![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What if I have to sneeze? |
Back up STRAIGHT back; do not turn your head, as the sneeze exits through the sides of your mask! |
|
|
What if I feel faint? |
Do not be a hero—say, “I feel faint. May I sit down?” This is no big deal and is very common (Note: It helps to always eat before going to the O.R.) |
|
|
What should I say when I first enter the O.R.? |
Introduce yourself as a student; state that you have been invited to scrub and ask if you need to get out your gloves and/or gown |
|
|
What is the normal order of sizes of gloves: small pair, then larger pair? |
No; usually the order is a larger size followed by a smaller size (e.g., women commonly wear a size #7 covered by a size #6.5) |
|
|
What items comprise the sterile field in the operating room? |
The instrument table, the Mayo tray, and the anterior drapes on the patient |
|
|
What is the tray with the instruments called? |
Mayo tray |
|
|
Can I grab things off the Mayo tray? |
No; ask the scrub nurse/tech for permission |
|
|
How do you remove blood with a laparotomy pad (“lap pad”)? |
Dab; do not wipe, because wiping removes platelet plugs |
|
|
Can you grab the skin with DeBakey pickups? |
NO; pickups for the skin must have teeth (e.g., Adson, rat-tooth) because it is “better to cut the skin than crush it” |
|
|
How should you cut the sutures after tying a knot? |
1. Rest the cutting hand on the noncutting hand 2. Slip the scissors down to the knot and then cant the scissors at a 45-degree angle so you do not cut the knot itself |
|
|
What should you do when you are scrubbed and someone is tying a suture? |
Ask the scrub nurse for a pair of suture scissors, so you are ready if you are asked to cut the sutures |
|
|
Why always wipe the Betadine® (povidone-iodine) off your patient at the end of the procedure? |
Betadine can become very irritating and itchy |
|
|
What is the most common intra-operative bladder “tumor”? |
Foley catheter |
|
|
Describe a stool with melena. |
Melenic—not melanotic |
|
|
Is amylase part of Ranson’s criteria? |
Amylase is NOT part of Ranson’s criteria! |
|
|
What is the most commonly pimped, yet the rarest, cause of pancreatitis? |
Pancreatitis from a scorpion bite (scorpion found on island of Trinidad) |
|
|
Where can you go to obtain an abdominal CT scan on a 600-pound, morbidly obese patient? |
The ZOO (used in the past, but now rare due to liability) |
|
|
Term for: localized collection of pus anywhere in body, surrounded and walled off by damaged and inflamed tissues? |
Abscess |
|
|
Term for: absence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach? |
Achlorhydria |
|
|
Term for: light-colored stool as a result of decreased bile content? |
Acholic stool |
|
|
Term for: prefix denoting gland or glands? |
Adeno- |
|
|
Term for: union of two normally separate surfaces? |
Adhesion |
|
|
Term for: adjoining parts, usually means ovary/fallopian tube? |
Adnexa |
|
|
Term for: outer coat of the wall of a vein or artery (composed of loose CT) |
Adventitia |
|
|
Term for: toward |
Afferent |
|
|
Suffix denoting pain? |
-Algia |
|
|
Term for: transient visual loss in one eye? |
Amaurosis fugax |
|
|
Term for: enlarged or dilated ending of a tube or canal? |
Ampulla |
|
|
Term for: drug that prevents pain? |
Analgesic |
|
|
Term for: connection between two tubular organs or parts? |
Anastomosis |
|
|
Prefix denoting blood or lymph vessels? |
Angio- |
|
|
Term for: any deviation from the normal (i.e., congenital or developmental defect) |
Anomaly |
|
|
Term for: cessation of breathing |
Apnea |
|
|
Term for: collapse of alveoli? |
Atelectasis |
|
|
Term for: point at which division into branches occurs? |
Bifurcation |
|
|
Term for: tender inflamed area of the skin containing pus? |
Boil |
|
|
Term for: electrocautery |
Bovie |
|
|
Term for: stone |
Calculus |
|
|
Term for: boil, small subcutaneous staphylococcal infection of follicle? |
Furuncle (think furuncle = follicle < car = carbuncle) |
|
|
Term for: collection of boils (furuncles) with multiple drainage channels? |
Carbuncle (CAR = big) |
|
|
Term for: destruction of tissue by direct application of heat? |
Cauterization |
|
|
Term for: surgical incision into the peritoneal cavity? |
