up fragments on a newly built strand of DNA, this world be a. DNA polymerase I b. DNA ligase c. RNA polymerase III d. helicase |
b. DNA ligase |
|
|
In the cell cycle, when would the process shown in Figure 1 occur? a. S phase b. G1 phase c. G2 phase d. M phase |
a. S phase |
|
|
Which of the following shows the correct order of phases as a cell divides using mitosis? a. Prometaphase - Prophase - Metaphase - Anaphase - Telophase and Cytokinesis b. Prophase - Prometaphase - Anaphase - Metaphase - Telophase and Cytokinesis c. Prophase - Prometaphase - Metaphase - Anaphase - Telophase and Cytokinesis d. Prometaphase - Metaphase - Prophase - Anaphase - Telophase and Cytokinesis e. Telophase and Cytokinesis - Anaphase - Metaphase - Prophase - Prometaphase |
c. Prophase - Prometaphase - Metaphase - Anaphase - Telophase and Cytokinesis |
|
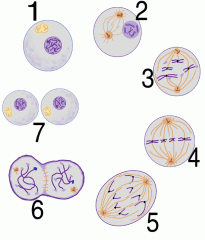
If diagram A is showing a cell in interphase, when do the sister chromatids connect with a centromere? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 |
b. 2 |
|
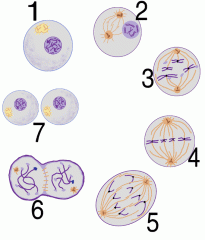
Which phase above is the shortest phase of mitosis? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 |
e. 5 |
|
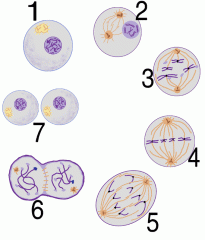
In which phase are the sister chromatids checked to see if the are attached to the mitotic spindle correctly and the M checkpoint completed? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 |
d. 4 |
|
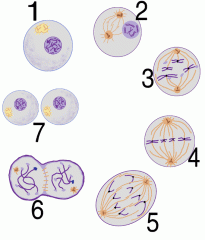
Which phase of mitosis does the diagram labeled 6 above demonstrate? a. cytokinesis b. prophase c. metaphase d. prometaphase |
a. cytokinesis |
|
|
An organism called a plasmodial slime mold is one huge cytoplasmic mass with many nuclei. Which step of cell division would have been skipped to create the multiple nuclei in one cell? a. metaphase b. prophase c. cytokinesis d. telophase e. anaphase |
c. cytokinesis |
|
|
Why is cancer more common in older people than in younger people? a. it takes many cells to produce cancer, and older people have more cells than younger people b. the DNA of older people is more susceptible to carcinogens than younger people c. our immune systems become stronger as we age d. harmful mutations that cause cancer accumulate over our lifetimes e. all of the above |
d. harmful mutations that cause cancer accumulate over our lifetimes |
|
|
A cell with 4 chromosomes is placed in medium containing radioactive phosphate, making any new DNA strand formed radioactive. The cell replicates and divides. Which of the following is true of the daughter cells (assume no mutations or errors are made in replication or cell division)? a. the daughter cells will contain no radioactive DNA for any of the chromosomes in either of the cells b. all of the DNA strands will be radioactive DNA and the other daughter cell will not contain any chromosomes that are radioactive c. one daughter cell will contain all of the radioactive DNA and the other daughter cell will not contain any chromosomes that are radioactive d. each daughter cell will contain one half of the radioactive DNA because each strand replicated would contain one old nonradioactive strand paired with one newly built radioactive strand |
d. each daughter cell will contain one half of the radioactive DNA because each strand replicated would contain one old nonradioactive strand paired with one newly built radioactive strand |
|
|
Each matching pair of chromosomes containing the same sequence of genes in a diploid cell are called? a. tetrads b. homologous chromosomes c. haploid chromosomes d. none of the above |
b. homologous chromosomes |
|
|
The exchange of segments of homolgous chromosmes or crossing over occurs in meiosis at a. phophase I b. metaphase I c. anaphase I d. telophase I |
a. phophase I |
|
|
Creating a genetically unique offspring occurs due to which of the following processes? a. random fertilization events b. crossing over c. independent assortment of chomosomes d. both a and b e. a, b, and c |
