![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which instrument has the appearance of a misshapen pancake spatula?
a. Allison lung retractor b. Bailey rib contractor c. Davidson scapula retractor d. Lovelace lung grasping forceps |
c. Davidson scapula retractor
p. 1002 |
|
|
How many ribs are considered "true" ribs with direct connection to the sternum with costal cartilage?
a. three b. seven c. nine d. twelve |
b. seven
p. 1004 |
|
|
For which of the following procedures would the rigid bronchoscope be preferred?
a. visualization of the upper lobe bronchi b. removal of foreign body in children c. transbronchial lung biospy d. bronchial washings |
b. removal of foreign body in children
p. 1010 |
|
|
Lung tissue has what kind of consistency?
a. friable b. slimey c. calcified d. elastic |
a. friable
p. 1011 |
|
|
Which nerve could be damaged during lung decortication resulting in paralysis or partial paralysis of the diaphragm?
a. accessory b. hypoglossal c. phrenic d. vagus |
c. phrenic
p. 1025 |
|
|
In which procedure would an incision NOT be required for insertion of the endoscope?
a. bronchoscopy b. mediastinoscopy c. pectus excavatum via VATS d. video-assisted thoracic surgery |
a. bronchoscopy
p. 1011 - the rest use a #15 blade |
|
|
Which structure within the respiratory tract is the proximal and superior?
a. bronchus b. diaphragm c. larynx d. trachea |
c. larynx
p. 1007 |
|
|
Which of the following are the final branchings of the respiratory tree?
a. alveoli b. bronchi c. bronchioles d. lobes of the lungs |
a. alveoli
p. 1007 |
|
|
The manubrium, body, and xiphoid process are portions of the:
a. ribs b. lungs c. sternum d. bronchial tree |
c. sternum
p. 1004 |
|
|
All of the following structures are found within the mediastinum EXCEPT:
a. heart b. thymus c. esophagus d. diaphragm |
d. diaphragm
p. 1004 |
|
|
Which membrane covers the surface of the lungs?
a. ciliated mucosa b. pericardium c. parietal pleura d. visceral pleura |
d. visceral pleura
p. 1004 |
|
|
What is the medical term for coughing up blood
a. asthma b. bronchitis c. hemoptysis d. pneumonitis |
c. hemoptysis
hemo = blood ptysis = spitting of matter |
|
|
How many lobes are there in the right lung?
a. two b. three c. four d. five |
b. three
p. 1006 |
|
|
In which part of the respiratory system does the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide take place?
a. alveoli b. bronchi c. bronchioles d. pulmonary vein |
a. alveoli
p. 1006 |
|
|
Which of the following regarding blood flow is correct?
a. right atrium, pulmonary vein, lungs, pulmonary artery, left ventricle b. right ventricle, pulmonary vein, lungs, pulmonary artery, left atrium c. right atrium, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, left ventricle d. right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, left atrium. |
d. right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, left atrium
p. 1007 |
|
|
What is the name of the device that is attached to suction for collection of mucous or bronchial washing specimens?
a. aerobic culture tube b. insufflation tubing c. myringotomy tube d. Lukens tube |
d. Lukens tube
p. 672 |
|
|
What is the medical term for visibile changes in the density on chest x-ray that indicates pulmonary pathology? a. hemoptysis b. hilum c. infiltrate d. inspiration |
c. infiltrate
p. 1010 |
|
|
Thymomas, neurogenic tumors, and pleuropericardial cysts can be biopsied during which procedure?
a. bronchoscopy b. laryngoscopy c. mediastinoscopy d. thoracoscopy |
c. mediastinoscopy
p. 1013 |
|
|
Where is the insertion point for the mediastinoscope?
a. suprasternal notch b. oropharynx c. subxiphoid d. umblicus |
a. suprasternal notch
p. 1015 #1 |
|
|
What is the name of the air-filled sac that has the appearance of a blister on the surface of lung tissue?
a. alveolar sac b. bleb c. bronchiole d. germ cell |
b. bleb
p. 1016 |
|
|
In the event that a VATS procedure had to be converted to an open procedure, which open case would be performed?
a. coronary artery bypass b. laparoscopy c. thoracotomy d. tracheotomy |
c. thoracotomy
p. 1017 |
|
|
Which of the following will be required upon completion of any procedure in which the pleural cavity has been opened?
a. passive wound drain such as a Penrose b. chest tube attached to a Pleur-evac system c. active wound drain such as a Jackson-Pratt d. compression dressing with Ace or tensor bandages |
b. chest tube attached to a Pleur-evac system
p. 1019 |
|
|
Which additional pain control measure is taken for patients undergoing pectus excavatum repair by VATS?
