![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
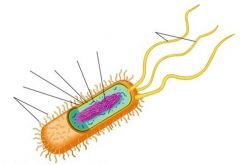
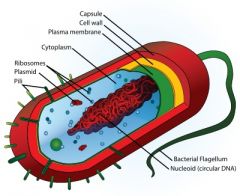
Label the parts of a prokaryotic cell
|
|
|
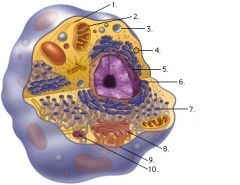
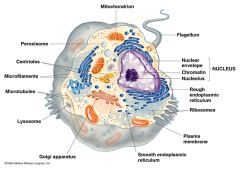
Label the components of the eukaryotic cell
|
|
|
|
The site for protein synthesis is
|
ribosomes
|
|
|
The roadway of the cell that allows for the transport of materials through and out of the cell is
|
endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
Name the two types of endoplasmic reticulum and state their function
|
Smooth: site of lipid synthesis
Rough: aid in synthesis of proteins that are membrane bound or destined for secretion |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells are found in
|
protists, fungi, plants, and animals
|
|
|
The most significant differentiation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that
|
eukaryotes have a NUCLEUS
|
|
|
Where are ribosomes made
|
the nucleolus
|
|
|
What is the function of lysosomes and where are they mainly found
|
break down food, viruses, damaged cell components, etc.
found mainly in animal cells |
|
|
large organelles that are the site of cellular respiration, the production of ATP (that supplies energy to the cell) are called
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
Where are plastids found
|
found in photosynthetic organisms such as plants
|
|
|
chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and amyloplasts are all types of
|
plastids
|
|
|
where are vacuoles found and what is their function
|
in plant cells
hold stored food and pigments, provide tugor pressure |
|
|
what type of cell is a cell wall found in
|
only plant cells
|
|
|
The ______, found in both animal and plant cells, provides a framework for the cell and aids in cell movement
|
cytoskeleton
|
|
|
prokaryotes consist only of
|
bacteria and cyanobacteria
|
|
|
prokaryotes or bacteria reproduce through
|
asexual reproduction, producing two identical cells
|
|
|
How do prokaryotic cells grow
|
absorb nutrients from environment through cell wall and membrane. Some perform photosynthesis
|
|
|
what do prokaryotic cells use as energy sources
|
organic or inorganic compounds
|
|
|
How do plants grow
|
obtain nutrients from soil and convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis
|
|
|
How do animals reproduce
|
sexually
|
|
|
How do plants reproduce
|
50% produce seeds
others reproduce by spores, bulbs, buds,etc |
|
|
fungi are
|
eukaryotic, mostly multi-cellular organisms
|
|
|
How do fungi grow
|
heterotrophs- obtain nutrients by digesting and absorbing nutrients from dead organisms
|
|
|
How do fungi reproduce
|
asexually and sexually
|
|
|
protists are
|
eukaryotic, single-celled organisms
|
|
|
how do protists grow and reproduce
|
heterotrophic-obtain nutrients by ingesting small molecules and digesting them in vacuoles
reproduce asexually |
|
|
Viruses are obligate parasites because
|
they rely on the host for their own reproduction
|
|
|
viruses are composed of
|
a protein coat and a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
|
|
|
What are the two types of viral reproductive cycles
|
lytic and lysogenic
|
|
|
Describe the lytic and lysogenic cycles
|
lytic: virus enters host cell, makes copies of its nucleic acids and protein coats and reassembles them into copies of itself. it then breaks out of the host cell and infects other cells
lysogenic: may remain dormant within cell until some factor activates it and stimulates it to break out of the cell (Herpes) |
|
|
what is the purpose of cell division
|
1. provide growth and repair in body cells
2. replenish or create sex cells for reproduction |
|
|
what are two forms of cell division and describe their function
|
mitosis: the dividsion of somatic (body) cells
meiosis: the division of sex cells (eggs and sperm) |
|
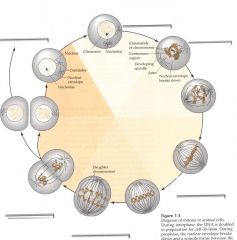
Describe the stages of the mitotic process
|
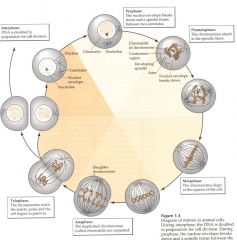
|
|
|
Diagram the structure of the cell membrane and relate the structure to its function