A, b and c; Random fertilization events, crossing over and independent assortment of chromosomes |
|
|
If a single diploid somatic cell with 26 chromosomes undergoes meiosis, how many chromosomes will one of the resulting cells contain? a. 2 b. 8 c. 13 d. 26 e. 32 |
c. 13 |
|
|
Cystic Fibrosis is a recessive genetic disorder. This mutation doesn't occur on the 'sex chromosome' or 23rd chromosome. In order for an individual to express this disease, they must be? a. homozygous dominant b. homozygous recessive c. heterozygous d. either a or c e. either b or c |
e. Either b or c; homozygous recessive or heterozygous |
|
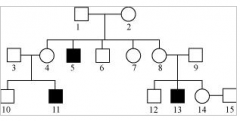
Black squares represent a person with the recessive disease, cystic fibrosis. What is the gender and genotype of the individual marked by the number 1? a. male NN b. female N c. female Nn d. male Nn e. male nn |
d. male Nn |
|
|
Mendel found purple and white flowers in his pea pants. These flower colors are different forms or versions of a gene and are known as? a. homologs b. crosses d. alleles d. pedigrees e. punnetts |
d. alleles |
|
|
A case like height where more than one gene impacts one phenotypic trait is known as?
a. incomplete dominance b. multiple alleles c. codominance d. pleiotrophy e. polygenic inheritance
|
d. pleiotrophy |
|
|
Most genes can be found in populations in more than two forms. For example, ABO human blood groups involve three alleles of a single gene. This is known as? a. incomplete dominance b. multiple alleles c. codominance d. pleiotrophy e. polygenic inheritance |
b. multiple alleles |
|
|
A student crosses a homozygous red snap dragon with a homozygous white snapdragon, 100% of the offspring are pink snapdragons. This in an example of? a. incomplete dominance b. multiple alleles c. codominance d. pleiotrophy e. polygenic inheritance |
a. incomplete dominance |
|
|
Any change in DNA, a gene or a chromosome is known as a(n)? a. X-linked trait b. allele c. mutation d. homolog |
c. mutation |
|
|
If the following leters represent genes along a chromosome, what kind of mutation would allow the genes to change from ABCDEF --> AEDFCBF? a. deletion b. duplication c. translocation d. inversion |
d. inversion |
|
|
What source material is used in the first step of protein synthesis to build the mRNA strand? a. amino acids b. mRNA strand c. tRNA strand d. rRNA strand e. DNA |
e. DNA |
|
|
Which of the following matches the first step of protein synthesis with its correct location in the cell? a. translation: in the nucleus b. transcription: in the nucleus c. translation: in the cytoplasm at a ribosome d. transcription: in the cytoplasm at a ribosome e. prophase: in the nucleus |
b. transcription: in the nucleus |
|
|
Which of the following matches the second step of protein synthesis with its correct location in the cell? a. translation: in the nucleus b. transcription: in the nucleus c. translation: in the cytoplasm at a ribosome d. transcription: in the cytoplasm at a ribosome e. prophase: in the nucleus |
c. translation: in the cytoplasm at a ribosome |
|
|
how many nucleotides are necessary to code for a protein that is 100 amino acids long? a. 3 b. 33 c. 100 d. 200 e. 300 |
e. 300 |
|
|
If the DNA code reads GTTCAT, then the mRNA complimentary? a. CAAGTA b. CAAGUA c. GTTCAT d. GUUCAU |
b. CAAGUA |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription in all the following ways except? a. add a modified guanine nucleotide cap to the start of the transcript b. add a repeating set of the adenine nucleotides to the end of the transcript c. cut the introns out of the transcript d. send the mRNA to the golgi apparatus for processing e. splice the exons together to be translated later |
d. send the mRNA to the golgi apparatus for processing |
|
|
The RNA that carries an amino acid on one end and an anticodon on the other end is? a. mRNA b. rRNA c. tRNA d. both a and b e. both b and c |
