![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The gate way to the brain |
The spinal cord |
|
|
Besides the cranial nerves, how else is the information going to be able to get into the brain ? |
The spinal cord |
|
|
The spinal nerves are part of the |
PNS |
|
|
The spinal cord has the ability to do what? |
Has the ability to do some integration. A lot of times it's just reflexes |
|
|
What's the integration? |
The integration is just where the connection to the motor output is happening at the level of the Spinal cord |
|
|
In adults the Spinal cord ends around: |
L 1 - L2 ( a little lower in children) |
|
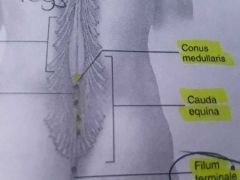
Cauda equina |
The part where all of the Spinal nerves are branching off forming a tail |
|
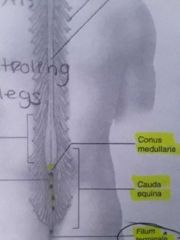
Conus medullaris |
The end of the Spinal cord ( the very tip of the Spinal cord) |
|
|
What are the 4 regions of the Spinal cord? |
• Cervical (8) • Thoracic (12) • Lumbar (5) • Sacral (5) |
|
|
Why does the Spinal cord have the cervical enlargement and lumbosacral enlargement? |
Because it's receiving alot of signals. (That's exactly where the nerves are coming in and exiting to control your appendages) |
|
|
What is the Lumbosacral enlargement for ? |
Controlling your legs |
|
|
What is the cervical enlargement for? |
Controlling your arms |
|
|
You have a lot of _____ that make the Spinal cord wider in those enlargements. |
Interneurons |
|
|
How long is the Spinal cord? |
40 to 50 cm long |
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves? |
31 pairs |
|
|
What's the Filum terminale? |
Is connective tissue that is pulling on that conus medullaris providing longitudinal support to the Spinal cord |
|
|
How is the Spinal cord and the brain protected? |
They are both protected with the Meninges |
|
|
The meninges are: |
Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater Pia Mater |
|
|
The Dura Mater |
The most superficial and thickest. Made of dense irregular connective tissue. |
|
|
The arachnoid mater |
The middle layer. Avascular layer. Thin. Does not deep into the sulci(sulcus). Has collagen and elastic fibers |
|
|
The Pia Mater |
Innermost layer. Does deep into the Sulci. Thin transparent layer. Vascular. Blood vessels. Has extensions called denticulate ligaments. |
|
|
Meningeal spaces |
• Epidural Space (above the dura) • Subdural space (bellow the dura) • Subarachoid space (bellow the arachnoid) |
|
|
Most of the the cerebrospinal fluid is located in the: |
Subarachnoid Space |
|
|
Anesthetics can be injected into which Meningeal space? |
Epidural Space |
|
|
White matter of the Spinal cord |
Contains Myelin Sheat. For information to travel up and down the Spinal cord. (ascending and descending) |
|
|
Gray matter of the Spinal cord |
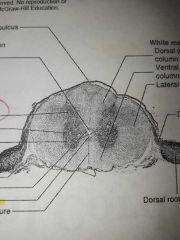
For your connections. Contains cell bodies, interneurons. Forms and H in the middle |
|
|
Connections between the 2 sides of the horns are called |
Commissures |
|
|
Commissures is: |
How information crosses from one side of the Spinal cord to the other |
|
|
Which commissure will be utilize if stepping on tack to be able to extend the other leg? |
Gray commissure |
|
|
The central canal is |
The hole in the middle of the Spinal cord. (For CSF) surrounded by gray matter |
|
|
Dorsal root ganglion |
Sensory information (Contains the cell bodies) |
|
|
Anterior Ventral Root |
Motor information |
|
|
Where are the lateral horns located ? |
Located in the thoracic and the beginning of the lumbar segment |
|
|
What are the lateral horns for? |
Sympathetic motor nuclei. |
|
|
When the spinal nerve is carrying both motor and sensory information it's called? |
Mix nerve |
|
|
Posterior gray horn handles what kind of information? |
Sensory information |
|
|
Anterior gray horn handles what kind of information? |
Motor information |
|
|
Lateral gray horn handles what kind of information? |
Sympathetic information |
|
|
Map of the nerves that supply the skin that is innervaded by the different spinal nerves. |
Dematome map |
|
|
Why is shingles only on one side of the body? |
it's one dorsal root ganglion that's harvesting the virus. So is going to travel down that nerve and the problem is only going to be on that one side. |
|
|
Where are nerve tracks located ? |
Within the white columns |
|
|
What do ascending nerve tracts carry? |
Carry sensory signals to the brain |
|
|
What do descending nerve tracts Carry? |
Carry motor information down the Spinal cord |
|
|
Descussation |
When nerves cross over and go to the other side |
|
|
Where does most of our descussation happen? |
In the brainstem around the medulla oblongata |
|
|
When we talk about reflexes we use the words : |
Contralateral and ipsilateral |
|
|
Contralateral |
When the origin happens on one side of the body but the destination in the end of that reflex ends on the opposite side of the body. |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
When the origin and destination are on the same side of the body. |
|
|
Give an Example for contralateral. |
Stepping on a tack with my right side but it also causes my left side to extend so I could shift my weight. |
|
|
Give an Example of ipsilateral. |
Touching the stove with the right hand and it's hot. You pull away that same hand. I sensed it on that side and it caused motor on that side. |
|
|
What are the 4 important properties about reflexes? |
• reflexes require stimulation • reflexes are quick • reflexes are involuntary • reflexes are stereotyped |
|
|
Sensory neuron can also be called |
Afferent neuron |
|
|
Motor neuron can also be called |
Efferent neuron |
|
|
What does it mean when the reflexes are somatic? |
Skeletal muscles |
|
|
Are skeletal muscles the only thing that can be involved in a reflex? |
No |
|
|
Besides sketeletal muscles, what else can be involved I a reflex? |
Glands, cardiac muscles, smooth muscles. |
|
|
Why we don't want muscle to be over stretch? |
You want to maintain muscle tone, optimal resting length , and you don't want it to pull it too tight so that way you tear the muscle fibers |
|
|
Muscle spindles |
They are measuring the tenisity or how stretched that muscle fiber is. |
|
|
Stretch reflex |
We have these things called muscle spindles that are going to wrap around the muscle fiber to sense how stretched a muscle is. |
|
|
Reciprocal innervation |
Prevents conflict between antagonist muscles. |
|
|
Head tips when falling asleep? |
(Reflex)You let it stretch too fast , too quickly |
|
|
Golgi tendon reflex |
Similar to a muscle spindle but it's in the tendon. It's measuring the tautness of the tendo. So for the same reason you don't want your muscles to be over stretched you don't want your tendons to be over stretched. |
|
|
Withdraw reflex |
The reason we will need to withdraw a body part is usually in response to pain. You step on a tack or you touch something that is really hot. You need to quickly move away so that way you don't further injure your self. |
|
|
Parralel after discharge circuit |
Removing your foot and than feeling the pain |
|
|
Intersegmental |
Different axons or nerves exit at different levels of the Spinal cord |
|
|
Cross Extensor reflex |
Is going to pair the withdrawal reflex with the cross extensor reflex |
|
|
Spinal nerves |
Contain sensory information, motor, or both( mixed ) |
|
|
Brachial plexus (if damaged ) |
Worry about paralysis |

