![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What structures go awry in acne rosacea?
|
Dysfunctions of the sebaceous glands of the face, neckand shoulders
|
|
|
What are the opthalmic symptoms of acne rosacea?
|
Redness
Blurring Foreign body sensation Pain |
|
|
What are the systemic findings of acne rosacea?
|
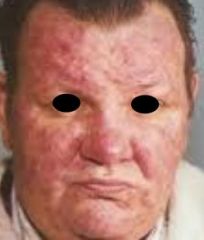
Midfacial erythema
Papules Pustules Rhinophyma |
|
|
What are the ocular findings of acne roseacia?
|
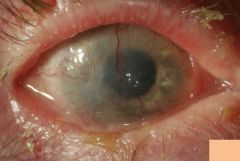
Blepharitis
Aqueous tear deficiency Eyelid margin telangiectasia Chronic conjunctivitis Corneal neovascularization |
|
|
What are the three components of the tear film? Which are ruined in acne roseacea?
|
Liquid
Lipid Mucosal Acne roseacea ruins the liquid, lipid |
|
|
What is the management of acne rosacea?
|
Systemic tetracyclines
Topical metronidazole Artificial tears If lots of inflammation, topical steroids |
|
|
How do tetracyclines alter the tear film in acne rosacea?
|
Altering lipid-->better film
Inhibition of MMPs Killing bacteria that are on the lid |
|
|
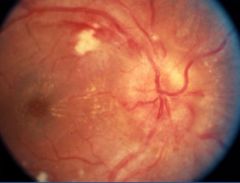
What are the findings on an eye exam during HIV retinopathy?
|
Cotton wool spots
Retinal hemorrhages |
|
|
What are some infections that people with HIV are particularly vulnerable to?
|
Cytomegalovirus
Toxoplasmosis Syphilis HSV, zoster Cryptoccus |
|
|
What is a type of neoplasm in HIV that can effect the eyelid?
|
Kaposi's sarcoma
|
|
|
When does CMV retinitis ocur?
|
CD4< 50
|
|
|
What are the treatments for CMV retinitis?
|
Ganciclovir
Foscarnet Cidofovir |
|
|
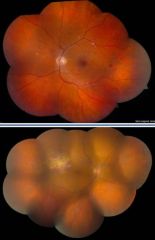
What does a retina look like during hypertensive retinopathy?
|
Variable spectrum
Arterial narrowing to retinal hemorrhages to disc edema |
|
|
What are the symptoms for hypertensive retinopathy?
|
Again, a spectrum.
Anywhere from no changes to a severe visual loss |
|
|
What is the management for hypertensive retinopathy?
|
KEEP THAT BP DOWN.
|
|
|
Where does giant cell arteritis take place?
|
Medium size branches of the carotid artery
|
|
|
What kind of a disorder is giant cell arteritis?
|
Autoimmune
|
|
|
Who gets giant cell arteritis?
|
Elderly people
|
|
|
What are the complications secondary to giant cell arteritis?
|
Arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy
Central retinal artery occlusion Ocular motor cranial nerve palsy |
|
|
What are the symptoms of giant cell arteritis?
|
Headache
Scalp tenderness Jaw claudication Fever, malaise Proximal muscle stiffness |
|
|
If you think that someone might have giant cell arteritis, what labs should you order?
|
Sed rate
CRP |
|
|
What is the treatment for giant cell arteritis?
|
High dose corticosteroids
|
|
|
What kind of a disease is Graves disease?
|
Autoimmune
|
|
|
What is the pathology that happens in Graves disease?
|
An autoimmune reaction takes place that binds to TSH receptors, causing super high levels of T3 and T4
|
|
|
What are the two phases of Graves disease?
|
Hypermetabolic state
Lymphocytic infiltrative state |
|
|
What are the sympoms of Graves disease?
|
Red, watery eyes
Eye prominence (THEY LOOK VERY SERIOUS.) Double vision |
|
|
What are the signs of Graves disease?
|
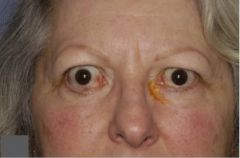
Lid retraction
Conjunctival injection Tearing Proptosis Reduced eye movement Optic neuropathy |
|
|
What happens to the eyes during the hypermetabolic state?
|
The muscles above the eyes are stimulated to contract: you can see the sclera both ABOVE and BELOW the cornea
|
|
|
What happens to the eyes during the infiltrative state of Graves' disease?
|
There's a lymphocytic infiltration of the extraocular muscles causing the eyes to bulge out
|
|
|
What is the treatment of Graves disease?
|
Symptomatic:
Artificial tears (for dry eyes) Immunosupression (for the acute lymphocytic infiltrate) Curative: SURGERY!!! Thyroid regulation |
|
|
What is a serious complication that can happen to the eyes in MS?
|
Optic neuritis
|
|
|
Where does ocular neuritis present in MS patients?
|
Retrobulbar without optic nerve edema
|
|
|
What's the treatment of optic neuritis in the context of optic neuritis?
|
High dose steroids
|
|
|
What are the ophthalmic complications related to myasthenia gravis?
|
Fluctuating ptosis
Diplopia |
|
|
What are some systemic medications that can cause problems with the eyes?