Celiotomy = Laparotomy |
|
|
Prefix denoting bile? |
Chole- |
|
|
Prefix denoting gallbladder? |
Cholecyst- |
|
|
Prefix denoting common bile duct? |
Choledocho- |
|
|
Prefix denoting the clavicle? |
Cleido- |
|
|
Term for: intermittent abdominal pain usually indicating pathology in a tubular organ (eg, small bowel)? |
Colic |
|
|
Term for: fluid with large particles (eg, albumin)? |
Colloid |
|
|
Term for: surgical operation in which part of the colon is brought through the abdominal wall? |
Colostomy |
|
|
Term for: enlargement of RV caused by lung disease and resultant pulmonary HTN? |
Cor Pulmonale |
|
|
Term for: scraping of the internal surface of an organ or body cavity by means of a spoon-shaped instrument? |
Curettage |
|
|
Term for: abnormal sac or closed cavity lined with epithelium and filled with fluid or semisolid material? |
Cyst |
|
|
Suffix denoting pain? |
-Dynia |
|
|
Term for: painful sexual intercourse? |
Dyspareunia |
|
|
Term for: difficulty in swallowing? |
Dysphagia |
|
|
Suffix denoting the surgical removal of part or all of an organ? |
-Ectomy (eg, Gastrectomy) |
|
|
Term for: surgical removal of an atheroma and the inner part of the vessel wall to relieve an obstruction? |
Endarterectomy (eg, carotid endarterectomy = CEA) |
|
|
Term for: inflammation of the small intestine, usually causing diarrhea? |
Enteritis |
|
|
Term for: lysis of peritoneal adhesions |
Enterolysis |
|
|
Term for: contrast study of the small bowel? |
Enteroclysis |
|
|
Term for: scab produced by the action of heat or a corrosive substance on the skin? |
Eschar |
|
|
Term for: biopsy with removal of entire tumor? |
Excisional biopsy |
|
|
Term for: sheet of strong CT? |
Fascia |
|
|
Term for: abnormal communication between two hollow, epithelialized organs or between a hollow organ and the exterior (skin)? |
Fistula |
|
|
Term for: surgical attachment of the stomach to the abdominal wall? |
Gastropexy |
|
|
Term for: benign tumor of blood vessels? |
Hemangioma |
|
|
Term for: accumulation of blood within the tissues, which clots to form a solid swelling? |
Hematoma |
|
|
Term for: surgical repair of a hernia? |
Herniorrhaphy |
|
|
Term for: opening or aperture? |
Hiatus |
|
|
Term for: inflammation of the apocrine glands, usually caused by blockage of the glands? |
Hidradenitis |
|
|
Term for: jaundice? |
Icterus |
|
|
Term for: surgical connection between the lumen of the ileum and the skin of the abdominal wall? |
Ileostomy |
|
|
Term for: abnormal intestinal motility (usually paralytic)? |
Ileus |
|
|
Term for: biopsy with only a "slice" of tumor removed? |
Incisional Biopsy |
|
|
Term for: abnormal hardening of a tissue or organ? |
Induration |
|
|
Term for: hard |
Inspissated |
|
|
Term for: telescoping of one part of the bowel into another? |
Intussusception |
|
|
Term for: appendectomy via laparoscopy? |
Lap appy |
|
|
Term for: visualization of the peritoneal cavity via a laparoscope? |
Laparoscopy |
|
|
Term for: surgical incision into the abdominal cavity? |
Laparotomy = Celiotomy |
|
|
Term for: cholecystectomy via laparoscopy? |
Lap chole |
|
|
Term for: benign tumor of smooth muscle? |
Leiomyoma |
|
|
Term for: malignant tumor of smooth muscle? |
Leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
Term for: denoting the spleen? |
Lieno- |
|
|
Term for: dead |
Necrotic |
|
|
Term for: failure to pass flatus or stool? |
Obstipation |
|
|
Term for: painful swallowing? |
Odynophagia |
|
|
Term for: surgical repair? |
-Orraphy (eg, Herniorrhaphy) |
|
|
Term for: any operation in which an artificial opening is created between two hollow organs or between one viscera and the abdominal wall for drainage or feeding purposes? |
Ostomy (eg, colostomy and gastrostomy) |
|
|
Suffix denoting surgical incision into an organ? |
-Otomy |
|
|
Term for: performed through the skin? |
Percutaneous |
|
|
Suffix denoting fixation? |
-Pexy |
|
|
Prefix denoting vein or relation to veins? |
Phleb- |
|
|
Term for: calcification in a vein - a vein stone? |
Phlebolith |
|
|
Term for: diffuse inflammation of soft tissue, resulting in a swollen mass of tissue (most commonly seen with pancreatic tissue)? |
Phlegmon |
|
|
Term for: fold or ridge? |
Plica |
|
|
