![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy of the human eye |
* anterior chamber * posterior chamber * vitreous chamber |
|
|
Myopia = |
nearsightedness |
|
|
Hyperopia = |
farsightedness |
|
|
optic vesicle |
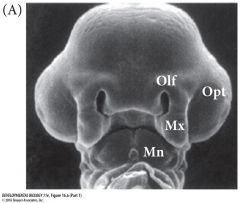
|
|
|
_____________ occur from the thickenings of the anterior surface ectoderm surrounding the presumptive neural plate |
Placodes |
|
|
Placodes generate sensory neurons that populate cranial ganglia/cranial nerves in conjunction w/ cranial neural ___________ derivatives |
crest |
|
|
Cranial placode induction requires transient ______ signalling then _________ signalling |
* Wnt * BMP |
|
|
Neural crest induction requirest ______ signalling the both _____ + _____ signalling |
* Wnt * Wnt + BMP |
|
|
Lens is derived from optic (lens) __________ |
placode |
|
|
Retna is _________ __________ derived |
neural tube |
|
|
Optic (lens) placode forms the lens vesicle, then the _______ |
lens |
|
|
Optic vesicle evaginates into the optic cup, then the _____________ |
retina |
|
|
Section of the _________ neural plate will become the retina. This is called _____ field |
* anterior * eye |
|
|
___________ ___________ transcription factor expression required in the eye field for eye development |
retinal homeobox (Rx) |
|
|
_____ derived from prechordal plate necessary for ____________ the eye field/forebrain into two parts |
* Shh * splitting |
|
|
Shh mutations or environmental manipulation lead to varying degrees of |
* cyclopia (single eye) * holoprosencephaly (single cerebral lobe) |
|
|
Optic vesicle and lens placode utilize _____ signalling to coordinate development |
FGF |
|
|
_________________ surrounds the developing eyeball (optic globe) between the 5th and 7th weeks fo form the choroid and sclera |
mesenchyme |
|
|
_____________ precursor cells are derived from migratory neural ____________ |
* corneal * crest |
|
|
Cells degrade nuclei and express ____________ to become transparent |
crystallins |
|
|
Ocular defects of they eyelids, lens, cornea, iris, ciliary body, zonules, choroid, retina and optic nerve |
colobomas |
|
|
Optic cup ________ layer differentiates into the retina |
inner |
|
|
Meticulously traced and studied retinal neurons using silver staining |
Santiago Ramon y Cajal |
|
|
Anatomical terms for ear |
* external ear * middle ear * internal ear |
|
|
otic ________ envaginates to form the otic vesicle |
placode |
|
|
The otic _________ appears in the surface ectoderm late in the 3rd week |
placode |
|
|
By day 25, the placode invaginates to form the otic _____- |
pit |
|
|
By the end of the 4th week, continued invagination forms the otic ______, which quickly detaches from the surface ectoderm |
vesicle |
|
|
cranial neural crest generate ___________ ossicles |
auditory |
|
|
auditory ossicles are a chain of small _____ in the middle ear |
bones |
|
|
Transmits sound to the inner ear |
auditory ossicles |
|
|
Waardenbur syndrome is due to neural _____ defects and can cause hearing loss |
crest |
|
|
The basilar membrane in the cochlea is line w/ ____ cells responsible for converting mechanical vibration into a chemical signal that stimulates your auditory nerve |
hair |
|
|
______ is a genetic mediator of congenital hearing loss |
DFNB1 |
|
|
_____________ - gap junctions that regulate K+ homeostasis |
Connexin 26 disruption can lead to damage of hair cells |

