![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
200 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
RAAS Drugs - Where they act |
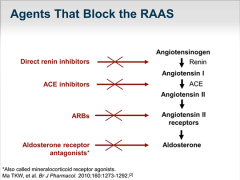
|
|
|
DRI - What do they do? |
Direct Renin Inhibitor - Renin inhibitors bind to the active site of renin and inhibit the binding of renin to angiotensinogen, which is the rate-determining step of the RAAS cascade. |
|
|
DRI - Drugs? |
Only available is Aliskeren taken only as tablet |
|
|
DRI - SE/Contraindications? |
Hypotension, generally safe drug |
|
|
ACEI - What do they do? |
ACE inhibitors produce vasodilation by inhibiting the formation of angiotensin II. They are nearly all prodrugs and end in ''Pril''. Used in Hypertension, Heart failure and Post-myocardial infarction. |
|
|
ACEI - Drugs? |
End in Pril E.G. Enalapril taken as a tablet 5, 10 or 20 mg. Note Lisinopril and Captopril are drugs not prodrugs unlike the rest. |
|
|
ACEI - SE/Contraindication |
SE- Dry cough (because ACE also breaks down bradykinin and breakdown is thus inhibited), Hypotension, Angioedema, Hyperkalemia (occurs because aldosteroneformation is reduced) CI- Impaired renal function Aortic valve stenosis cardiac outflow obstruction Hypovolemia dehydration Hemodialysis Pregnancy |
|
|
Angiotensin 2 Receptor blocker (AT1) - ARB - What do they do? |
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are medications that block the action of angiotensin II by preventing angiotensin II from binding to angiotensin II receptors on the muscles surrounding blood vessels thus vasodilate. For hypertension, heart failure, kidney failure in people with diabetes. |
|
|
ARB - Drugs? |
- End in Sartan - Vasopril - Oral Tabl 80 mg general or oral sol. - Losartan Tabl |
|
|
ARB- SE/Contraindications? |
SE - cough - Hypotension - Rash - Kidney and liver failure CI - Cat D so no use in pregnancy - Kidney DMG - Renal Artery Stenosis |
|
|
Aldosterone Antagonists |
Aldosterone acts on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron, increasing reabsorption and excretion of ions out of and into the tubular fluids of the kidney, to cause the conservation of sodium, secretion of potassium, and thereby indirectly influencing water retention. AA blocks this. |
|
|
Aldosterone Antagonist - Drugs? |
Spironolactone - film coated tabl - causes hormonal imbalance can be good for women and bad for men. Eplerenone - film coated tabl |
|
|
Aldosterone Antagonist - SE/Contraindications |
SE - mild nausea or vomiting - diarrhea - breast swelling or tenderness - dizziness, headache, mild drowsiness - leg cramps - impotence, difficulty having an erection. CI - Pregnancy - Anuria - not producing urine - Acute kidney failur - High potassium (Hyperkalemia) - Addison's disease - Concomitant use of eplerenone |
|
|
Q. Which if these is an Angiotensin Antagonist? Losartan Aliskerin Atenolol Perindopril |
Losartan |
|
|
Q. How do ACEI and ARB difference in Mech? |
ACEI block ACE to convert Angiotensinogen to get converted to Angiotensin 1. ARB block the action of Angiotension 2 on its receptor (AT1) |
|
|
Q. ACEI and ARBS are used in? Hypertension Chronic heart failure Cardiac Arrhythmias Diabetic Nephropathy |
Hypertenion, chronic heart failure and diabetic nephropathy |
|
|
Q. SE of ACEI? Hypotension Dry cough Ventricular arrhythmias Angioedema hyperkalemia Hypercalcemia |
hypotension, dry cough, angioedema, hyperkalemia |
|
|
Q. ACEI and ARBS are contraindicated in? 1DM 2Bronchial Asthma 3Pregnancy 4Bilateral renal artery Stenosis |
1,3,4 |
|
|
Q. ACEI/ARB + Saluratics? |
Dangerous both produce hyperkalemia causing cardiac arrest and death. |
|
|
Q. ACEI/ARB + Betablockers |
This combination has proved to be more effective than monotherapy in a number of studies, some of which are reviewed. Moreover, there is evidence that this combination may be beneficial after myocardial infarction. Combined use of ACE inhibitor and beta-blocker therapy therefore warrants further investigation. |
|