Term for: circular (complete circles) folds in the lumen of the small intestine? |
Plicae circulares |
|
|
Term for: folds (semicircular) into lumen of the large intestine? |
Plicae semilunares |
|
|
Term for: passage of urine containing air? |
Pneumaturia |
|
|
Term for: collapse of lung with air in pleural space? |
Pneumothorax |
|
|
Term for: fluid-filled cavity resembling a true cyst, but NOT lined with epithelium? |
Pseudocyst |
|
|
Term for: liquid product of inflammation, consisting of dying leukocytes and other fluids from the inflammatory response? |
Pus |
|
|
Term for: redness |
Rubor |
|
|
Term for: fatty stools as a result of decreased fat absorption? |
Steatorrhea |
|
|
Term for: abnormal narrowing of a passage or opening? |
Stenosis |
|
|
Term for: area covered by sterile drapes or prepped in sterile fashion using antiseptics (eg, Betadine)? |
Sterile field |
|
|
Term for: fluid |
Succus |
|
|
Term for: urge to defecate with ineffectual straining |
Tenesmus |
|
|
Term for: surgical opening of the chest cavity? |
thoracotomy |
|
|
Term for: to divide transversely (to cut in half)? |
Transect |
|
|
Term for: patient posture with pelvis higher than the head, inclined about 45 degrees? |
Trendelenburg (aka "head-down-enburg") |
|
|
Term for: damp gauze dressing placed on a wound and removed after the dressing dries tot he wound, providing microdébridement? |
Wet-to-dry dressing |
|
|
What are the ABCDs of melanoma? |
Asymmetric Border irregularities |
|
|
What is the Allen’s test? |
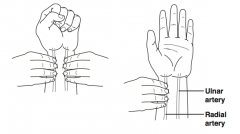
Test for patency of ulnar artery prior to placing a radial arterial line or perform- ing an ABG: Examiner occludes both ulnar and radial arteries with fingers as patient makes fist; patient opens fist while examiner releases ulnar artery occlusion to assess blood flow to hand |
|
|
What is Ballance’s sign? |
Constant dullness to percussion in the left flank/LUQ and resonance to percussion in the right flank seen with splenic rupture/hematoma |
|
|
What is Barrett's Esophagus? |
Columnar metaplasia of the distal esophagus (GERD related) |
|
|
What is Battle's Sign? |
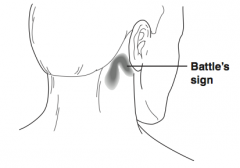
Ecchymosis over the mastoid process in patients with basilar skull fractures |
|
|
What is Beck's Triad? |
Seen in patients with cardiac tamponade: 1. JVD 2. Decreased or muffled heart sounds 3. Decreased blood pressure |
|
|
What is Bergman's Triad? |
Seen with fat emboli syndrome: 3. Dyspnea |
|
|
What is Blumer's Shelf? |
Metastatic disease to the rectouterine (pouch of Douglas) or rectovesical pouch creating a “shelf” that is palpable on rectal examination |
|
|
What is Boas' Sign? |
Right subscapular pain resulting from cholelithiasis |
|
|
What is Borchardt's Triad? |
Seen with gastric volvulus: 2. Epigastric distention |
|
|
What is Carcinoid Triad? |
Seen with carcinoid syndrome (Think: “FDR”): 1. Flushing |
|
|
What is Charcot's Triad (Pronounced “char-cohs”)? |
Seen with cholangitis:
|
|
|
What is Chvostek's Sign? |
Twitching of facial muscles upon tapping the facial nerve in patients with hypocalcemia (Think: CHvostek’s = CHeek) |
|
|
What is Courvoisier's Law (Pronounced “koor-vwah-ze-ay”)? |
Enlarged nontender gallbladder seen with obstruction of the common bile duct, most commonly with pancreatic cancer
Note: not seen with gallstone obstruction because the gallbladder is scarred secondary to chronic cholelithiasis |
|
|
What is Cullen's Sign? |
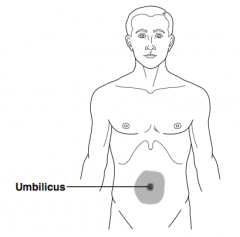
Bluish discoloration of the periumbilical area due to retroperitoneal hemorrhage tracking around to the anterior abdominal wall through fascial planes (e.g., acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis) |
|
|
What is Cushing's Triad? |
Signs of increased intracranial pressure: 1. Hypertension |
|
|
What is Dance's sign? |
Empty right lower quadrant in children with ileocecal intussusception |
|
|
What is Fothergill's Sign? |
Used to differentiate an intra-abdominal mass from one in the abdominal wall; if mass is felt while there is tension on the musculature, then it is in the wall (i.e., sitting halfway upright) |
|
|
What is Fox's Sign? |
Ecchymosis of inguinal ligament seen with retroperitoneal bleeding |
|
|
What is Goodsall's Rule? |
