![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carina |
Ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi |
|
|
What can pancrelipase treat? |
Someone with cystic fibrosis |
|
|
What is a common source of airway obstruction in an unconscious client? |
Tongue (so, practice head-tilt chin-lift) |
|
|
Homans sign |
Elicited by bending patient's leg slightly at the knee and dorsiflexing the ankle to see if there is deep calf pain |
|
|
Obstructive respiratory condition - upper respiratory |
Anaphylaxis, angioedema, facial trauma, foreign body obstruction, sleep apnea, croup and epiglottitis |
|
|
Obstructive - lower respiratory |
Emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma (primarily inflammatory) |
|
|
Asthma |
Lower airway obstruction, bronchospasm (wheezing), edema, mucus, cough....attacks stimulated by irritants, infection, & emotional distress |
|
|
Chronic bronchitis |
Inflammation & excess mucus |
|
|
Emphysema |
Alveolar membranes break down. "Destruction and enlargement of the lung alveoli." Old air cannot get out AND new air cannot get in |
|
|
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases |
Restrict lung expansion and result in decreased lung volume, increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Intrinsic (occupational disease, immunological) or extrinsic (burns, muscle weakness from other disease, scoliosis, morbid obesity) |
|
|
Pulmonary edema |
Fluid buildup in lungs. Rales, wheezes. Left-sided heart failure |
|
|
Pulmonary embolism |
Blood clot that breaks off, circulating through venous system. Ventilation/perfusion mismatch |
|
|
Spontaneous/Closed Pneumothorax |
Causes: Post op chest surgery, rib fracture, rupture of lining of parenchyma of lungs- bullae/bleb |
|
|
Open pneumothorax |
Can become tension pneumothorax! |
|
|
Pleural effusion |
Collection of fluid outside the lung; caused by irritation, infection (like TB), or cancer. |
|
|
Symptoms of acute pulmonary embolism |
Chest pain, increased or irregular heartbeat, dizziness, difficulty catching breath, rapid breathing, dry cough (or w blood), facial cyanosis |
|
|
Bronchiolitis |
Lower respiratory infection (caused by RSV - virus), coughing, can cause hypoxemia which then leads to increased HR and RR and wearing the child out |
|
|
COPD |
Progressive, abnormal inflammatory response leading to systemic effects (airflow limitation, alteration of function and structure of large & small airways and parenchyma). Characterized by chronic airflow limitation that is not fully reversable. Prolonged expiration- can get air out |
|
|
Late findings of COPD - 3 C's |
Cyanosis, cachexia (weight loss), cor pulmonale (right heart failure and edema) |
|
|
Definitive diagnosis of COPD by... |
CT scan! |
|
|
Bronchiectasis |
Abnormal dilation of bronchi and destruction of the bronchial walls. Results from chronic inflammatory changes associated with repeated damage by bacteria or viruses to bronchial walls... |
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis: symptoms |
Lightheadedness, paresthesia numbness or tingling in arms and legs) |
|
|
Respiratory acidosis: symptoms |
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea |
|
|
Weaning criteria (off a ventilator) |
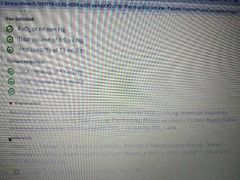
|

