![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is matter? |
Anything that has mass and occupies space. |
|
|
What are the common hazard warnings? |
Flammable, toxic, explosive, irritant, corrosive, biological, and electrical. |
|

|
Electric |
|

|
Toxic |
|

|
Flammable |
|

|
Explosive |
|

|
Irritant |
|

|
Corrosive |
|

|
Biological |
|

|
Means Caution |
|

|
Means Warning |
|

|
Means Danger |
|
|
What does WHIMIS stand for? |
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System |
|

|
Compressed gas, WHIMIS. |
|

|
Dangerously reactive material, WHIMIS. |
|

|
Oxidizing Material, WHIMIS. |
|

|
Poisonous and infectious causing immediate and serious toxic affects, WHIMIS. |
|

|
Poisonous and infectious causing other toxic affects, WHIMIS. |
|
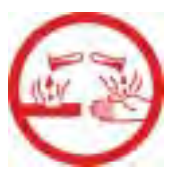
|
Corrosive material, WHIMIS. |
|

|
Flammable and combustable material, WHIMIS. |
|

|
Biohazardous infectious material, WHIMIS. |
|
|
What are the states of matter? |
Solid, liquid, and gas. |
|
|
A change from solid to liquid is.. |
MELTING. |
|
|
A change from liquid to gas is.. |
EVAPORATION OR VAPORIZATION. |
|
|
A change from a gas to a liquid is.. |
CONDENSATION. |
|
|
A change from a liquid to a solid is.. |
FREEZING. |
|
|
A change from a solid to a gas is.. |
SUBLIMATION. |
|
|
A change from a gas to a solid is.. |
DEPOSITION. |
|
|
What are properties? |
Characteristics that can be used to describe a substance. |
|
|
All mater has _ types of properties, and name them. |
2, physical and chemical. |
|
|
Examples of physical properties of matter? |
Hardness, lustre, density, solubility, ductility, CONDUCTIVITY, etc.. |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes from a solid to a liquid. |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which its liquid phase changes to the gasphase. |
|
|
HARDNESS |
Hardness is a substance’s ability to resist being scratched. Hardness is usually measured on theMohs’ hardness scale from 1 to 10. The mineral talc is the softest substance on the scale (1).Diamond is the hardest (10). |
|
|
Malleability |
A substance that can be pounded or rolled into sheets is said to be malleable. |
|
|
Ductility |
Any solid that can be stretched into a long wire is said to be ductile. EX - COPPER |
|
|
Crystal shape |
The shape of a substance’s crystals can help identify it. Silicon crystals, for example, are diamondshaped. |
|
|
Solubility |
The ability of a substance to be dissolved in another. |
|
|
Density |
The amount of mass in a given volume of a substance. |
|
|
Conductivity |
The ability of a substance to conduct electricity or heat. A substance that conductselectricity or heat is called a conductor. A substance with little or no conductivity is an insulator. |
|
|
FOR FUN, what is Moh's hardness scale? |
Talc, Gypsum, Calcite, Fluorite, Apatite, Feldspar, Quartz, Topaz, Corundum, Diamond |
|
|
What does a chemical property describe? |
It describes how a substance interacts with other substances, such as acids. |
|
|
A chemical change always results in... |
The formation of a different substance or substances. |
|
|
What is a colloid? |
Also a cloudy mixture, but the particles of the suspended substance are so small they cannot be easily separated out from the other substance. Examples - milk and ketchup. |
|
|
What's a pure substance? |
A pure substance is made of only one kind of matter, and had a unique set of properties that sets it apart from any other kind of latter. |
|
|
A pure substance may either be an ___ or a ___. |
ELEMENT OR COMPOUND |
|
|
What is an element? |
A material that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance. Basically the building blocks for all compounds. |
|
|
How is a compound formed? |
When two or more elements combine chemically, in fixed and specific proportions. |
|
|
What is a mixture? |
A combination of pure substances. However, unlike compounds, they do not combine chemically. |
|
|
Explain a mechanical mixture |
The different substances that make up the mix are visible. Examples - soil, mixed vegetables. All HETEROGENEOUS. |
|
|
Explain a solution |
The different substances are not separately visible, one substance is dissolved into another, creating what looks like one HOMOGENEOUS substance. Examples - sugar in hot coffee, carbon dioxide gas in water to make carbonated pop. |
|
|
Chemists call a substance dissolved in water an.. |
Aqueous solution !¡! |
|
|
What is a suspension? |
A cloudy mixture in which tiny particles of one substance are held within another m. Example - tomato juice |
|
|
A chemical change always results in... |
The formation of a different substance or substances. |
|
|
What is a colloid? |
Also a cloudy mixture, but the particles of the suspended substance are so small they cannot be easily separated out from the other substance. Examples - milk and ketchup. |
|
|
What is a physical change? |
When a material changes from from one state to another. It can also change back to its original state. |
|
|
What's a chemical change? |
Occurs when two or more materials reach and create new materialsz |
|
|
What's a pure substance? |
A pure substance is made of only one kind of matter, and had a unique set of properties that sets it apart from any other kind of latter. |
|
|
A pure substance may either be an ___ or a ___. |
ELEMENT OR COMPOUND |
|
|
What is an element? |
A material that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance. Basically the building blocks for all compounds. |
|
|
How is a compound formed? |
When two or more elements combine chemically, in fixed and specific proportions. |
|
|
What is a mixture? |
A combination of pure substances. However, unlike compounds, they do not combine chemically. |
|
|
Explain a mechanical mixture |
The different substances that make up the mix are visible. Examples - soil, mixed vegetables. All HETEROGENEOUS. |
|
|
Explain a solution |
The different substances are not separately visible, one substance is dissolved into another, creating what looks like one HOMOGENEOUS substance. Examples - sugar in hot coffee, carbon dioxide gas in water to make carbonated pop. |
|
|
Chemists call a substance dissolved in water an.. |
Aqueous solution !¡! |
|
|
What is a suspension? |
A cloudy mixture in which tiny particles of one substance are held within another m. Example - tomato juice |
|
|
Examples of chemical changes |
Changes in colour, odour, state, or thermal energy during, or as a result of,the reaction between the original substances. |
|
|
EXAMPLES OF CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
• reaction with acids • ability to burn • reaction with water • behaviour in air • reaction to heat |

