![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Platonic view of vision and the world?
|
The 'real world' exists but mortal sense are only capable of sampling a small fraction of it.
|
|
|
Friedrich Nietzsche's view of vision and the world?
|
There is no real world, only the world inside your head. Vision as construction.
|
|
|
The world that we visually sense is entirely dependent upon...
|
- our individual perceptions
- light |
|
|
Excitation refers to...
|
a state/response due to external stimuli, an application of energy.
|
|
|
Sensation refers to...
|
the detection of external stimuli by sensory organs.
|
|
|
At what stage in the visual pathway is an action potential first generated?
|
Ganglion cells
|
|
|
What do L, M & S denote when applied to cones?
|
Long (red), Medium (green) & Short (blue) wavelengths of light.
|
|
|
Why are photoreceptors anchored to the retina despite there being neural matter between between the light source and receptor?
|
Inverted retinal neural design, reason for blind-spot.
Protection and insulation of photoreceptors. Transportation of nutrients. |
|
|
A colour space is...
|
an abstract model/representation of colour in space.
e.g. RGB & CYMK |
|
|
Orthogonality in the vector representation of signal-coding confers which of the following properties upon that stage of the system?
|
- Orthogonality allows overlapping stimulus-coding.
- Positive and negative interactions |
|
|
Which statement best describes a receptive field?
|
Receptive fields are an abstract construction describing the sensitivity of a sensory neuron.
|
|
|
What is the most likely format of the first spatially structured (or differentiated) receptive fields in the visual system?
|
Centre - Surround organisation. Donut shape.
|
|
|
The receptive field arrangement referred to in Question 12 confers what properties to the system?
|
The property of opponency.
|
|
|
The term "opponency" refers to...
|
Theory of opponency records the differences/opposites between colour or stimuli.
|
|
|
Why, when considering the processing of the neural signal, is the actual physical location of any visual neurone other than the photoreceptors, arbitrary?
|
Information from the receptive fields relate to the same x,y,t space and photoreceptors are the only thing in direct contact with the stimuli. It doesn't matter after that point.
|
|
|
Why, however, is the relative location of any sensory neurone potentially important?
|
Information (shapes, lines and contours) in the real world has to be represented the same way in the brain.
|
|
|
What is meant by the term "retinotopic mapping"?
|
Retinotopic map is the topopgraphic map of the retina as represented in the brain. It maintains relative relationship of neurons whilst the actual location is irrelevelant/arbitrary as long as they are in close proximity. (Visual cortex)
|
|
|
What is meant by the term "tonotopic mapping"?
|
Tonotopic map is the topographic map of the audio input from the cochlea represented in the primary audio cortex of the brain.
|
|
|
The term "phase-coherence" refers to the hypothesis that...
|
an edge/border is signalled consistently across all scales of analysis.
|
|
|
The idea of modularity in visual processing refers to...
|
different modules in the brain have differentiated functions.
|
|
|
What reason may you have for questioning the assumption that the LGN is just a relay station fo signals travelling from the retina to the cortex?
|
There are more neural pathways from the visual cortex to the LGN than from the LGN to the visual cortex.
|
|
|
Taken as a population, primary visual cortical (v1) neurones have what critical property?
|
V1 cortex (striate) are responsible for representing everything in the raw form. All visual information enters at this point.
- Cortical magnification - Orientation sensitivity |
|
|
An example of context-dependency in vision is...
|
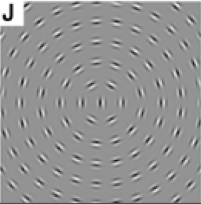
Matchsticks arranged in circles.
|
|
|
What is red?
|
Red is definitive as a specific wavelength but sensation and perception of it differs between individuals.
|
|
|
An attentionally-controlled motion system may...
|
Attention modulated motion is the isolation of a particular aspect of motion so that we are not overwhelm by input of information.
e.g. Keeping the world still as you move your eyes. |
|
|
The visual system appears to dissociate motion-signals elicited by eye-movements or from the retinal motion by...
|
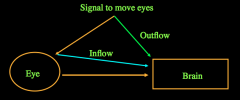
the In-Flow Hypothesis: feedback from the eye-movement.
the Out-Flow Hypothesis: feedback from the commanding signal. |
|
|
The spatial structure of natural textures is consistent with the properties of the system because...
|
Receptive fields are more selective to natural textures due to evolution???
|
|
|
"Adaptation" refers to...
|
reduced sensitivitity to the stimulus as a result of repeated exposure.
|
|
|
What is meant by the term "parallel processing"?
|
It is the ability of the brain to process information simultaneously.
|
|
|
A form of parallel processing in the auditory system is implemented in the cochlea nucleus by...
|
Divergence of auditory signals received from the cochlea before its input into the auditory cortex.
|
|
|
One critical similarity between the auditory system and visual system is...
|
Inputs are both topographically mapped out onto the brain in their respective cortexes.
|
|
|
One critical difference between the auditory system and visual system is...
|
Visual information is processed contra-laterally whilst auditory information is processed bilaterally.
|
|
|
The terms M and P in the context of the visual system refer to...
|
two types of LGN cells: Magnocellular (input from Parasol Ganglion cells) and Parvocellular (input from Midget Ganglion cells). Oh the irony.
|
|
|
Information is...
|
What stimuli is translated into for the brain to process.
|
|
|
A vector is...
|
Direction + Magnitude. A single directional signal.
|
|
|
The theoretical hierarchy established by David Marr is...
|
Problem -> Algorithm -> Implementation
|
|
|
"Retino-cortical expansion" refers to...
|

Cortical expansion. Where there is a larger number of neurones corresponding to the centre of the visual field compared to the peripheral.
|
|
|
Which of the two structures listed below exploit orthogonality in the representation or operation?
|
semicircular canals? Orientation receptive fields in V1 cortex.
|
|
|
What computational role does the cochlea play in audition other than simply transduce the auditory signal?
|
It also has a function in the vestibular system, spatial awareness.
|
|
|
Psychophysics is...
|
The relationship between a physical stimuli and the sensation and perception they affect.
|
|
|
What aspect of the relationship between the stimulus and the cortical representation is different between vision and audition?
|
The visual system exhibits some form of cortical magnification whereas the auditory system does now. (Varies a bit but relatively constant)
|
|
|
The two most likely kinds of motion detector in the human visual system are called...
|
- Delay&Compare/Correspondence/Hassenstein-Reichardt/Fly&Beetle Detector
- Spatiotemporal Gradient Detector |
|
|
The three critical dimensions of vision are...
|
X axis, Y axis and time. (x,y,t)
|
|
|
The term "Biological motion" describes...
|
Movement made by biologically active stimuli. e.g. Stick figures. Dots fit our expectations and fill in gaps of biological movement.
|
|
|
Interaction between V1 orientation-selective receptive fields follow what laws?
|
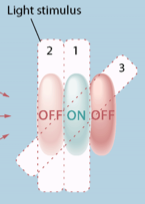
Aligned V1 receptive cells positively interact whilst orthogonal receptive cells negatively interact.
|
|
|
The visual system is sensitive to...
|
The visual wavelengths of 380 - 760?
|
|
|
What critical neural interaction is affected by hallucinogenic drugs?
|
Affects neurotransmitter receptors, particularly serotonin. Disrupts action potentials and signalling.
|
|
|
Your experience of reality is...
|
Subjective and individual.
|
|
|
Synaesthesia is...
|
a cross wiring of different senses.
|
|
|
One fish, two fish,...
|
Red fish, blue fish.
|