|
Q. ACEI/ARB + Aldosterone antagonist |
Dangerous - spironolactone K sparing and acei causes hyperkalemia
|
|
|
Q. ACEI/ARB + NSAIDS
|
NSAIDs inhibit cox1 so no PG so no vasodilation. So have Vasoconstrictive effect which is causes higher bp and ACEI and ARB try to reduce it. |
|
|
Cardioinotropic drugs: Cardiac Glycosides - What do they do? |
If you have heart disease, Digoxin is a medication that helps an injured or weakened heart work better to send blood through the body. It strengthens the force of the heart muscle's contractions, slows the heart rate, and improves blood circulation. Used in chron heart failure specially by atrial fibrillation and when nothing is working. |
|
|
Cardioinotropic drugs: Cardiac Glycosides - Drugs
|
Digoxin - tabl 0.25 mg. and inf/inj Blocks Nak atpase leading to more ca staying inside increasing Inotropy ectopic beats extended refractory period decreased hr Increasing vagal outflow Metildigoxin - Tabl |
|
|
Cardioinotropic drugs: Cardiac Glycosides - SE/CI |
SE - Dizziness - faintingfast, - pounding, or irregular heartbeat or pulse slow - heartbeat - Arrhythmias - ventricular tachycardia - vision disturbances CI - Ventricular fibrillation - Electrolyte imbalance - Hypokalemia very dangerous with digoxin so can use with saluratics |
|
|
Drugs used in Digoxin toxication? |
- Magnesium (digoxin antagonist) and potassium aspartate - KCl - for arrythmias Liocaine (sol inj iv) or phenytoin (tabl) - for av conductance disorders atropine (sol inj) - for overal effect digoxin immune fab |
|
|
Cardioinotropic Drugs - Adrenomimetic |
Dobutamine -sol inf - selective b1 agonist |
|
|
Cardioinotropic Drugs - Adrenomimetic
|
Dopamine - conc for sol. inf. |
|
|
Q. Seletive b1 agonist for a cardioinotropic drug? |
Dobutamine |
|
|
Q. Statements of Digoxin. which are true? 1. well absorbed orally 2. renal excretion 3. liver excretion 4. elimination half life in 36 hrs 5. narrow therapeutic conc |
1, 2, 4 and 5 |
|
|
Q. Where is the site of action of digoxin? |
Na/K atpase |
|
|
Q. Effects of Cardiac Glycosides on the heart? |
+inotropy -dromotropy -chromotropy |
|
|
Q. Cardiac Glycosides slow AV conductance by? |
Increasing vagal outflow |
|
|
Q. Cardiac glycosides used in the treatment of? |
atrial fibrilation heart failure not ischemic heart disease and ventricular tachycardia |
|
|
Q. Dobutamine is? 1. for acute heart failure 2. for chronic heart failure 3. oral 4. IV |
1 and 4 |
|
|
Q. Signs of Digoxin poisoning 1. Nausea and vomitting 2. bronchospasm 3. vision disturbances 4. Ventricular arrythmias |
1, 3, 4 |
|
|
Q. What kind of electrolyte disbalance causes Digoxin toxicity and what is used to treat it? |
Hypokalemia and Hypomagnesia so you can give magnesium and potassium aspartate. Saluratics, ACEI |
|
|
Periphral Vasoactive Drugs - Vasodilators - Acting on Periphral blood vessels |
Purine Derivative - pentoxifylline Tabl 100mg, prolonged 400-600mg and sol inf 5 ml@ 20mg/ml Papaverine - Papaverine. tab sol inf |
|
|
Periphral Vasoactive Drugs - Vasodilators - Erectile Dysfunction |
Sildenafil - film coated tabl, chew, orodis, tabl vardenafil - roal Tadalafil - oral |
|
|
Periphral Vasoactive Drugs - Vasodilators - Brain |
Ca2+ channel blockers Cinnarizine - tabl flunarizine - caps, tabl nimodipine - film coated tabl, sol inf other Vinpocetine - tabl, sol inf naftdrofuryl - film coated tabl, prolonged release table caps betahistine - tabl, oral sol. |
|
|
Periphral Vasoactive Drugs - Venotonic and Capillarotonic Drugs |
Diosmin - film coated tabl. 500mg tabl 600 mg Bioflavanoids (diosmin+flavanoids) Troxerutin - caps, gel Endotelon - gastro resistant tabl Ascorbic acid - tabl, pro release, sol inj |
|
|
Q. Vasodilator in the brain? 1. Sildenafin 2. Vinpocetine 3. Cinnarizine 4. Pentoxifylline |
2,3 |
|
|
Q. Which is a Venotonic drug? 1. Troxerutin 2. Naftidrofuryl 3. Pentoxifylline 4. Diosmin |
1,4 |
|
|
Diuretic - Saluretic - what are they? |