|
Anticholinergics
Corticosteroids Ethambutol hydrochloride Hydroxychloroquine sulfate Isoniazid Minocycine hydrochloride Sidenafil citrate Tamulosin Topiramate |
|
|
What is the prototypic anticholinergic drug?
|
Atropine
|
|
|
What are indications for anticholinergics?
|
GI/UT disorders
Parkinson's Psychotic disorders Reactive airway disease |
|
|
What is the effect of the anticholinergics on the eyes?
|
Loss of accommodation
Pupil dilation RARE BUT TERRIBLE: angle closure glaucoma |
|
|
What are some of the corticosteroids that can have an effect on the eyes?
|
Prednisone
Fluticasone |
|
|
What are the clinical indications for the corticosteroids?
|
Immunosuppression
Asthma |
|
|
What are the effects of corticosteroids?
|
CATARACTS!!!
Open angle glaucoma Intracranial hypertension in kids |
|
|
What's the indication for ethambutol hydrochloride?
|
TB treatment
|
|
|
What is the effect of ethambutol hydrochloride on the eyes?
|
Optic neuropathy in high doses
|
|
|
Why is ethambutol such a worry with ophthalmic manifestations?
|
People are on it for very long time
|
|
|
What is the indication for hydroxychloride sulfate?
|
Immunosuppression
|
|
|
What is the ophthalmic effect of hydroxychloroquine sulfate?
|
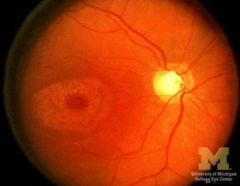
irreversible retinopathy in high doses over a long period of time (BULLS EYE RETINOPATHY!)
|
|
|
What are the uses of isoniazid?
|
TB treatment
|
|
|
What is the ophthalmic effect of isoniazid?
|
Optic neuropathy in high doses
|
|
|
What are the uses of minocycline hydrochloride?
|
Acne
Antibiotics |
|
|
What are the ophthalmic effects of minocycline hydrochloride?
|
Papilledema from intracranial HTN
Young people especially get this guy. |
|
|
What are the uses of sidenafil citrate?
|
Erectile dysfunction
|
|
|
What are the ophthalmic effects of sidenafil citrate?
|
Transient bluish vision
Ischemic optic neuropathy |
|
|
What is tamulosin used for?
|
Benign prostatic hyperplasi
|
|
|
What are the ophthalmic manifestations of tamulosin?
|
It causesa floppy iris: hard to operate on.
|
|
|
What are the uses of topiramate?
|
Seizure, migrane prophylaxis
|
|
|
What are the ophthalmic effects of topiramate?
|
Angle-closure glaucoma
Myopic shift |
|
|
What are the uses of alpha2 adrenergic agonists with relation to the eyes?
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
What is the mechanism by which alpha2 adrenergic agonists act at the eyes?
|
Reduce the aqueous humor production, increase aqueous outflow
|
|
|
What are the systemic effects of alpha2 adrenergic agonists?
|
Dry mouth
Lethargy Hypotenson Seizures ENCHAOPATHY IN KIDS! |
|
|
What population should you not prescribe alpha2 adrenergic agonists to?
|
KIDS.
|
|
|
What are the clinical indications for beta-adrenergic antagonists?
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
What is the mechanism in the eyes that beta adrenergic agonists?
|
Decreasing aqueous humor production
|
|
|
What are the systemic effects of the beta adrenergic angagonists?
|
Bradycardia
Bronchospasm Hypotension Reduced libido Depression |
|
|
What are some of the oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Acetazolamide
Methazolamide |
|
|
What are the clinical indications of the oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of the oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Decrease aqueous humor production
|
|
|
What are some of the systemic side efects of the oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Kidney stones Tingling Abnormal taste K depletion Blood dyscrasias |
|
|
What are some of the topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Brinzolamide
Dorzolamid |
|
|
What are the clinical indications for the topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of the topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Decrease aqueous humor production
|
|
|
What are the systemic effects of the topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Bitter taste
|
|
|
What kinds of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are first line?
|
The oral ones before the topical ones
They're more effecacious |
|
|
What are some of the different prostaglandin analogs?
|
Bimatoprost
Latanoprost Travoprost |
|
|
What are the indications for the prostaglandin analogs?
|
Glaucoma
Hypotrichosis |
|
|
What is the mechanism for the prostaglandin analogs?
|
Increased aqueous outflow
|
|
|
What are the systemic effects of the prostaglandin analogs?
|
Flu-like symptoms (rare)
|
|
|
What are some of the parasympotholytics used in ophthalmology?
|
Atropine
Cyclopentolate Homatropine Scopolamine Tropicamide |
|
|
What are the clinical indications for the parasympatholytics?
|
Dilation of the eyes
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of the parasympatholytics?
|
Block the muscarinic receptors of the iris sphincter and ciliary muscles
|
|
|
What are some of the systemic effects of the parasympatholytics?
|
Fever
Skin flush Tachycardia Confusion Seizures (rarely) |
|
|
What are some of the sympathomimetics used in ophthalmology?
|
Phenylephrine
|
|
|
What are the clinical indications for the sympathomimetics?
|
Dilation of the eyes by stimulating the iris dilator muscle
|
|
|
What are the side effects of the sympathomimetics?
|
Very rare!
HTN Cardiac arrhythmia MI |

