![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Seed plants |
Seed plants share two important characteristics. They have vascular tissue and they use pollen and seeds to reproduce. |
|
|
Vascular Tissue |
Most seed plants live on land. Challenges including standing upright and supplying all their cells with food and water. Like ferns seed plants meet those two challenges with vascular tissue. Food water and nutrients are transported throughout vascular tissue. |
|
|
Pollen and seeds |
Unlike seedless plants seed plants can live in a wide variety of environments.
Seedless plants need water in their surroundings for fertilization to occur. Seed plants do not water for sperm to swim to the eggs.
Pollen delivers sperm cells that will later become sperm cells. Seeds protect the young plant from dying out. |
|
|
Seeds become new plants |
Inside a seed is a partially developed plant. If a seed lands in an area where conditions are favorable, the plant sprouts out of the seed and begins to grow.
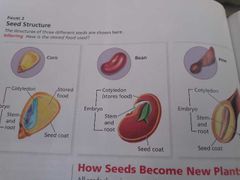
Seed structure:
A seed has 3 main parts an embryo stored food and a seed coat.
The embryo has the beginning of roots stems and leaves.
Stop growing when it is quite small. Some familiar skins on lima beans and peanuts. Seeds are surrounded by a structure called a fruit.
|
|
|
Seed Dispersal |

Some animals eat fruits such as cherries or grapes. Animal digestive system and pass through and deposited into new areas.
The second means dispersal is water. Water can disperse seeds that fall into oceans and rivers. A third dispersal involves wind. Lightweight seeds that often have structures to catch the wind such as those of the dandelions and maple trees. Finally some eject there seeds by ejecting like popcorn. |
|
|
Germination |
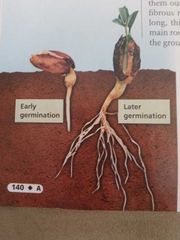
After a seed is dispersed it begins germination and germination begins when the seed absorbs water from the enviroment. Then the embryo uses it to store food so it can grow.
Roots: Roots anchor a plant in the ground absorb water and minerals from the soil and sometimes store food
Types of Roots: Fibrous root system similar sized roots and form a dense tangled mass. Lawn grass corn and onions have fibrous root systems.
Taproot system has one long thick main root many smaller roots branch off the main root. A plant with a taproot system is hard to pull out of the ground carrots dandelions and cacti have taproots. |
|
|
The structure of a Root |
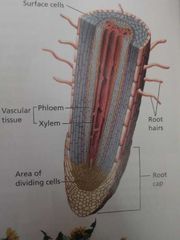
Root hairs grow out of roots surface These tiny hairs can enter the spaces between soil particles where they absorb water and minerals
Locate the vascular tissue in the center of the root. The water and nutrients that are absorbed quickly move into the xylem. From there these substances are transported upward to the Plants stems and leaves. Phloem transports food manufactured in the leaves to the root. The root tissues may then use the food for growth or store it for future use by the plant. |
|
|
Roots |

Yes |
|
|
Stems |

The stem carries substances between the plants roots and leaves. The stem also provides support for the plant and holds up the leaves so they are exposed to the sun. In addition some stems such as asparagus store food. The structure of a stem Stems can be either Herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous stems contain no wood and are often soft. Coneflowers and pepper plants have herb stems. Woody stems are hard and rigid difference. Maple trees and roses have woody stems. Both phloem and xylem tissue as well as many other supporting cells. The outer layer is bark Bark includes an outer protective layer and an inner layer of living phloem which transports food into the stem. Next is a layer of cells called the cambium. It is xylem that makes up most of what you call " wood". Sapwood is active xylem that transports water and minerals through the stem. The older darker heartwood is inactive but provides support. |
|
|
Annual Rings |

Tree stum circled looks like a target are called annual rings because they represent a trees yearly growth. Annual rings are made up of xylem. Form in the spring large grow rapidly thin walls xylem cells. They produce wide light brown ring. Xylem cells form in summer and grow slowly small have thick walls. They produce a thin dark ring. One pair light and dark rings represent one year growth. You can estimate a trees age by counting it's annual rings. |
|

Leaves |
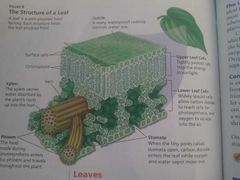
Leaves pine trees Birch trees Leaves capture the sun's energy and carry out the food-making process of photosynthesis. The structure of a leaf: between the layers of leaves cells veins that contain Xylem and phloem stomata singular stoma Greek meaning "mouth" and stomata look like tiny mouths. When the stomata is open carbon dioxide enters the leaf and oxygen and water vapor exit. The leaf of photosynthesis: The structure of the leaf |