Saluretic = Thiazide Diuretic or Loop Diuretic cause loss of salt due to excretion of salt. |
|
|
Diuretic - Saluretic - Drugs - Thiazide |
Thiazide Hydrocholothiazide - tabl 25 mg chlortalidone - tabl -Cause initial decrease in BP due to decreased blood volume and then heart compensates then the BP stays low due to decreased peripheral resistance. -Distal Tubule - block NaCl syntrasported so na exchanges with h leading to metabolic acidosis |
|
|
Diuretic - Saluretic - Thiazide - SE/CI |
SE - Hypokalemia, - DM, - Gout (hyperuricemia) - metabolic alkalosis - Hyperlipidemia - Hypercalecemia - Allergic reactions |
|
|
Diuretic - Saluretic - Drugs - Loop
|
LoopFurosimide - tabl 40 mg sol inj 2 ml @10 mg/mlTorasimide - tabl, prolonged relaease. sol inj
-in edemos -severe heart failure - unlike thiazides effective in renal failure |
|
|
Diuretic - Saluretic - Loop - SE/CI |
SE: - Hyponaturemia - hypotension - hypokalemia - hypersensitivity - Dyslipidemia - deafness - Hypocalecemia - Hypemagnesia - dont use in pregnancy |
|
|
Diuretic - k sparing - What do they do? |
Acting on the collecting tubule on aldosterone receptors. Aldosterone causes increase in NA reuptake thus water so we block this. K is preserved. Used in liver Disease with ascites, Conn's and severe heart failure |
|
|
Diuretic - k sparing - Drugs? |
Aldosterone antagonist -Spironolactone - film coated tab -Eplerenone - film coated tab (more specific thus less SE than spironolactone) Blockers of amilorid-sensitive sodium channel -Triamterene + always a drug combo like hydrochlorothiazide in a tabl |
|
|
Diuretic - k sparing - SE/CI? |
Be careful of drugs with hyperkalemic action like k sparing drugs - Antiandrogenic - impotence - weakness |
|
|
Diuretic - Osmotic |
Mannitol - sol inf Literally pulls out water with itself |
|
|
Diuretic - Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - What they do? |
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. So increased Na, bicarbonate and water excreation. Bicarbonate loss leads to metabolic acidosis so used in altitude sickness. Very Weak |
|
|
Diuretic - Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors |
Acetazolamide CAI's used in glaucoma Brinzolamide - eye drop susp Dorzolamide - Eye drop sol |
|
|
Q. Which is a K sparing drug? 1. Furosimide 2. mannitol 3. Hydrochlorothiazide 4. Spironolactone |
4 |
|
|
Q. A diuretic only given IV? |
Mannitol |
|
|
Q. Drug with the longest Plasma half Life? 1. Chlortalidone 2. Mannitol 3. Furosimide 4. Hydrochlorothiazide |
4 |
|
|
Q. where do Furosimide, Spironolactone, Acetazolamide and Hydrocholothiazide act? |
Furosimide - Thick ascending loop of henle Spironolactone - Collecting tubule Acetazolamide - proximal tubule Hydrocholothiazide - Distal tubule |
|
|
Q. Indications of Furosimide? |
Acute pulmonary edema hypotension acute renal faulure hypertensive crisis chron heart failure cerebral Edema |
|
|
Q. Indications of Spironolactone? |
Chron heart faulire Liver cirrhosis with ascites |
|
|
Q. Indications of Brinzolamide (CAI)? |
Glaucoma |
|
|
Q. Indications of Hydrocholothiazide? |
idiopathic hypercalciuria Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Cerebral edema |
|
|
Q. Indications of Mannitol? |
Glaucoma cerebral edema |
|
|
Q. Thiazides contraindicated in? |
Gout and DM |
|
|
Q. ADR of Thiazides? |
Hypokalemia Dyslipidemia Hyponaturemia Hypersinsitivity glucose tolerance hyperuricemia |
|
|
Q. ADR of Loops? |
Hypokalemia Hypocalecemia Hypomagnesia Hypocl hypotension Hypersistivity dyslipidemia ototoxicity hyperuricemia impaired glucose tolerance |
|
|
Q. Does Mannitol cause hypersensitivty? |
no |
|
|
Q. Which Drug contraindicated in Acute pulmonary edema as a result of acute heart failure? |
Mannitol increase blood volume increase heart faulure |
|
|
Q. Which diruetic to use with Digoxin? |
K sparing. low K very dangerous with digoxin because cardiotoxicity is reached easier |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers - Selective - Dihydropyradine - What do they do?
