![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Pulsed sound |
Diagnostic ultrasound imaging short bursts or pulses acoustic energy which are used to create an atomic images. A collection of cycles that travel together. Must have a beginning and an end otherwise the sound is continuous wave. |
|
|
|
Two components of pulsed ultrasound |
The cycles (on or transmit time) The dead time (off or receive time) |
|
|
|
Parameters of pulsed sounded |
Pulses duration Spatial Pulse Pulse repetition period Length Pulse repetition frequency Duty factor |

|
|
|
Pulse duration |
The time from the start of a pulse to the end of that pulse, The actual time that the pulse is on. Sound source Pulse duration is determined by multiplying the number of cycles in the pulse and the period of each cycle. In clinical imaging a pulse is comprised of 2-4 cycles |

|
|
|
Equation of pulse duration |
= #cycles in pulse x period (Msec)
= # cycles in pulse/frequency (MHz) |

|
|
|
Pulse repetition period |
The time from the start of one pulse to the start of the next pulse. It includes one pulse duration and one listening time. Seconds, msec Sound source Operator can change only the listening time (when adjusting the depth of view) never pulse duration. |

|
|
|
PRR is determined by |
The depth of view Depth⬆️ PRP ⬆️ Depth⬇️ PRP ⬇️ |
|
|
|
PRR is determined by |
The depth of view Depth⬆️ PRP ⬆️ Depth⬇️ PRP ⬇️ |

|
|
|
Pulse repetition frequency |
The number of pulses that occur in one second Herts, Hz, per second Sound source Clinical imaging from 1000-10,000Hz (1-10kHz)♥️ Depth ⬆️PRF⬇️(inverse relationship) |

|
|
|
PRP and PRF relationship |
Are reciprocals Both depend on imaging depth |

|
|
|
Duty factor |
The percentage or fraction of time that the system transmits sound. Important when discussing intensities If the duty factor is 100% or 1.0, then the system is always producing sound. This is continuous wave.❤️ Sound source |
|
|
|
Duty factor equation |
Pulse duration (msec)/ pulse repetition period (msec) x 100
% with little talking, lots of listening ❤️ CW sound cannot be used to make anatomical images❤️ |
|
|
|
Duty factor important concept |
Shallow imaging High PRF High duty factor Short PRP
Deep imaging Low PRF Low duty factor Long PRP |
|
|
|
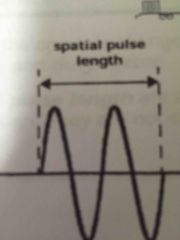
Spatial pulse length |
Length or distance that an entire pulse occupies in space. The distance from the start to the end of one pulse. mm, meters Source and medium Determines axial resolution Short pulses high quality |

|
|
|
Spatial pulse length equation |
= # of cycles x wavelength (mm) |
|
|
|
Parameters that describe both pulsed and continuous waves |
Period Frequency Wavelength Propagation speed CW and PW are both comprised of cycles |
|
|
|
Parameters of pulse waves |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Pulse wave cheat sheet |

Back (Definition) |
|