|
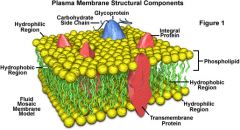
1. Hydrogen bonding holds the membrane together through the phospholipids they are made of.
2. The hydrophilic phosphate group and two hydrophobic lipid tails allow the membrane to orient itself facing the fluid inside and outside the cell 3. Proteins act as channels for transport, receptor sites, stick cells together, attach to the cytoskeleton to give the cell shape 4. contain cholesterol which alters the fluidity of the membrane 5. contain oligosaccarides on the outside of the membrane. these act as markers to help distinguish one cell from another 6. contain receptors made of glycoproteins that can attach to certain molecules like hormones |
|
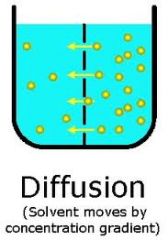
Explain diffusion as a method of transport across a membrane
|
The ability of molecules to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. it normally invloves small uncharged particles like oxygen
|
|
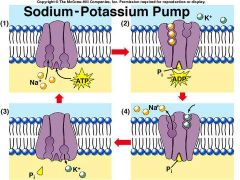
Explain active transport as a method of transport across a membrane
|
It requires energy which comes from ATP or an electrical charge difference. It may move materials either with or against a concentraion gradient
Ex: Sodium-Potassium pump: maintains an electrical difference across the cell, it exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions across the plasma membrane in animal cells |
|
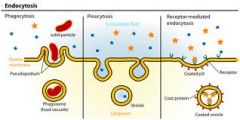
Explain the three types of endocytosis in animal cells as a method of transport across the membrane
|
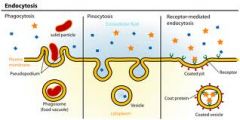
Phagocytosis: when a particle is engulfed by pseudopodia and packaged in a vacuole
Pinocytosis: when a cell takes in extracellular fluid in small vesicles Receptor-mediated endocytosis: when the membrane vesicles bud inward to allow a cell to take in large amounts of certain subtances. the vesicles have proteins with receptors that are specific for the substance |
|
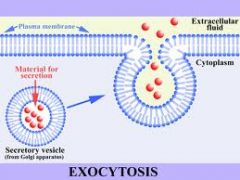
Explain exocytosis as a method of transport across a membrane
|
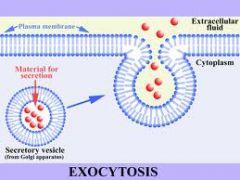
the release of large particles by vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane
|
|
|
What is cellular communication
|
the interaction of cells facilitated by the release, diffusion, and reception of molecules
|
|
|
the site of photosynthesis is
|
chlorpplasts
|
|
|
the site of cellular respiration (the production of ATP that supplies energy to the cell)
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
why is the cristae important to the mitochondria
|
provide a large surface area for cellular respiration to occur. oxidation phosporylation takes place here
|
|
|
why is the matirx important to the mitochondria
|
the site of the Kreb cycle and it contains copies of mitochondrial DNA genome, specialized ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymes
|
|
|
What are enzymes
|
act as biological catalysts to speed up reactions
|
|
|
Are enzymes used up after a reaction
|
they are not used up and are recycleable
|
|
|
what is a substrate
|
the material to be broken down or put back together
enzymes act on substrates |
|
|
The _____ theory states that an enzyme can stretch and bend to fit the substrate
|
induced fit
|
|
|
temperature affects enzyme activity as it can
|
affect the rate of reaction within an enzyme
|
|
|
ph can affect enzyme activity. what is the optimal ph for enzymes
|
between 6 and 8
|
|
|
noncompetitive inhibitors alter the _____ of an enzyme
|
shape
|
|
|
describe an experiment to test the catalytic role of enzymes
|
we can conduct 2 trials of the same reaction, one with the enzyme and one without
compare the rate of the 2 reactions |
|
|
metabolism consists of two contrasting processess including
|
anabolism and catabolism
|
|
|
Catabolism is the
|
breaking down of macromolecules obtained from the environment or cellular reserves to produce energy in form of ATP
|
|
|
the energy produced by catabolism drives
|
the anabolic pathways of the cell
|
|
|
anabolism is the ______ of complex macromolecules from simple precursers
|
formation
|
|
|
the basic reaction of catabolism is _______ the addition of a water molecule across a covelent bond
|
hydrolysis
|
|
|
What is the function of the circulatory system
|
to carry oxygenated blood and nutrients to all cells of the body and return carbon dioxide waste to be expelled from the lungs
|
|
|
What is the function of the digestive system
|
to break down food adn absorb it into the blood stream where it can be delivered to all the cells of the body for use in cellular respiration
|
|
|
What is the function of the respitory system
|
function in the gas exchange of oxygen (needed) and carbon dioxide (waste). delivers oxygen to the bloodstream and picks up carbon dioxide for release out of the body
|
|
|
what is the function of the excretory system
|
to rid the body of nitrogenous wastes in the form of urea.