|
- Work more on Systemic vasculature than the heart so we use to treat systemic vas resistance. - Not used in Angina because we vasodilate to cause hypotension causing reflex tachycardia -First gen high SE and third is Low - Exceptions to the rule are Amlodipine (third gen), nifedipine (second) so we can use these for angina. |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers - Selective - Dihydropyradine - Drugs |
First gen - Nifedapine - tabl coated - Nitrendipine - tabl - Nimodipine - Film- coated tabl, sol inf Second gen - Felodipine - film cted, prolonged release - Nifedapine - prolonged rel Third gen - Amlodipine - tabl 5 mg and 10 mg - Lercanidipine - film coated - Lacidipine - film |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers - Selective - Non-Dihydropyradine - What do they do?
|
- Phenylalylamine cardioselective and benzothiazapine both heart and vessels - Do no cause reflec tachycardia so used in andchine and ischemic heart disease - verapamil reduce heart o2 demand and reduce coranary vasospasm, -Benzothiazapine works on heart and vessel, cardiac depressent and vasodilation so no reflex tachycardia |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers - Selective - Non-Dihydropyradine - Drugs |
Phenylalkylamines - Verapamil - tabl 40/80 mg, prolonged release 120/240mg, sol inf 2 ml @ 25 mg/ml Benzothiazapines - Diltiazem - Tabl, prolong rel |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers - Selective - Non-Dihydropyradine - SE/CI? |
-Prolonged use of verapamin = death and atrial fibrilation due to high Ca in myocardial cells |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers - Non-Selective |
Cinnarizine - tabl Flunarizine - caps, tabl Act on brain blood vessels as a vasodilator in atherosclorsis |
|
|
Q. Name a Non-dihydropyradine? |
diltiazem (vaso and cardio) and verapamil (cardio) |
|
|
Q. Which Ca ion channel blocker has longed plasma half life? |
Amlodipine |
|
|
Q. comment on the Chromotropy, Dromotropy, and inotropy of nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem? |
nifedpine + 0 0 Verapamil - - - Diltiazem 0 - - |
|
|
Q. Coronary Vessels are dilated by? Dihydropyradines or non-dihydropyradines? |
Dihydropyradines |
|
|
Q. clinical use of amlodipine and verpamil? |
amplodipine - angina, hypertention verapamil - angina, hypertension, supraventricular tachycardia |
|
|
Q. ADR of nifedipine and Verpamil? |
Nifedipine - tachycardia, flushing, headache and ankle edema, constipation Verpamil - bradycardia, constipation |
|
|
Drugs Reducing adrenergic activity - B Blockers |
Non- selective - Propanolol - tabl B1 - metaprolol - tabl 25/50/100mg pro release and sol inj vasodilating - carvedilol - tabl 3.125/6.25/ 12.5/25 mg tabl |
|
|
Drugs Reducing adrenergic activity - A1 selective blockers |
prazosin - tabl 2 mg doxazosin - tabl |
|
|
Drugs Reducing adrenergic activity - centrally acting sympatholytics |
a2 agonist - clonidine tabl 150 mcg - mthyldopa - tabl agonist of I1- imadozoline recep - moxonidine - film tabl - rilmenidine - tabl |
|
|
Drugs Reducing adrenergic activity - Pre-synaptic sympatholytic drugs |
Reserpine |
|
|
Direct vasodilator in hypertension |
Nitroprusside - sol inf NO acting |
|
|
Q. Drugs used in acute hypertension? |
Furosimide, nitroprusside, clonide |
|
|
Anti-hypertensive Drug - Vasoconstrictor |
Midodrine - tabl |
|
|
Anti-hypertensive Drug - cardioinotropic |
dopamine - sol inf dobutamine - sol inf |
|
|
Anti-hypertensive Drug - hormonal |
Fludrocortisone - tabl |
|
|
Q. agonist of i1-imodozoline? |
moxonidine |
|
|
Q. Antihypertensive only IV with low plasma half life? |
Nitroprusside |
|
|
Q. What is Prazosin? |
a1 antagonist |
|
|
Q. Antihypertensive monotherapy? |
ABCD |
|
|
Q. Antihypertensive drug for DM? |
DRI, mannitol? |
|
|
Q. Antihypertensive drug for elderly patient with hypervolemia? |
Hydrochlorothiazide |
