![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
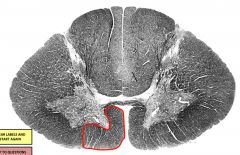
anterior funiculus - contains tracts of the medial descending system - reticulospinal tracts - vestibulospinal tracts - anterior corticospinal tract - controls posture and balance |
|
|
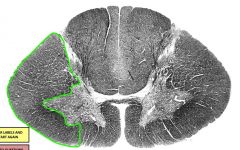
lateral funiculus |
|
|
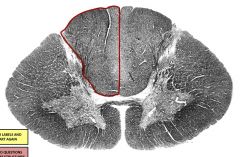
posterior funiculus |
|
|
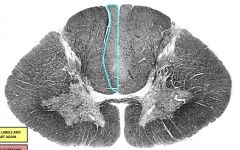
fasciculus gracilis |
|
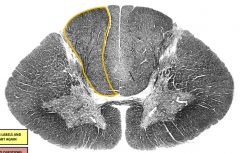
|
fasciculus cuneatus - only present T6 and above |
|
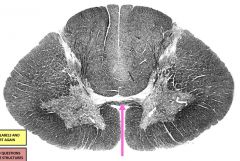
|
anterior white commissure - fibers carrying pain, temp, light touch cross (from the zone of lissauer) |
|
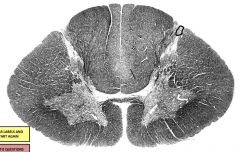
|
zone of lissauer - primary afferents of anterolateral spinothalamic system (pain, temp, light touch) |
|
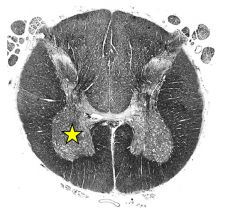
|
ventral horn |
|
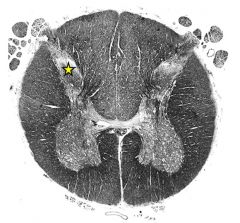
|
dorsal horn |
|
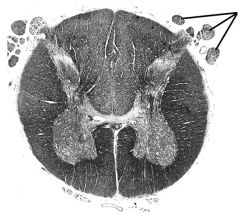
|
dorsal roots - damage = disruption of afferent limb of myotatic reflex |
|
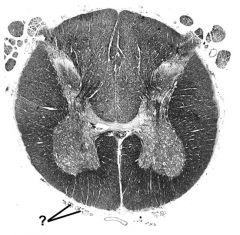
|
ventral roots - damage = reduced myotatic reflexes in efferent limb muscles |
|
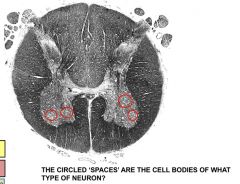
|
alpha-motor neurons in ventral horn - associated with lower motor neurons, so peripheral LMNs damage = atrophy, reduced reflexes |
|
|
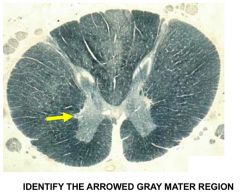
lateral horn (upper thoracic spinal cord) - aka intermediallateral nucleus (IML) - contains sympathetic preganglionic neurons of CNS ( - most synapse in sympathetic trunk via white rami communicantes |
|
|
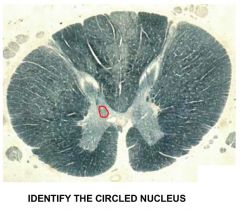
dorsal nucleus of clarke (upper thoracic section) - posterior spinocerebellar tract originates here - ascends ipsilaterally to cerebellum - proprioceptive inputs from muscles/joints in lower limb |
|
|
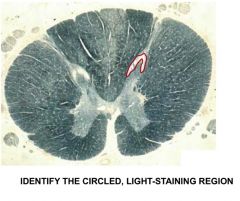
substantia gelatinosa (rexed's lamina II) (upper thoracic section) - contains inhibitory neurons to mediate pain - rubbing skin activates mylinated fibers in posterior column that activate inhibitory interneurons, which synapse on ALSTT neurons to reduce pain (gate theory of pain) |
|
all |
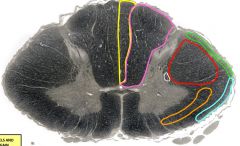
yellow= fasciculus gracilis orange= anterolateral spinothalamic tract green= posterior spinocerebellar tract red= lateral corticospinal tract purple= fasciculus cuneatus blue= anterior spinocerebellar tract white= descending autonomic fibers |
|
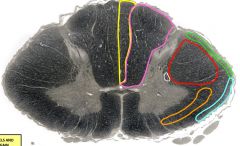
yellow |
fasciculus gracilis - T7 and below (leg and lower trunk) - terminates in nucleus gracilis in medulla - degeneration = vitamin B12 deficiency - tacticle discrimination, vibration, pressure, conscious proprioception - large diameter, myelinated, primary afferent axons; enters dorsal roots; ascend ipsilaterally in posterior columns |
|
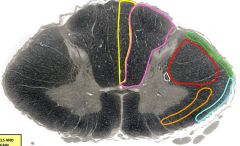
orange |
anterolateral spinothalamic tract - crosses in anterior white commissure, so damage affects contralateral side below lesion - damage = loss of pain and thermal sensation (touch is not affected b/c it has redundancy)` |
|
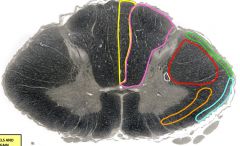
green |
posterior spinocerebellar tract - unconscious proprioception |
|
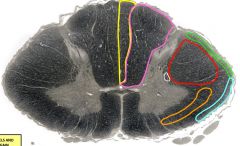
red |
lateral corticospinal tract - pyramidal decussation (spinomedulary junction), so damage below medulla = ipsilateral - upper motor neuron - damage = weakness (spasticity) - symptoms: Babinski sign, increased resistance to passive stretch, hypertonia, hyperflexia |
|
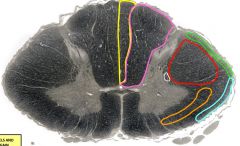
purple |
fasciculus cuneatus - T6 and above (upper trunk, upper limb, neck) - terminates in nucleus cuneatus in medulla - tacticle discrimination, vibration, pressure, conscious proprioception- large diameter, myelinated, primary afferent axons; enters dorsal roots; ascend ipsilaterally in posterior columns |
|
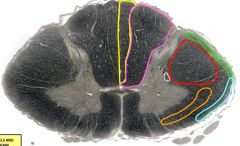
blue |
anterior spinocerebellar tract - unconscious proprioception |
|
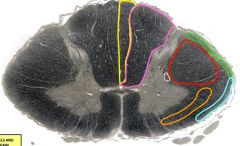
white |
descending autonomic fibers - synapse in ipsilateral intermediolateral nucleus - originates in hypothalamus and brainstem - controls sympathetic neurons in IML - damage = constriction of ipsilateral pupil (Horner's syndrome) |

