![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the three devisions of the ear |
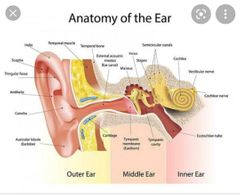
• external ear • middle ear (tympanic cavity) • internal ear (labyrinth) |
|
|
List the 2 units of the external ear |
• auricle (pinna) • external accoustic meatus (ends at the tympanic membrane) |
|
|
Describe the features of the auricle |
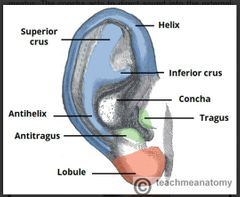
• most of the ear consist of elastic cartilage except the lobe/lobule • the cartilaginous structure an outer an inner curvature - helix (outer curvature) - antihelix (inner curvature) runs parallel with the helix • the antihelix branches into to cura: superior and inferior crus • hollow depression in the auricle (concha) directs sound into the external meatus • anterior to the external meatus is the tragus. Opposite the tragus is the antitragus |
|
|
Describe the function of the auricle |
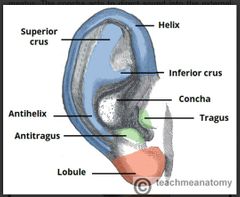
Capture and directs sound waves towards the external acoustic meatus |
|
|
Describe the feature of the external accoustic meatus |
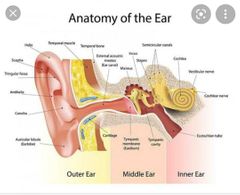
•Sigmoid-shaped (S-shaped) tube that extends from the concha of the auricle to the tympanic membrane • the external 3rd of the meatus is formed by cartilage. • the last 2 3rds of the meatus is formed by temporal bone |
|
|
Describe the function of the external accoustic meatus |
Pathway for sound waves to hit the tympanic membrane (transmit sound to the middle ear) |
|
|
Describe the feature of the tympanic membrane |
• lies at the distal end of the acoustic meatus • connective tissue structure • external membrane covered with skin, internal membrane covered with mucous • attaches to the tympanic bone by a fibrocartilagenous ring |
|
|
List the cavities of the middle |
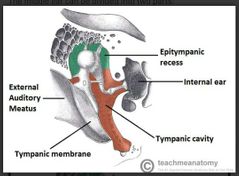
• tympanic cavity - (contain the auditary bone) lies medially to the tympanic membrane • epitympanic recess - lies superior to the tympanic cavity |
|
|
Which structure marks the end of the external auditory meatus |
Tympanic membrane |
|
|
The tympanic membrane is connected to the surrounding bone by a fibrocartilaginous ring. Which bone is the ring connected to? |
Temporal bone |
|
|
List the auditory bones/ossicles in the tympanic cavity of the middle ear |
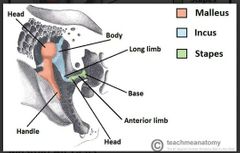
• malleus • incus • stapes
Mneumonic MIS |
|
|
What is the overall function of the auditar ossicles in the inner ear |
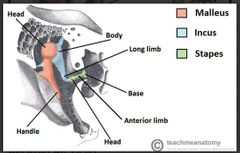
Sound vibrations cause the tympanic membrane to vibrate which cause oscillation of the ossicle that transmit the sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the inner ear |
|
|
Which structure forms the roof of the middle ear |
Petrous part of the temporal bone |
|
|
Where are the mastoid air cells in relation to the epitympanic recess? |
Posterior |
|
|
What are the 2 main functions of the vestibulocochlear organs in the inner ear? |
• convert mechanical signals from the middle ear to electrical signals (to the brain) • maintain balance by detecting position and motion |
|
|
Where in the temporal bone is the inner ear located? |
Petrous part of the temporal bone |
|
|
List the two main components of the inner ear |
Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth |
|
|
List the three parts of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear |

• cochlea • vestibule • 3 semi-circular canals |
|
|
Describe the vestibule of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear and name the parts of the membranous labyrinth that it houses |

• central part of the bony labyrinth • separated from the middle ear by the oval window • communicates anteriorly to the cochlea and posteriorly to the semi-circular canals • houses the saccule and utricle of the membranous labyrinth |
|
|
Describe the cochlea of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear and which part of the membranous labyrinth does it house? |

• houses the cochlea duct of the membranous labyrinth • twists itself around the modiolus bone which produces a cone that point anterolaterally • contains two perilymph-filled chambers: - scala vestibuli - scala tympani (terminates at the round window) |
|
|
Describe the semi-circular canals of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear |

• three canals at right angles from each other: - anterior - lateral - posterior • contain semi-circular ducts which are responsible for balanca • situation superoposterior to the vestibule • swelling at their bases - ampullae |
|
|
List the 4 membranous labyrinths in the inner ear |
• cochlear duct • saccule and utricle • semi-circular duct |
|
|
Describe the cochlear duct of the membranous labyrinth in the inner ear |
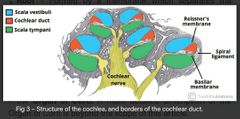
• located within the bony scaffold of the cochlea • the presence of the duct creates two canals: one above (scala vestibuli) and one below (scala tympani)
|
|
|
Describe the saccule and utricle of the membranous labyrinth in the inner ear |
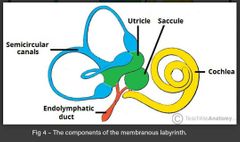
• membranous sac in the vestibule • detect movement in the verticle plane and acceleration in the horizontal planes • the utricle receives three semi-circular ducts • the saccule receives the cochlear duct |
|
|
Describe the semi-circular ducts of the membranous labyrinth in the inner ear |
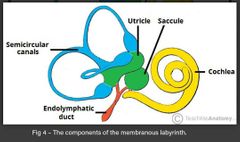
• located within the semi-circular canals • upon movement, the endolymph in the ducts change speed and/or direction • sensory receptors in the ampulla (base of the semi-circular canals) detect the change in endolymph and transmit this info to thr brain for processing balance |