|
|
Q. Antihypertensive drug for pts with isolated systolic hypertension? |
Verapamil |
|
|
Q. Antihypertensive drug for asthma? |
Hydrochlorothiazide |
|
|
Q. Which class has the rebound hypertension linked to it? |
Beta Blockers |
|
|
Q. ADR of Clonidine |
Sedation and Dry mouth |
|
|
Q. ADR of Clonidine, Hydrocholorthiazide, Atenolol and Prozasin. |
Clonadine, A2 agonist dry mouth Hydroclorothiazide Thiazide diuretic hyperuricemia atenolol b blocker, av block prozasin, a1 blocker orthostatic hypotenision |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Beta Blockers -How? |
-dont give in asthmatics -rebound hypertension -only in stable angina -Used post MI -decrease heart ''power'' so less work so better for it more 02 gets to it |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Beta Blockers - Drugs |
Non- selective- Propanolol - tablB1- metaprolol - tabl 25/50/100mg pro release and sol injvasodilating- carvedilol - tabl 3.125/6.25/ 12.5/25 mg tabl
|
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Beta Blockers - ADR |
-av block bradycardia hypotension dizzyness |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Ca ion channel blockers - How?
|
For varient Vasospastic angina redce hr and inotropy |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Ca ion channel blockers Drugs?
|
First gen - Nifedapine - tabl coated- Nitrendipine - tabl- Nimodipine - Film- coated tabl, sol inf Second gen - Felodipine - film cted, prolonged release- Nifedapine - prolonged rel Third gen - Amlodipine - tabl 5 mg and 10 mg- Lercanidipine - film coated- Lacidipine - film Phenylalkylamines - Verapamil - tabl 40/80 mg, prolonged release 120/240mg, sol inf 2 ml @ 25 mg/ml Benzothiazapines - Diltiazem - Tabl, prolong rel |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Ca ion channel blockers - ADR?
|
-Dihydropyradine - reflex tachy but can use with BB - non - check other card |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Organic Nitrates - How? |
Release NO causing direct vasodilation |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Organic Nitrates - Drugs
|
Glyceryl trinitrate fast onset short duration -Nitroglycerin - subling tabl 500 mcg - nitrolingual - spray - peringanit - sol inf Use transdermal therapeutic system to extend effect - no first pass metabolism - reflex tachycardia - high tolerence need to recover sulf hydryl groups -any angina |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Organic Nitrates - Drugs
|
Organic Nitrates with long duration Isosorbide Dinitrate - tabl 5/10 mg pro rel 20 mg or oromucal spray. isosorbide mononitrate - tabl, pro release prolonged release tabs caps Pentaerithrityl tetranitrate - tabl |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Organic Nitrates - Drugs |
Sydnonimines - molsidomine - tabl prodrug - NO - vasodilate - reflex tachycardia - sharp headache - hypotension - edema - flush - methamoglobinemia |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Inhibitors of If current (Direct Bradycardia agents) |
Ivabradine - tabl block If current so -ve dromotropy Causes Phosphene Contraindicated in bradycardia, cardio shoc, acute MI, Renal failure, Pregnancy used in stable angina and contra in Unstable |
|
|
Anti-Anginal Drugs - Metabolic modulators
|
Trimetazidine - prolonged release tabl, film coat Ranolazine - Pro relaease tabl Increase glucose use by inhibit FA utilization used for stable angina on physical exertion |
|
|
Q. How do organic nitrates work? |
increase in NO - guanylyl cyclase activated - gtp to cGMP - PKG activated leading to 1. MLC unphosphorylated to no contraction 2. more K secretion so more hyperpolarization 3. ca pumped out and kept in sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Q. Which Drug reduces the predominantly the preload? 1. Trimetazidine 2. isosorbide dinitrate 3. Propanolol 4. Verapamil |