c. tRNA |
|
|
Which of he following is the name of the specialized proteins that recognize a sequence of DNA and cut DNA at those specific sites? a. PCR b. organismal cloning c. gel electrophoresis d. restriction enzymes |
d. restriction enzymes |
|
|
Which of the following allows small sections of DNA to be copied outside of a cell? a. PCR b. organismal cloning c. gel electrophoresis d. restriction enzymes |
a. PCR |
|
|
Appearance of traits for an individual |
Phenotype |
|
|
Box device used to predict offspring genotype and phenotype ratios |
Punnett Square |
|
|
Always expressed when at least one allele is present |
Dominant Alleles |
|
|
Genotype containing only one type of allele |
Homozygous |
|
|
To alleles for the same trait separate during gamete formation |
Mendel's Law of Segregation |
|
|
Adds a short RNA sequence to start replication |
Primase |
|
|
Builds new RNA strand in transcription |
RNA Polymerase |
|
|
Untwists and unzips DNA at replication fork |
Helicase |
|
|
Proofreads DNA strand for mistakes |
Nuclease |
|
|
Removes RNA primers and switches them to DNA |
DNA Polymerase I |
|
|
A scientist works in a lab with DNA and RNA but forgets to label one collection tube. Name 2 ways the scientist would be able to tell the two chemicals apart. |
1. RNA: single stranded, Ribose sugar 2. DNA: Double helix shape, Dexyribose sugar |
|
|
How many daughter cells are produced at the end of each process? Mitosis: Meiosis: |
Mitosis: 2 Meiosis: 4 |
|
|
How many rounds of division does each process do? Mitosis: Meiosis: |
Mitosis: 1 Meiosis: 2 |
|
|
Are the cells created in the process identical to the parent cell or different from the parent cells? Mitosis: Meiosis: |
Mitosis: Identical Meiosis: Different |
|
|
Describe whether the daughter cells created are haploid or diploid? Mitosis: Meiosis: |
Mitosis: Diploid Meiosis: Haploid |
|
|
How are the processes of transcription and translation important for your life? |
Helps build protein traits from DNA code |
|
|
Mendel allows two heterzygous axial flowers (flower grows from the middle of the stem) to breed. If axial flower position is dominant to terminal flower position (flower grows from the end of the stem), complete a Punnett Square and state the genotype and phenotype ratios for the offspring. Use the letter A or a for the alleles and make sure the two letters are clearly distinguishable. F1 Genotype Ratios: F1 Phenotype ratios: |
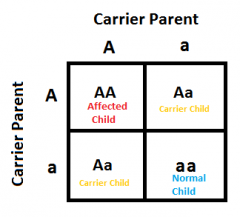
F1 Genotype Ratios: AA (25%) : Aa (50%) : aa (25%) F1 Phenotype ratios: Axial (75%) : Terminal (25%) |
|
|
G1= growth of cell S= DNA is copied G2= growth and cell division prepping M= mitosis/cell division |
the cell cycle phases that a cell goes through in its life |
|
|
Copies new DNA |
DNA polymerase III |
|
|
Seals up fragments |
DNA ligase |
|
|
2 alleles are different |
heterozygous |
|
|
Combination of genes for an individual |
Genotype |
|
|
Family tree diagram that helps describe how a trait is being inherited in a family |
Pedigree |
|
|
Alleles for different traits are independently sorted during gamete formation |
Mendel’s law of independent assortment |
|
|
DNA replication makes a copy of all the chromosomes |
S Phase |
|
|
chromosomes pack upcrossing over: homologous chromosomes line up in tetrads and exchange links of DNA that carry the same genes (gives genetic variation; AKA synapsis)longest step of meiosis |
Prophase I |
|
|
diploid number = 46 haploid = 23 sperm = 23 chromosomes egg = 23 chromosomes fertilization = 46 chromosomes |
Humans |
|
|
creates 2 identical daughter cells new cells are diploids |
Mitosis |
|
|
creates 4 unique cells new cells are haploids (half the number of chromosomes as a diploid cell) new cells are different from their parents sperm/egg are created using this process |
Meiosis |
|
|
mRNA: rRNA: tRNA: |
messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA |

