![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What 2 species will most often develop chronic allergic bronchial disease? |
cats - feline asthma and allergic bronchitis horses - recurrent airway disease (COPD)
|
|
|
A cat presents with gelatinous exudate from nostrils. What other signs should you look for? What do you suspect? |
Neurological signs; Crytococcus
|
|
|
A young horse that is new to owner presents with small, diffuse nodules on the roof and wall of the pharynx, what do you call this? Tx? |
Pharyngeal lymphoid hyperplasia; this is a normal immunological even - rest and anti-inflammatories if painful or reduced appetite or frequent swallowing is observed
|
|
|
Name the 2 most common pathogens to infect the guttural pouch? |
Guttural pouch mycosis - Aspergillis Empyema of guttural pouch - Steptococcus equi |
|
|
What are the 2 most common possible consequences of guttural pouch infection? |
Dysphagia and epistaxis |
|
|
You examine several young calves (6 months old) that are coughing, exhibiting inspiratory dyspnea and stridor, what do you suspect? |
necrotic laryngitis (calf diptheria) |
|
|
What is the pathogen behind necrotic laryngitis and what are predisposing factors and their importance? |
Fusobacterium necrophorum; viral infection, rough tubing. important b/c F. necrophorum is a commensal opportunistic that needs damaged mucosa to infect |
|
|
What is the most common family of pathogens that cause tracheitis? What complicates this? |
viral; secondary bacterial infections
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of nasal/laryngeal/tracheal inflammation you're likely to encounter in dogs? cats? horses? cattle? |
dogs - Bordetella bronchispetica + viral, other bacterial, allergic cats - chronic upper resp disease, various bacterial and viral agents horses - EHV-1,-4, influenza, strep equi, fungal cattle - Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (BHV), necrotic laryngitis |
|
|
What type of neoplasms occur in the nasal cavity and sinuses? Which species are usually affected?Which is the most common nasal cavity tumor in cats? |
osteosarcomas, chondrosarcoma, carcinoma/adenocarcinoma, lymphoma dogs and cats Lymphoma is the most common nasal cavity tumor in cats |
|
|
An older horse presents with unilateral, periodic, progressive epistaxis, what is this lesion? |
progressive ethmoidal hematoma |
|
|
T/F Mass lesions of any type in the nasal passage are often ulcerated and prone to developing secondary bacterial infections. |
true, its a dirty world. |
|
|
List the 4 important diffuse abnormalities of the lung. Which are really common? |
1. hyperemia/congestion 2. hemorrhage 3. pulmonary edema 4. interstitial lesions First 3 are really common |
|
|
Of the 4 diffuse lung lesions, which doesn't interfere with gas exchange? |
hyperemia/congestion |
|
|
What are the possible causes of pulmonary hyperemia/congestion? |
congestive heart failure hypostatic congestion (gravity) acute inflammation |
|
|
3 most common lesions detected in lungs at necropsy |
hemorrhage edema congestion |
|
|
What are ARDS and NARDS? |
Acute (adult) respiratory distress syndrome and Neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome - both are diffuse alveolar injuries |
|
|
In vet med, in whom is NARDS most often seen? |
foals |
|
|
A dog has severe chronic uremia, what diffuse lung change could be a consequence? |
Uremic pneumonopathy or pneumonitis, a toxic injury that results in dystrophic mineralization of the alveolar walls |
|
|
Allergic alveolitis and toxic pulmonary injury are similar to ... |
diffuse alveolar injury |
|
|
What are the possible causes of diffuse interstitial fibrosis? |
severe alveolar injury chronic viral infection chronic heart failure idiopathic |
|
|
In which species is multifocal interstitial fibrosis seen? What other processes can this mimic grossly and on radiographs? |
Cats and horses (linked to EHV-5 infection) lesions can mimic pulmonary neoplasia or fungal infection |
|
|
What is almost always the cause of bronchopneumonia? |
bacteria |
|
|
What's a granuloma? |
distinct type of granulomatous inflammation that occurs when macrophage infiltration organizes into a district mass |
|
|
What is granulomatous inflammation? How is it different than chronic inflammation? |
cellular exudate predominantly composed of activated macrophages, multinucleate giant cells; difference is that macrophage aggregates begin to replace portions of normal stroma |
|
|
What is granulation tissue? |
exposed connective tissue that forms within a healing wound (arrangement of CT fibers, fibroblasts, blood vessels) |
|
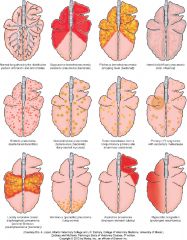
Name the likely cause of patterns of the top row |
