![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Acoustic Propagation Properties |
the effects of the medium upon the sound wave |
|
|
|
Biological Effects |
the effects of the sound wave upon the biologic tissue |
|
|
|
Sound |
A type of wave that carries energy, not matter, from place to place |
|
|
|
How sound travels |
Vibration of a moving object Compression (increase pressure/density) Rarefactions (decreased pressure/density) Travels in a medium Straight line Mechanical and longitudinal |
|
|
|
Three acoustics variables |
Pressure Density Distance |
|
|
|
Pressure |
Concentration of force within an area Force/area. Pascals (Pa) |
|
|
|
Density |
Concentration of mass within a volume kg/cm3 |
|
|
|
Distance |
Measure of particle motion cm, feet, miles |
|
|
|
Parameters describe sound waves |
Period Speed Frequency
Amplitude Power Intensity Wavelength |
|
|
|
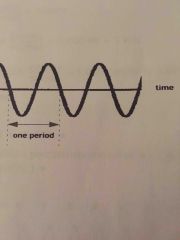
Period |
Time required to complete a single cycle Seconds, Mses, hours Sound source |
|
|
|
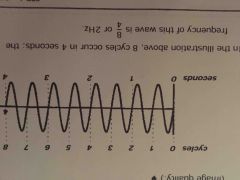
Frequency |
Number of certain events that occur in a particular time duration (# cycles per second) Per second, 1/second, hertz, Hz Hertz=per second Sound source 2 MHz-15 MHz Affects penetration and axial resolution (image quality) |
|
|
|
Ultrasound |
A wave with a frequency exceeding 20,000Hz (20kHz) Too high and is not audible to man |
|
|
|
Audible sound |
Frequencies between 20Hz and 20,000Hz. Heard by man |
|
|
|
Infrasound |
Frequencies less than 20Hz. Too low for man to hear. |
|
|
|
Frequency and Period |
Are reciprocals
Equation Frequency (Hz) x period (sec) =1 Period (sec) = 1/frequency (Hz) Frequency (Hz) = 1/ period (sec) |
|
|
|
Three Bigness Parameters |
Amplitude Power Intensity |
|
|
|
Amplitude |
The difference between the average value and the maximum value of an acoustic variable. Pressure-Pascals Density-grams/cubic cm Particle motion-cm, inches, unit of distance Can be expressed in decibels,dB Sound source |

|
|
|
Power |
The rate that is performed or rate of energy transfer. Watts Sound source Power proportional (Amplitude)2 |
|
|
|
Intensity |
Concentration of energy in a sound beam = power (watts)/ beam area(cm2) Sound source Proportional or directly related to the power proportional to amplitude2 |
|
|
|
Wavelength |
The length or distance of a single cycle Meters, mm Source and medium = propagation speed (mm/Ms)/ Frequency (MHz) |

|
|
|
Propagation speed |
The rate that sound travels through a medium also called velocity or speed Meters per second, mm/Ms Medium only = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (meters) |
Speed and wavelength are directly related. Sound in a slow medium has a short wavelength. Sound in a fast medium has a long wavelength |
|
|
Average speed of sound |

Soft tissue = 1.54km/s = 1,540m/s = 1.54mm/Ms Lung (air) << fat < soft tissue < |
|
|
|
Average speed of sound |

Soft tissue = 1.54km/s = 1,540m/s = 1.54mm/Ms Lung (air) << fat < soft tissue < |
|
|
|
Rule of thumb propagation speed |
Stiffness ⬆️and speed⬆️ - same direction Density ⬆️and speed⬇️ - opposite direction Bulk modulus is the same as stiffness. When bulk modulus increases speed increases Compressibility and elasticity are opposites of stiffness |
|
|
|
Parameters of continuous waves |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Parameters of continuous waves |
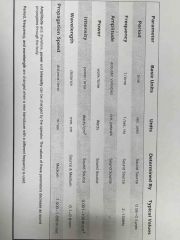
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Continuous wave Cheat sheet |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Phase relationships |
Interference -in phase -out of phase Constructive interference Destructive interference |
|
|
|
Constructive interference |
Occurs when the amplitude of the new, combined wave is greater than the original two waves. In-phase waves interfere constructively. |

|
|
|
Destructive interference |
The amplitude of the new wave is less than one of the original waves. Out-of-phase waves interfere destructively. Out-of-phase waves are said to have a phase difference |

|