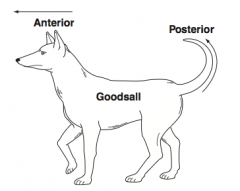
Anal fistulae course in a straight path anteriorly and a curved path posteriorly from midline (Think of a dog with a straight anterior nose and a curved posterior tail) |
|
|
What is Grey Turner's Sign? |
Ecchymosis or discoloration of the flank in patients with retroperitoneal hemorrhage as a result of dissecting blood from the retroperitoneum
(Think: TURNer’s = TURN side-to-side = flank) |
|
|
What is Hamman's Sign/Crunch? |
Crunching sound on auscultation of the heart resulting from emphysematous mediastinum; seen with Boerhaave’s syndrome, pneumomediastinum, etc. |
|
|
What is Howship-Romberg Sign? |
Pain along the inner aspect of the thigh; seen with an obturator hernia as the result of nerve compression |
|
|
What is Homan's Sign? |
Calf pain on forced dorsiflexion of the foot in patients with DVT |
|
|
What is Kehr's Sign? |
Severe left shoulder pain in patients with splenic rupture (as a result of referred pain from diaphragmatic irritation) |
|
|
What is Kelly's Sign? |
Visible peristalsis of the ureter in response to squeezing or retraction; used to identify the ureter during surgery |
|
|
What is Krukenberg Tumor? |
Metastatic tumor to the ovary (classically from gastric cancer) |
|
|
What is Laplace's Law? |
Wall tension = pressure * radius (thus, the colon perforates preferentially at the cecum because of the increased radius and resultant increased wall tension) |
|
|
What is McBurney's Point? |
One third the distance from the anterior iliac spine to the umbilicus on a line connecting the two |
|
|
What is McBurney's Sign? |
Tenderness at McBurney’s point in patients with appendicitis |
|
|
What is the Rule of 2's? |
- 2% of the population have a Meckel’s diverticulum - 2% of those are symptomatic - They occur within 2 feet of the ileocecal valve |
|
|
What is Mittelschmerz? |
Lower quadrant pain due to ovulation |
|
|
What is Murphy's Sign? |
Cessation of inspiration while palpating under the right costal margin; the patient cannot continue to inspire deeply because it brings an inflamed gallbladder under pressure (seen in acute cholecystitis) |
|
|
What is the Obturator Sign? |
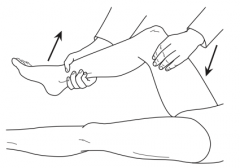
Pain upon internal rotation of the leg with the hip and knee flexed; seen in patients with appendicitis/pelvic abscess |
|
|
What is the symptoms triad of Pheochromocytoma? |
Think of the first three letters in the word pheochromocytoma—“P-H-E”: Palpitations Headache |
|
|
What is the Rule of 10s? |
Pheochromocytoma: 10% bilateral 10% malignant 10% in children 10% extra-adrenal 10% have multiple tumors |
|
|
What is the Psoas Sign? |
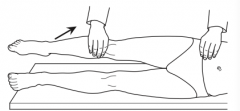
Pain elicited by extending the hip with the knee in full extension, seen with appendicitis and psoas inflammation |
|
|
What are Raccoon Eyes? |
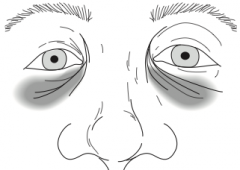
Bilateral black eyes as a result of basilar skull fracture |
|
|
What is Reynold's Pentad? |
1. Fever
in patients with suppurative cholangitis |
|
|
What is Rovsing's Sign? |
Palpation of the left lower quadrant resulting in pain in the right lower quadrant; seen in appendicitis |
|
|
What is Saint's Triad? |
1. Cholelithiasis |
|
|
What is the silk glove sign? |
Indirect hernia sac in the pediatric patient; the sac feels like a finger of a silk glove when rolled under the examining finger |
|
|
What is the Sister Mary Joseph Sign? |
Metastatic tumor to umbilical lymph node(s) |
|
|
What is Virchow's Node? |
Metastatic tumor to left supraclavicular node (classically due to gastric cancer) |
|
|
What is Virchow's Triad? |
Risk factors for thrombosis: 1. Stasis 2. Abnormal endothelium 3. Hypercoagulability |
|
|
What is Trousseau's Sign? |
Carpal spasm after occlusion of blood to the forearm with a BP cuff in patients with hypocalcemia |
|
|
What is Valentino's Sign? |
Right lower quadrant pain from a perforated peptic ulcer due to succus/ pus draining into the RLQ |
|
|
What is Westermark's Sign? |
Decreased pulmonary vascular markings on CXR in a patient with pulmonary embolus |
|
|
What is Whipple's Triad? |
Evidence for insulinoma: Hypoglycemia (<50) CNS and vasomotor symptoms (e.g., syncope, diaphoresis) Relief of symptoms with administration of glucose |