Top row - normal, bacterial bronchopneumonia (middle 2), diffuse (interstitial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, toxic lung injury) |
|
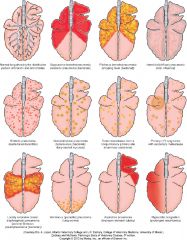
Name the likely cause of the patterns in the middle row |
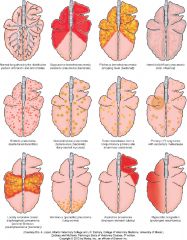
embolic pneumonia, granulomatous pneumonia, tumor metasteses |
|
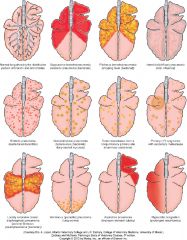
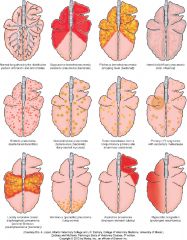
Name the likely cause of the patterns in the bottom row |
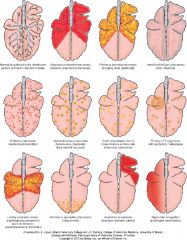
locally extensive (not important), penumonia due to parasite Dictyocaulus in cattle, aspiration pneumonia, hypostatic congestion |
|
|
Which viral infections are part of the respiratory disease complex (shipping fever) of pigs? What is an important consequence of these viral infections? |
Swine influenza, Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), Post-weaning Multisystemic Wasting Syndrome (PMWS); viruses predispose animals to secondary bacterial infections |
|
|
Shipping fever in horses leads to what type of pneumonia? |
aspiration pneumonia likely from nasal secretions not draining properly if head is tied up |
|
|
What viral infection predisposes cattle to secondary bacterial infections leading to bronchopneumonia? |
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis virus (herpesvirus) |
|
|
Name 2 important bacterial agents involved in bovine bronchopneumonia? |
Manheimia heamolytica, Histophilus somni also mycoplasma |
|
|
Gross pathologic findings that indicate interstitial pneumonia |
size of lungs = expanded surface features = rib imprints scream lung expansion! heavy, rubbery texture
|
|
|
2 main routes of entry of agents that cause interstitial pneumonia/diffuse alveolar injury |
hematogenous aerogenous |
|
|
Seeing what type of cells in the alveoli indicate injury? Can this injury heal? |
Type II pneumocytes indicate regeneration but do not exchange gases so will need oxygen support to allow healing |
|
|
What are the most common general causes of interstitial pneumonia in any species? |
Viral infection and septicemia |
|
|
Likely causes of interstitial pneumonia in cattle |
Toxic (fog disease, pit gases) Hypersensitivity |
|
|
What is fog disease? What are the clinical signs? |
occurs when cattle are moved to lush pasture and clara cells attempt to detoxify L-tryptophan into a toxic substance |
|
|
What are some likely causes of interstitial pneumonia in pigs? |
viral (influenza, PRRS, PMWS) hypersensitivity (Ascaris suum migrations)
|
|
|
What are some likely causes of interstitial pneumonia in horses? |
Viral (influenza, herpesvirus, adenovirus) severe fatal interstitial pneumonia of foals multifocal interstitial pulmonary fibrosis |
|
|
What are some likely causes of interstitial pneumonia in dogs? |
viral (influenza, adenovirus, distemper) CARDS |
|
|
What are some likely causes of interstitial pneumonia in cats? |
viral (influenza, herpesvirus, calicivirus) Chlamydophila Toxoplasmosis Multifocal interstitial pulmonary fibrosis |
|
|
What are some likely causes of interstitial pneumonia in sheep and goats? |
Retroviruses in older animals Parasites (muellerius lungworms --> hypersensitivity) |
|
|
What is the most common type of primary tumors arising in the lung? |
Carcinoma of normal pulmonary epithelial cells |
|
|
Examples of tumors that metastasize to lungs? |
Carcinomas - mammary or thyroid Sarcomas - Osteo-, hemangio-, malignant melanoma, lymphoma, fibrosarcoma (vx-assoc)
|
|
|
What are general agents that commonly cause granulomatous or pyogranulomatous pneumonia? |
fungi or intracellular bacteria (mycobacterium) |
|
|
Common cause of granulomatous/pyogranulamatous pneumonia in birds? cats? foals? ruminants? multiple species including pigs and people? |
birds - Aspergillus (fungus) cats - FIP, cryptococcus, histoplasmosis foals - Rhodococcus equi ruminants - Mycobacteria bovis, muellerius parasites spp, pigs, people - Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
Name two bacteria that cause granulomatous/pyogranulomatous pneumonia? |
Rhodococcus equi and Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
|
|
In what species is pleural calcification (mineralization) occur? What is the most likely underlying cause? |
Dogs; renal failure --> uremic pleuritis |
|
|
Define effusion |
escape of fluid from blood or lymph vessels into tissues or cavity |
|
|
What are the passive and active events that can lead to thoracic effusions? |
passive (from pressure changes) - cardiogenic, hypoproteinemia, fluid overload, hemorrhage active - trauma, pleuritis, pleuropneumonia, neoplasia
|
|
|
What is chylothorax? What does it look like? |
lymph effusion; looks like milk or strawberry milk |
|
|
What are some functional consequences of pleural effusions? |
difficult for lungs to expand pleural adhesions |