a. Bier block b. epidural c. local with epinephrine d. topical Lidocaine jelly |
b. epidural
p. 1020 |
|
|
What is the name of the procedure performed to release constriction of the lungs by fibrin layers?
a. pectus excavatum b. upper lobectomy c. pneumonectomy d. lung decortication |
d. lung decortication
p. 1025 |
|
|
The name of the condition created when pus is not cleared from the pleural cavity and makes a fibrous constrictive layer is:
a. COPD b. pleurisy c. empyema d. pneumonia |
c. empyema
p. 1025 |
|
|
Prior to the closure of a lobectomy procedure, the anesthesia provider performs a Valsalva maneuver to check for:
a. air leakage from bronchial closure b. bleeding from dissection bed c. functionality of the diaphragm d. perfusion of the unaffected lobes |
a. air leakage from bronchial closure
p. 1028 |
|
|
What is the term for collapsed lung?
a. atelectasis b. decortication c. emphysema d. pneumonitis |
a. atelectasis
Mayo Clinic website |
|
|
Which type of incision is made for a pneumonectomy?
a. Chevron b. McBurney c. epigastric d. posterolateral |
d. posterolateral
p. 1029 #1 |
|
|
Which of the following is a crushing clamp with sharp spikes in the jaws used on the bronchus?
a. Bailey b. Doyen c. Mixter d. Sarot |
d. Sarot
p. 1002 |
|
|
Which instrument is a rib shear?
a. Alexander b. Bethune c. Davidson d. Satinsky |
b. Bethune
p. 1002 |
|
|
What is a commonly used rib self-retaining retractor available in adult and pediatric sizes?
a. Balfour b. Bookwalter c. Finochietto d. Greenburg |
c. Finochietto
p. 1003 |
|
|
Which instrument is a lung-grasping forceps that resembles a very large Pennington?
a. Doyen b. Duckbill c. Lovelace d. Langenbeck |
c. Lovelace
p. 1002 |
|
|
Which of the following thoracic procedures would require the patient to be put on cardiopulmonary bypass?
a. pneumonectomy b. upper lobectomy c. decortication of the lung d. pulmonary thromboendarterectomy |
d. pulmonary thromboendarterectomy
p. 1023 |
|
|
Following lung transplantation, the surgeon will perform which procedure to aspirate secretions and check for leaks?
a. bronchoscopy b. laryngoscopy c. mediastinoscopy d. video-assisted thoracoscopy |
a. bronchoscopy
p. 1035 |
|
|
The main bronchi, pulmonary arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels enter the lung on the medial surface through the:
a. hilum b. trachea c. diaphragm d. mediastinum |
a. hilum
p. 1006 |
|
|
How many pulmonary veins are there?
a. one b. two c. three d. four |
d. four
p. 1006 |
|
|
Which diagnostic study is MOST useful for verification of thoracic aortic dissection?
a. AP chest x-ray b. CT scan c. MRI scan d. stress test |
b. CT scan
p. 1000 |
|
|
Which statement regarding the anatomical placement of the heart is CORRECT? a. It is positioned exactly midline in the thoracic cavity. b. It is positioned in the thoracic cavity with nearly its entirety on the left side. c. It is positioned in the mediastinum with approximately 2/3 of the heart on the left side. d. It is positioned in the mediastinum with approximately 2/3 of the heart on the right side. |
c. It is positioned in the mediastinum with approximately 2/3 of the heart on the left side.
p. 1039 |
|
|
Which structure is considered the "pacemaker" of the heart?
a. AV node b. SA node c. bundle of His d. Purkinje fibers |
b. SA node
p. 1040 |
|
|
Which chamber of the heart is responsible for pumping blood into the pulmonary artery?
a. left atrium b. right atrium c. left ventricle d. right ventricle |
d. right ventricle
p. 1007 |
|
|
Which portion of the heart is responsible for pumping blood into the ascending aorta?
a. left atrium b. right atrium c. left ventricle d. right ventricle |
c. left ventricle
p. 1040 |
|
|
The coronary arteries originate from the:
a. ascending aorta b. descending aorta c. pulmonary artery d. subclavian artery |
a. ascending aorta
p. 1040 |
|
|
What is the name of the area between the visceral and parietal pleura that contains serous fluid to prevent friction?
a. hilum b. mediastinum c. pleural space d. pericardial window |
c. pleural space
p. 1004 |
|
|
What is the thickest part of the heart?
