![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How can you diagnose cutaneous parasites
|
Direct observation
skin scrapings |
|
|
What are general guidelines for cutaneous parasite treatment
|
duration >> life cycle
treat all animals clean and disinfect environment consider human risk with treatment |
|
|
What are the follicular mites occur on the dog
|

Demodex canis - MOST common mite in dogs
D. injai |
|
|
What are the follicular mites occur on the cat
|
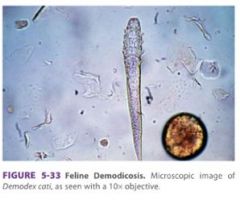
Demodex cati
|
|
|
What are the surface mites occur on the dog
|

D. cornei
|
|
|
What are the surface mites occur on the cat
|
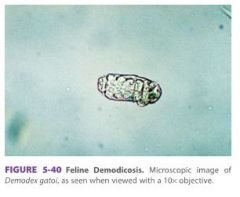
Demodex gatoi - MOST common mite in cats
Contagious! |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Demodicosis
|
normal commensal passed after birth
overgrowth associated with mite specific immunoincompetency suppresion of T lymphocytes secondary infections (pyoderma) additional immunosuppression |
|
|
When is Demodicosis most common
|
<1 year of age (can outgrow)
all animals at risk |
|
|
What is localized demodicosis
|
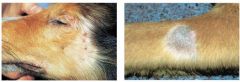
Lesions restricted to one or two body areas (face)
Lesion: alopecia, erythema, mild scaling not pruritic |
|
|
How do you treat localized demodicosis
|
treat secondary pyoderma with ab
90% spontaneously resolve topical treatment (1-3% benozyl peroxide) may make lesion look worse initially - rub out hairs lesion persists - miticidal treatment |
|
|
What are the characteristics of generalized demodicosis
|
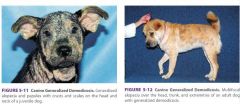
Multiple lesions (anywhere) - alopecia, scaling, crusts, pustules, erythema, draining tract
bacterial infection with Staph folliculitis and furunculosis (causes pruritis) |
|
|
What causes pruritis with Demodicosis
|
secondary pyoderma
not Demodex itself |
|
|
what is the key sign of furunculosis
|
Small draining tracts
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of adult onset demodicosis
|
1-2 years of age
50% identifiable systemic disease - immunocompromised caused by any mite species |
|
|
How do you diagnose demodicosis
|
history and clinical features
skin scrape trichogram biopsy |
|
|
How do you treat localized demodicosis
|
Time
Topical: benzoyl peroxide, rotenone, amitraz Advantage multi dont treat |
|
|
How do you treat generalized demodicosis
|
-treat underlying pyoderma - systemic antibiotics, topical antimicrobial / antiseborrheic shampoo; hydrotherapy
-topical: organophosphates, amitraz, metiflumazone, moxidectin -systemic: milbemycin oxime, moxidectin, ivermectin |
|
|
What is the most important first step in managing generalized demodicosis
|

Antibiotics to treat pyoderma
Stop glucocorticoids |
|
|
How do you use Amitraz / Mitaban
|
total body clip
shampoo 10-15 min rinse contact time allowed to dry rinse once weekly for 8-12 rinses |
|
|
How long do you use Amitraz rinses
|
treat for 2 rinses past 2nd negative scraping
|

