![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
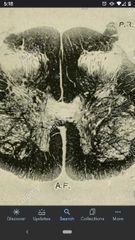
Sacral Spinal Cord |
Less white matter, a lot of gray matter. |
|
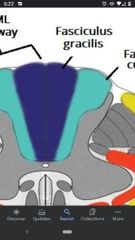
Fasciculus Gracilis |
Conveys proprioception and fine tactile discrimination from the caudal half of the body. Made up of mostly primary afferent axons. |
|
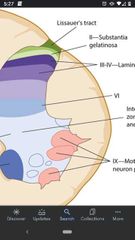
Substantia gelatinosa |
A long nucleus found in the dorsal horn. Neuronal activity serves to modulate pain transmission. |
|
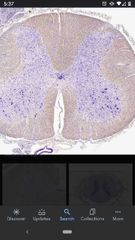
Lumbar spinal cord |
More white matter surrounding the gray matter. |
|
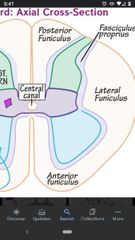
Lateral Funiculus |
The area of white matter between the dorsal lateral sulcus and the central lateral sulcus. Many ascending and descending pathways are located here. |
|
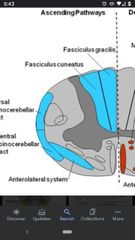
Anterolateral system |
Conveys pain and temperature. Called a system instead of a tract because axons have variety of targets in the brainstem and diecephalon. |
|
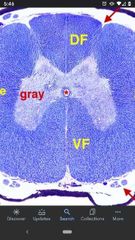
Ventral funiculus |
White matter between the ventral lateral sulcus and the ventral median sulcus. Contains mostly descending tracts projecting to lower motor neurons. |
|
|
Lower motor neurons |
Located in the ventral horn, these are the final cells through which the CNS can affect muscle contraction. |
|
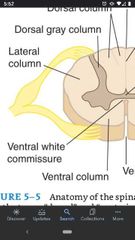
Anterior White Commissure |
Contains myelinated axons crossing the midline. |
|
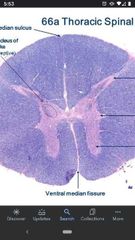
Thoracic spinal cord |
Much less grey matter, a lot more white matter. |
|
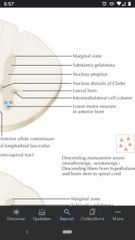
Interomediolateral cell column |
A long nucleus found in spinal cord T1-L2. The small neurons give rise to sympathetic preganglionic axons that exit ventral roots and end on periphery ganglia. |
|
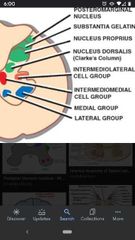
Nucleus Dorsalis (of Clarke) |
Found in spinal cord T1-L2. Fairly large neurons have axons that join ipsilateral dorsal spinocerebellar tract. |
|
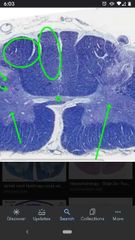
Cervical Spinal Cord |
Similar to thoracic, has a lot of white matter, but has 2 dorsal columns (fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus. |
|
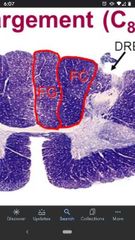
Fasciculus cuneatus |
Conveys proprioception and fine tactile discrimination from the upper thorax, upper extremity, and neck. |
|
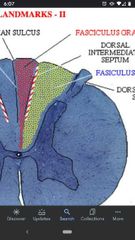
Dorsal intermediate sulcus |
The sulcus marks the separation of the fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus. A longitudinal groove seen in cervical and thoracic spinal levels. |