a. epicardium b. endocardium c. myocardium d. pericardium |
c. myocardium
p. 1039 |
|
|
Where is the apex of the heart located within the mediastinum?
a. superiorly on the right side b. inferiorly on the right side c. superiorly on the left side d. inferiorly on the left side |
d. inferiorly on the left side
p. 1039 |
|
|
Which one of the following is NOT one of the cardiac valves?
a. aortic b. mitral c. septal d. tricuspid |
c. septal
p. 1039-1040 |
|
|
Which heart valve is also known as the bicuspid valve?
a. aortic b. mitral c. pulmonary d. tricuspid |
b. mitral
p. 1039 |
|
|
The apex of the lung is located:
a. inferiorly and laterally b. medially where the bronchus enters c. medially just above the diaphragm d. superiorly and just above the clavicle |
d. superiorly and just above the clavicle
p. 1008 |
|
|
All of the following are components of the "heart-lung" machine EXCEPT:
a. pump b. oxygenator c. defibrillator d. heat exchanger |
c. defibrillator
p. 1041 |
|
|
Where are the cannulae MOST commonly placed for cardiopulmonary bypass procedures? a. carotid artery and subclavian vein b. right atrium and ascending aorta c. right ventricle and descending aorta d. femoral artery and brachiocephalic vein |
b. right atrium and ascending aorta
p. 1040 |
|
|
Which of the following is a commonly used method of preserving the heart by reducing its metabolic needs?
a. hypothermia b. lung deflation c. left ventricular venting d. warming with heat exchanger |
a. hypothermia
p. 1042 |
|
|
Which suturing technique maintains the aortic and venous cannulae?
a. figure of eight b. purse-string c. horizontal mattress d. vertical mattress |
b. purse-string
p. 1042 |
|
|
The force and rate of contraction of the heart is controlled by which part of the central nervous system (CNS)?
a. phernic nerve b. vagus c. Purkinje system d. medulla oblongata |
d. medulla oblongata
p. 1040 |
|
|
What is the first step in the formation of an atheroma?
a. accumulation of cholesterol and lipids b. collagen deposition and scar tissue formation c. growth of new smooth muscle tissue d. injury to endothelial lining |
d. injury to endothelial lining
p. 1044 |
|
|
Which of the following is the main underlying pathogenic cause of coronary atherosclerosis and clinical manifestations?
a. age b. diet c. ischemia d. hypertension |
c. ischemia
p. 1045 |
|
|
Which artery accounts for approximately 50% of occlusive coronary lesions?
a. circumflex branch b. left anterior descending c. mammary d. right coronary |
b. left anterior descending
p. 1046 |
|
|
What is the name of the acute condition in which heart muscle dies from ischemia and may lead to sudden cardiac death? a. heart block b. atherosclerosis c. cardiac tamponade d.myocardial infarction |
d. myocardial infarction
p. 1046 |
|
|
Where is a Swan-Ganz catheter placed? a. ascending aorta b. coronary artery c. pulmonary artery d. vena cava |
c. pulmonary artery
p. 1047 |
|
|
Which suture is frequently used for anastomosis of the saphenous vein or internal mammary artery in CABG?
a. 6-0 or 7-0 polypropylene b. 2-0 or 3-0 polyester c. 6-0 or 7-0 polyglactin d. 2-0 or 3-0 poliglecaprone |
a. 6-0 or 7-0 polypropylene
p. 1049 |
|
|
Which instrument is used to make a small opening into the ascending aorta after the Satinsky partial occlusion clamp is placed?
a. aortic punch b. Potts-Smith scissors c. #11 blade d. 5 mm trocar |
a. aortic punch
p. 1050 |
|
|
With what is the median sternotomy closed?
a. fine gauge polypropylene b. fine gauge surgical silk c. heavy gauge stainless steel wire d. heavy gauge chromic gut |
c. heavy gauge stainless steel wire
p. 1051 |
|
|
Medtronic OCTOPUS and Guidant Ultima OPCAB are what type of devices for coronary artery bypass done off-pump?
a. retractors b. stabilizers c. cannulae d. grafts |
b. stabilizers
p. 1056 |
|
|
What is the name of the device used for patients who are unable to be weaned off of cardiopulmonary bypass? a. intra-aortic balloon pump b. left ventricular vent c. cardiac pacemaker d. vena cava filter |
a. intra-aortic balloon pump
p. 1058 |
|
|
Which device is used for patients awaiting heart transplant that allows them to be ambulatory and has both internal and external components to the system?
