![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 methods of knowing |
authority, rationalism, intuition, and scientific method |
|
|
4 methods of knowing: authority |
because someone of authority tells you so |
|
|
4 methods of knowing: rationalism |
using reasoning to arrive at knowledge |
|
|
4 methods of knowing: Intuition |
Gut reaction, idea popping into your head fully formed |
|
|
4 methods of knowing: Scientific method |
testing it out |
|
|
Independant Variable |
Manipulated by the investigator |
|
|
Dependant variable |
what changes b/c of the independant variable |
|
|
Statistic |
A statistic is a number calculated on sample data that quantifies a characteristic of the sample. |
|
|
Parameter |
a number calculated on population data that quatifies a characteristic of the population |
|
|
Observational studies |
No variables manipulated. They can use naturalistic observation, parameter estimation (estimating the level of something in the population), correlational studies. |
|
|
Descriptive statistics |
Is concerned with techniques that are used to describe or characterize the obtained data |
|
|
Inferential statistics |
involves techniques that use the obtained sample data to infer popultions |
|
|
Xn |
total number of subjects (or scores)
Ie age X1= subject 1 (age 8) X2= subject 2 (age10) |
|
|
Xi |
the "i"th score which can vary from 1-N |
|
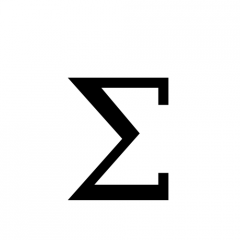
|
Sigma (capital) |
|
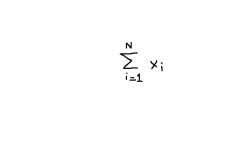
|
Sum of all the scores from i=1 to n |
|
|
Nominal scale |
lowest level of measurement, used for qualitative info which is then put into categories and measured |
|
|
ordinal scale |
higher level of measurement. Rank things a>b, a=b, or b>a. Says nothing about magnitude orf the level of variable. |
|
|
Interval Scale |
Higher level of measurement: Like the ordinal scale but units between measurements are equal (like measuring in celcius, same amount of energy is needed to go a degree) but contains no absolute zero. |
|
|
Ratio scale |
Highest level of measurement. Like interval scale but has an absolute zero point (like using kelvin, where 0 is the complete absence of heat). Having an absolute zero lets you do computations. |
|
|
Continuous variable |
something where there are infinite numbers of possibilities between two numbers (Like time where theres 1 second on a clock, but btwn 1 and 2 seconds there is .1 sec, .01 sec, .001 sec etc) This means all measurements are approximate |
|
|
Discrete variable |
variable changes in fixed amount (ie how many kids you have) |
|
|
Real limits of a continuous variable |
are those values that are above or below the recorded value by 1/2 of the smallest measuring unit of the scale |