3 |
|
|
Q. Anti-Anginal activity of trimetazide?
|
Modulation of mechanism of the heart
|
|
|
Q. Anti-Anginal activity of Ivabradine?
|
Reduces HR |
|
|
Q. Anti-Anginal activity of Metapolol?
|
Reduces HR and contractility
|
|
|
Q. Anti-Anginal activity of Amlodipine?
|
Dilation of arterial blood vessels (reducing afterload)
|
|
|
Q. Anti-Anginal activity of Verapamil?
|
Reduction in hr and contractility
|
|
|
Q. Anti-Anginal activity of Glyceryl trinitrate?
|
Dilation of venous and arterial vessels leading to a reduction in preload and afterload.
|
|
|
Q. Which Drugs dilate coronary blood vessels? |
Glyceryl ditrate and fenlodipine
|
|
|
Q. Drug of choice in Angina from acute MI? |
Nitroglyerine
|
|
|
Q. Which drug is used for varient angina?
|
Calcium blockers
|
|
|
Q. ADR of nitrates.
|
Reflex tachycardia, hypotension, throbbing heaadache and increase in intracranial pressure
|
|
|
Q. Which of these Drugs produce Tachycardia? 1. Isosorbide dinitrate 2. Verapamil 3. pronolol 4. diltiazem |
1, 4
|
|
|
Q. which Drug is given to prevent tachycardia?
|
B blockers.
|
|
|
Q. Which drug group has a high tolerance rate?
|
Oraganic nitrates
|
|
|
Q. How to prevent tolerence to Organic nitrates? |
Have a 12 hour recovery period to suposidly inease sulfhydryl groups again
|
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Sodium Channel Blockers - How they work? |
They block VGIC so action potentions are prolongate action potentials. This increases refractory period.
|
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Sodium Channel Blockers - Drugs
|
Class 1a - atrial fibrillation, flutter; supraventricular & ventricular tachyarrhythmias Quinidine - tabl - Class 1b - ventricular tachyarrhythmias Lidocaine - sol inj 5 mg/ml - 10 ml 20ml phenytoin - tabl sol inj - Class 1c - supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (SVT) and ventricular tachyarrhythmias dont use after MI Propafenone - film coated tabl, sol inj |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Sodium Channel Blockers - SI/CI
|
-tachycardia, dry mouth, urinary retention, blurred vision and constipation. Diarrhea, nausea, headache and dizziness are also common side effects of many Class I drugs. Quinidine enhances digitalis toxicity, especially if hypokalemia is present - 1c proarrhytmic affects |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Class 2 B blockers - how?
|
- -ve chrontropy, inotropy, bathmotropy, dromotropy |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Class 2 B blockers - Drugs?
|
Non-selective - propanolol - tabl ect b1 selective - metaprolol - tabl 25/50/100 mg, prolonged release table, sol inj |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Class 2 B blockers - SE/CI?
|
av block
bradycardia hypotension dizzyness edema rebound |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Class 3 drugs prolonging action potential how and drugs?
|
Prolong so decrease HR by k blocking Amioderone - ventricular tachycardia, includuing ventricular fibrillation; atrial fibrillation and flutter so used in both atria andnd vent and very long half life - tabl 200mg sol in 150mg/ml 3 ml sotalol- ventricular tachycardia; atrial flutter and fibrillation - tabl |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - Class 4 non-dihydropyradines - how and drugs?