a. ventricular assist device b. left ventricular vent c. cardiac pacemaker d. vena cava filter |
a. ventricular assist device
p. 1060 |
|
|
What is the general term for incurable diseases of the heart for which the only treatment would be heart transplantation?
a. atherosclerosis b. arrhythmias c. cardioplegia d. cardiomyopathies |
d. cardiomyopathies
p. 1062 |
|
|
Aortic valve stenosis and aortic regurgitation are often as a result of:
a. rheumatic fever b. tuberculosis c. heart block d. angina |
a. rheumatic fever
p. 1069 |
|
|
Which diagnostic method provides the MOST extensive details regarding valvular disorders? a. cardiac catheterization b. CT scanning c. electromyogrphy d. MRI scanning |
a. cardiac catheterization
p. 1070 |
|
|
A heart murmur is often heard with auscultation and indicative of involvement of which structure?
a. aortic valve b. mitral valve c. right ventricle d. left ventrile |
b. mitral valve
p. 1074 |
|
|
What is the average lifespan of biologic and mechanical heart valve replacements?
a. 1 to 5 years b. 5 to 10 years c. 10 to 15 years d. indefinite |
c. 10 to 15 years
p. 1070-1071 |
|
|
What is the term for a localized stricture of the aorta found in a pediatric patient? a. coarctation b. stenosis c. prolapsed d. arteriosis |
a. coarctation
p. 1082 |
|
|
Which singular congenital defect involves failure of closure of the connection between the pulmonary artery and aorta? a. atrial septal defect b. ventricular septal defect c. patent ductus arteriosus d. tetralogy of Fallot |
c. patent ductus arteriosis
p. 1080 |
|
|
What is frequently used to repair atrial and ventricular septal defects in pediatric patients?
a. Dacron patch b. porcine valve c. fascia lata d. fibrin glue |
a. Dacron patch
p. 1077 |
|
|
Which congenital defect has four components and is characterized by cyanosis causing appearance of "blue babies"?
a. coarcation of aorta b. patent ductus arteriosus c. ventricular septal defect d. tetralogy of Fallot |
d. tetralogy of Fallot
p. 1086 |
|
|
Which surgical approach is used for repair of coarctation of the aorta and patent ductus arteriosus?
a. supine b. prone c. frog-legged d. posterolateral |
d. posterolateral
p. 1080 |
|
|
Commissurotomy is a surgical separation of the flaps of the: a. mitral valve b. left ventricle c. pulmonary valve d. right atrium |
a. mitral valve
p. 1074 |
|
A heart rate that exceeds 100 beats per minute |
h. Ventricular tachycardia p. 250 |
|
Chaotic and disorganized stimulation of the ventricle, making it unable to effectively pump blood |
d. Ventricular fibrillation p. 250 |
|
Abnormally slow electrical impulses and heartbeat below 40 to 60 beats per minute |
e. Bradycardia p. 250 |
|
Disorganized stimulation of the atria that prevents atrial contraction and does not allow for ventricular filling |
i. Atrial fibrillation p. 1069 |
|
Absence of a heartbeat; cardiac standstill |
a. Asystole p. 1046 |
|
Percentage of blood volume pumped out of the heart into the systemic circulation; indicator of ventricular function |
j. Ejection fraction p. 401 |
|
Noninvasive study used to diagnose mitral valve stenosis or other valvular disorders |
g. Echocardiography p. 403 |
|
Monitoring procedure that records electrical activity of the heart |
b. Electrocardiograph p. 407 |
|
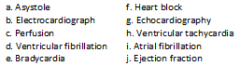
Electrical conduction disorder requiring permanent pacemaker |
f. Heart block |
|
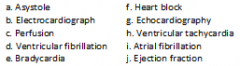
The function accomplished by the cardiopulmonary bypass machine |
c. Perfusion p. 1041 |
|
|
The saphenous vein used for coronary artery grafting must be reversed before anastomosis due to the presence of valves in the vein.
True or False |
True
p. 1049 |
|
|
Video-assisted thoracic surgery procedures use carbon dioxide for distention.
True or False |
False
p. 1017 |
|
|
The ventricles of the heart have thicker myocardium than the atria.
True or False |
True
p. 1039 |
|
|
Lung reduction surgery is performed for patients with emphysema.
True or False |
True
p. 1016, 1019 |
|
|
The drainage and collection device attached to chest tubes relies on a water seal to reestablish negative pressure in the pleural cavity.
True or False |
True
p. 287, 1016 |

