![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
infection |
invasion and multiplication of microorganisms in/on body tissues which result in clinical signs and symptoms |
|
|
nosocomial infection |
occurs or is acquired in a hospital. (HAI) - wound, urinary, bowel, resp, bloodstream |
|
|
exogenous infection |
arises from external microorganisms not normal to the individual flora (HAI) - ex) salmonella
|
|
|
endogenous infection |
patients flora becomes altered + overgrowth results. (HAI) - ex) infections caused by enterococci, yeasts + streptococci - caused by transfer of microorg. from one part of body to another
|
|
|
HAI |
Health care associated infection
|
|
|
endemic |
singular person with disease |
|
|
epidemic |
whole community with disease, one region outbreak
|
|
|
pandemic |
several countries/continents effected by disease |
|
|
who is most at risk for infection/disease? |
young/old poor nutrition stress immuno-comprimised individuals chronic illness |
|
|
significance of infection to health care system/workers
|
increase in:
-nosocomial infections - cost to system - motbidity -mortality |
|
|
latrogenic infection |
infection caused by treatment or diagnostic procedures |
|
|
chain of infection |
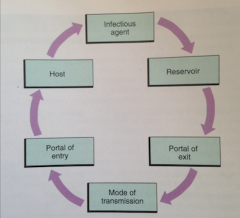
- infectious agent - reserviour - portal of exit - mode of transportation -portal of entry - host -infectious agent
** all links must be present for an infection to occur
|
|
|
infectious agent |
any micro-organism capable of causing disease |
|
|
reservoir |
environment human, animal, or inanimate in which the organisms lives and multiply
1) food 2) oxygen (anaerobic and aerobic) 3) water 4) temp 35-37 5) pH 5-8 6) minimal light |
|
|
portal of exit |
means by which the infectious organism leave their reserviour
- respiratory - urinary - GI - GU
|
|
|
pathogens carried through.. |
- blood - body fluids - excretions - secretions
|
|
|
mode of transmission (6 ways) |
1) direct (handshake) 2) indirect (ball) 3) droplet (less than 1 meter) 4) airborne (more than 1 meter) 5) vehicle ( water, drugs, food) 6) vectorborne (mosquistoes, skunks etc) |
|
|
droplet vs airborne |
droplet = less than 1 meter - more than 5 but less than 20 microns airborne = more than 1 meter - less than 5 microns |
|
|
portal of entry |
means by which the infectious agent gains entry into a new host via resp, urinary, GI, GU |
|
|
susceptible host |
final link is another person, people in hospitals have lower resistance to infection
|
|
|
susceptibility depends on: |
-age -nutritional status (decreased protein) - stress - immune status -disease process - heredity - medical therapy (some drugs lower immune system) |
|
|
body system defenses? |
non-specific - normal flora - organ system defenses - inflammatory response - local - systemic specific - immune response |
|
|
2 types of inflammatory response |
localized response: - pain/tenderness -redness -swelling -heat -decreased/loss of function
systemic response: - fever - malaise - anorexia - N+V - lymph node enlargement - leukocytosis - increase in WBC |
|
|
signs and symptoms of infection depend on: |
- pathogen causing the infection - localized and or systemic - body system - strength of response |
|
|
health promotion strategies |
- proper nutrition - adequate hydration - hygiene - lower stress - R&R - immunization
|
|
|
asepsis: define |
decreased # organisms + prevent transfer of microorganisms from 1 person or another |
|
|
2 types of Asepsis |
medical asepsis (clean technique) -ways to reduce & prevent spread of microorganisms surgical asepsis (sterile technique) - practices that keep an area/object free from all microorganisms |
|
|
Break the chain of infection (6 parts) |
1) infectious agents 2) reserviors/sources 3) portals of exit 4) transmission 5) portals of entry 6) susceptible host |
|
|
getting rid of infectious agents: |
cleaning: - removes all foreign matter - precedes other precesses - may need to wear protective equipment disinfection: - eliminates many or all organisms exept SPORES - chemical disinfection, pasteurization, UV light sterilization: - eliminates ALL organisms including spores - stream under pressure is the most sommon method - time limited effectiveness
|
|
|
efficient sterilization depends on: |
1) concentration of solution + duration of contact 2) type + # of pathogens 3) all surface areas must be treated 4) temp of environment 5) presence of soap 6) presence of organic matter. |
|
|
reservoirs/ sources protection |
- elimination of sources harboring organisms - environmental sanitation - hygiene/bedside/ wound care - employee health - surveillance with routine swabs |
|
|
portals of exit |
wound drainage GI products resp secretions (coughing containment) |
|
|
modes of transmission |
handling/disposal of body fluids specimen collection fomites needle disposal (safety devices) food handeling |
|
|
portals of entry: prevention |
-maintaining skin integrity -avoiding interruptions in drainage tubes, catheters, IV tubing - keep draining wounds covered - sterile technique for sterile cavities - carefully discard used items: sharp objects, needles, dressings, tissues etc. - use of barrier precautions |
|
|
how to protect the susceptible host |
- protect normal defense mechanisms - recognize high risk clients - maintain healing processes - use barrier precautions for all care
|
|
|
use personal protection equipment when? |
- dealing with body fluids containing visible blood (not sweat) - non-intact skin - mucous membranes
|
|
|
2 tiered precautions |
1) routine practices (AKA standard precautions) - apply to blood, all body fluids, secretions, excretions, non-intact skin, mucous membranes 2) Additional (isolation precautions)
|
|
|
minimum alcohol % in hand sanitizer? |
60% |
|
|
nursing responsibilities |
- identify potential concerns - establish & maintain precautions - provide for the teaching & emotional support of those affected |
|
|
colonization |
presence of bacteria on/in body - not necessarily causing harm yet |
|
|
carriers |
animals or persons who show no symptoms of illness but who have pathogens in or on their bodies that can be transferred to others |
|
|
normal flora |
Microorganisms that normally reside at a given site and under normal circumstances do not cause disease. |
|
|
transient flora |
not your bodies normal flora - transferred from someone else |
|
|
when do MRSA + VRE symptoms begin? |
72 hours after hospitilization (if aquired there) |
|
|
MRSA+VRE have in common? |
both resistant to normal antibiotics/penicillin etc.. |
|
|
colostridum difficile (C diff) |
is a bacterium that causes mild to severe diarrhea and intestinal conditions like pseudomembranous colitis (inflammation of the colon). |