|
Ca ion channel blockers Verapamil and Diltiazem |
|
|
Antidysrrhythmic drugs - others |
Digoxin increasing inotropy used for atrial fib and stimulates vagal activity - tabl 0.25 mg sol inj Atropine for bradycardia - sol inj adenosine - for supraventricular problems |
|
|
Q. Name a drug from the 1c category?
|
Propafenone
|
|
|
Q. Why is lidocaine give IV?
|
To avoid first pass metabolism
|
|
|
Q. nti dysrhytmic drug with the longest half life?
|
amioderone 1-100 days so we can give 2 times a week or every other day
|
|
|
Q. Antiarrythmic drug only used in Supraventricular arrhytmias? verapamil, propaffenone or lidcaine |
Veramil propafenone use in both lido used in vent |
|
|
Q. Drug used in emotionally provoked arrhythmias?
|
propanolol
|
|
|
Q. Drug for vent arrythmias and digoxin poisoning?
|
Lidocaine
|
|
|
Q. drug used in atrial fib? 1. Atropine 2. Lidocaine 3.Digoxin |
3 atropine for brady cardia lidocain for vent |
|
|
Q. Give one ADR of Lidocaine, quinidine and amioderone? |
lido - paresthsia Quinidine - prolonged QT Amioderone - thyroid dysfunction |
|
|
Q. name a anti arrhytmic drug with a proarrhythmic affect?
|
Quinidine
|
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Statins - How they work? |
Inhibit HMG CoA reductase leading to less cholesterol in liver so more ldl receptor expressed so lowering of plasma ldl and can cause increase in Hdl |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Statins - Drugs
|
Simvastatin - film coated tabl 10 mg, 20 mg 40 Atorvastatin - flm Lovastatin - tabl Fluvastatin - caps pro release Pravastatin - tabl Rosuvastatin bold metabolised my cyp p450 3a4 |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Statins - SE/CI?
|
SE - Myopathy CI - Pregnancy - Liver Disease |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Resins - How they work?
|
Bind to bile acids so can't be reabsored so less C in liver so more ldl recep expression lowing ldl in plasma |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Resins - Drugs |
Cholestyramine |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Resins - SE/CI? |
SE - GIT problems like bloating, constipation, diarrhea, cramps |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Inhibitors of intestinal Sterol Absorbtion - how they work? |
Stops C absorbion thus lowers plasma Ldl good with statins |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Inhibitors of intestinal Sterol Absorbtion - Drugs? |
Ezetimibe - tabl |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Inhibitors of intestinal Sterol Absorbtion - SE |
no huge SE |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Fibrates - How they work? |
Work by decreasing ldl increasing HDl but big decrease in triglycerides. Act as lignand for PPAR-a (peroxismal proliferator-activated factor alpha) and stimulate LPL |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Fibrates - Drugs? |
Fenofibrate - film tabl, caps |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Fibrates - SE/CI? |
Myositis |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Nicotinic acid - How?
|
lowers VLDL release, more HDL |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - nicotinic acid - Drugs |
Nicotinic Acid - pro release |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - nicotinic acid - SE/CI |
Prostaglanding mediated Flushing, dizziness, palpitations almost never used |
|
|
Lipid Lowering Drugs - Omega 3's
|
Inhibit cox 1 - so lower PGs And TXs so blood thining activity |
|
|
Q. Inhibitor of HMG CoA Reductase? 1. Rovustatin 2. Fenofibrate 3. Ezetimibe |
1 |
|
|
Q. Name C3A4 statins? |
Lovastatin Simvastatin Atorvastatin |
|
|
Q. Mech of statin? |
Inhibit HMG CoA reductase leading to less cholesterol in liver so more ldl receptor expressed so lowering of plasma ldl and can cause increase in Hdl |
|
|
Q. Mech of Fenofibrate? |
Work by decreasing ldl increasing HDl but big decrease in triglycerides. Act as lignand for PPAR-a (peroxismal proliferator-activated factor alpha) and stimulate LPL |
|
|
Q. Mech of Cholestyrlamine? |
Bind to bile acids so can't be reabsored so less C in liver so more ldl recep expression lowing ldl in plasma
|
|
|
Q. Mech of Nicotinic Acid? |
lowers VLDL release, more HDL |
|
|
Q. A drug decreasing LDL? |
