![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How long does Earth’s rotation take? |
24 hours |
|
|
How long does it take Earth to complete one revolution around the sun? |
1 year |
|
|
Why does Earth have seasons? |
Because Earth’s axis is tilted as it moves around the sun. |
|
|
When the north end of Earth’s axis is tilted toward the sun, describe the sunlight and day length in North America. |
More direct rays and longer days |
|
|
What does the moon phase we see from Earth depend on? |
how much of the sunlit side of the moon faces Earth |
|
|
How must the Earth, sun and moon be ordered to experience a solar eclipse? |
the moon must be directly between Earth and the sun |
|
|
What did Galileo see on the moon’s surface? |
round pits called craters |
|
|
How do scientists think the moon was formed? |
a large object struck Earth, and ejected material from the collision combined |
|
|
Describe the position of the Earth during an equinox. |
neither end of Earth’s axis is tilted toward or away from the sun |
|
|
When does the moon appear to be cut in half? |
first quarter and third quarter phase |
|
|
What law says that all objects are attracted to each other? |
the force of gravity |
|
|
What event began the Space Race? |
The Soviet Union launched Sputnik I |
|
|
Who was competing in the Space Race? |
the United States and the Soviet Union |
|
|
What is the space shuttle? |
A reusable spacecraft that can be used many times to carry astronauts into orbit |
|
|
What do both reflecting and refracting telescopes do with visible light? |
gather and focus visible light |
|
|
What characteristics are used to classify stars? |
size, brightness, temperature, color, composition |
|
|
When nuclear fusion starts, what is happening to a star? |
it is dying |
|
|
What does the lifetime of a star depend on? |
it’s mass |
|
|
What is a supernova? |
the explosion of a dying high-mass star |
|
|
What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? |
spiral galaxy |
|
|
What is the name of the theory that scientists believe formed the universe? |
Big bang theory |
|
|
What did the solar system form from? |
a giant cloud of gas and dust |
|
|
What happens to Earth in a heliocentric system? |
Earth revolves around the Sun |
|
|
What do all of the inner planets have in common? |
They all are small and have rocky surfaces |
|
|
Where is the asteroid belt located in the solar system? |
between Mars and Jupiter |
|
|
Where do meteoroids come from? |
comets or asteroidsliquid water |
|
|
What are the conditions necessary for life on Earth? |
liquid water |
|
|
What are the reasons that scientists think that Mars once may have had life? |
evidence that liquid water was once present |
|
|
What are Saturn’s rings made mostly of? |
chunks of ice and rock |
|
|
Why is Uranus different from most other planets? |
rotates on its side |
|
|
Why is Jupiter unique? |
It is the largest and most massive planet |
|
|
What causes day and night? |
Earth’s rotation on its axis |
|
|
What are the flat areas on the moon’s surface? |
maria |
|
|
Because galaxies are moving away from each other, what can be said about the universe? |
it is expanding |
|
|
What is the minimum number of stars in a star system |
2 |
|
|
What model shows Earth as the center of the solar system |
geocentric |
|
|
Where is the Great Red Spot found? |
Jupiter |
|
|
. Why can the moon be seen from the Earth? |
because sunlight reflects off the moon’s surface |
|
|
When a shuttle returns from a mission, how does it land? |
like an airplane |
|
|
Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust. What is this called? |
nebula |
|
|
Draw a picture of and name each of the 8 moon phases in the order that they occur. |

|
|
|
How much time passes between a new moon and a full moon? |
about 15 days |
|
|
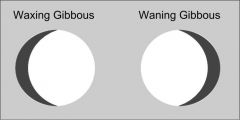
Draw the two gibbous moons. |
|