Simvastatin |
|
|
Q. A drug lowering VLDL? |
Nicotinic Acid |
|
|
Q. A drug increasing HDL |
Nicotinic Acid |
|
|
Q. Non lipid related effects of statins? |
Increase endothelial func Decrease vascular inflamation Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaque |
|
|
Q. Primary and Secondary Prevention of Acute cardio event? |
1. statin 2. Fibrates/ omega 3 |
|
|
Q. Drug causing Myalgia and rhabdomyolysis? |
Statins |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - Iron - What they do? |
They replace iron in microlytic anemia |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - Iron - Drugs |
Contain ferrous iron (fe2+) - Ferrous sulphate - pro release containing Ferric Iron (fe3+) - ferric oxide polymaltose complex - syrup oral drops Parenteral iron prep - Ferric oxide dextran complex - sol inf |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - Iron - how to get rid? |
Iron chelator - Deferoxamine - powder sol inj 500 mg - Deferasirox - disp tablet - hemosiderosis |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - Iron - SE/CI? |
GIT problems - constipation, diarrhea, |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - B12 and folic acid - how? |
prevent and treat megalobastic anemias |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - B12 and folic acid - Drugs? |
Cyancobalamin (vit b12) sol inj - to prevent cns problems Folic acid - sol inj used in pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects |
|
|
Drugs used in Anemias - Hemopoietic Growth factors |
-Erythropoitin - sol inj given inj so doesnt rely on intrinsic factor impaired in pernicious anemia. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor - Filgrastin - sol inj - Pegrastin - sol inj thrombopoietin -Romiplostim - Sol inj - activates platelets in thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Vit K antagonist - What they do? |
Antagonists vit k which helps blood to clot thus less blood venous thrombosis. used in atrial fibrilation |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Vit K antagonist - Drugs? |
Warfarin - Tabl 3 and 5 mg Acenocoumarol - tabl Antagonist - Phytomemadione - vit k - sol inj |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Vit K antagonist - CI/SE? |
Dont give in pregnancy or when someone is bleeding |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Heparin - how? |
Binds to Antithrombin III to form more complexes with Thrombin to inactivate it inhibits factor Xa and II but LMW only inhibits Xa but longer half life and long duration of action |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Heparin - drugs? |
Heparin - sol inj LMW - Nadroparin and Enoxaparin - inj Synthetic Pentasaccharides -Fondaparinux - sol inj dont use in pregnancy smallest heparin angtagonist - Protamine sulphate sol inj 10 10 |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Direct thrombin inhibitors |
Dabigatran - caps short term prophylaxis of vernous thrombosis |
|
|
Anticoaguant - Xa inhibitors |
RivaroXaban - tabl |
|
|
Fibrinolytic - How? |
Therpy can be post MI with venous or arterial Thrombus not used in prophylaxis |
|
|
Fibrinolytic - Drugs? |
Streptokinase - powder for sol inj Alteplase - powder and solvent for sol inj Reteplase - powder for sol inj |
|
|
Anti-Platelet Drugs - Inhibitors of TxA2 |
Acetyl salicylic acid - tabl 100 mg irreversible, cox 1 inhibitor CI in peptic ulcer disease |
|
|
Anti-Platelet Drugs - Adenoside p2y12 antagonist |
Clopidogrel - film coated tabl - pro Prasugrel - tab - pro Ticagrelor - tabl - no pro Pro inhibited by omaprazol |
|
|
Anti-Platelet Drugs - Phosphodiestase inhibitors |
Stop cAMP activation so less Platelet aggregation |
|
|
Anti-Platelet Drugs - Glycoprotien IIB and IIIA receptor antagonist |
eptifibatide - sol inj abciximab - sol inj |
|
|
Anti-Platelet Drugs - synthetic PgI2 |
Epoprostenol - sol inj |
|
|
Bleeding disorders - vit K agonist |
Phytomenadione - oral drops or sol inj (basically vit K) |
|
|
Bleeding Disorders - Antifibrinolytic drugs |
Para aminomethylbenzoic acid Aminocaproic acid |
|
|
Bleeding Disorders - Coag factors VIIa VIII IX
|
Same |
|
|
Bleeding Disorders - hemostatics |
Systemic - Etamsylate tabl sol inj - Terlipressin - sol inj Local - Gelaspon - collAGEN AND THROMBIN CONTAINING |