|
|
|
relate the activity of major body systems to provide cells with oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products
|
The circulatory and respitory systems are linked
Through breathing, the respitory system, binds oxygen to hemoglobin. Oxygen is then carried to muscles via the circulatory system. It also removes carbon dioxide waste. The digestive and excretory system are linked. the digestive system breaks food down into nutrients to be absorbed into the blood stream (circulatory system) where they can be delivered to cells for cellular respiration. by-products from digestion are compacted and excreted from the body by the excretory system. |
|
|
The human nervous system is responsible for
|
relaying messages between the brain and body
|
|
|
what are the two parts of the nervous system
|
central nervous system
peripheral nervous system |
|
|
what is the role of the central nervous system (CNS) and what does it consist of
|
It consists of the brain and spinal cord.
It is responsible for the bodys response to environmental stimuli. It sends out motor commands for movement in repsonse to stimuli and controls and responds to the senses The CNS response is a reflex- unconscious, automatic response. |
|
|
what are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and what does it consist of
|
It consists of nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
the sensory division BRINGS info TO the CNS from sensory receptors the motor division SENDS signals FROM the CNS to effector cells |
|
|
What systems does the motor division of the PNS consist of and what are their functions
|
Somatic nervous system: controls large muscles of the body; controlled CONSCIOUSLY in response to external stimuli
Autonomic nervous system: controls movement of the smooth and cardiac muscles (beating of heart, digestion of food) UNCONSCIOUSLY controlled by hypothalmus of brain to regulate internal environment |
|
|
What is homeostasis
|
the control of differences between the internal and external environment
|
|
|
Explain the homeostatic role of the kidneys
|
The kidneys are the site of osmoregulation and excretion.
They maintain the appropriate level of water and salts in body fluids so that cells may function at the optimum level (osmoregulation) They also eliminate metobolic (nitrogeneous) waste from the body in the form of urea. The process of sweating is also a form of excretion of fluids and wastes (excretion) |
|
|
What is the functional unit of excretion
|
the nephron which make up the kidneys
|
|
|
Explain the homeostatic role of the heart
|
The heart helps in thermoregulation or the maintainance of internal or core body temperature. It does this by producing a drop in metobolic rate and decreasing heart rate to keep and organism warmer
|
|
|
How do nephrons maintain osmoregulation in the kidneys
|
Nephrons in the kidneys filter fluid waste, reabsorb water, an excrete excess water to maintain osmoregulation
|
|
|
What is the function of feedback loops
|
they serve to regulate bodily functions in relation to environmental conditions
|
|
|
Where is the site for thermoregulation
|
the hypothalmus
|
|
|
Explain the homeostatic role of the brain
|
The hypothalmus in the brain is the reception site of many hormones and acts as a processing area. It works with the brain to integrate nervous impulses and command activity
|
|
|
Explain the function of positive feedback loops and give an example
|
positive feedback loops ENHANCE the bodys natural response to environmental stimuli and PROMOTE processes that involve rapid deviation from the initial state
Ovulation is an example. Before ovulation, the ovary secretes estrogen to stimulate the maturation of the ovum. The level of estrogen gives a signal to the hypothalmus and it stimulates production of FSH so the estrogen level will be increasing until it reaches its peak |
|
|
Explain the function of the negative feedback loops and give an example
|
negative feedback loops help MAINTAIN stablility in spite of environmental changes and function in homeostasis
regulation of blood glucose levels are an example as well as the maintainance of body temperature |
|
|
Predict the effects of disturbances on the negative feedback loops.
|
A possible disturbance would be the development of diabetes due to the pancreas no longer being able to produce insulin. Can cause damage to the liver, eyesight, etc. the person has to be givin insulin by shot or mouth to regulate their blood glucose level
|
|
|
What hormones are released during "fight or flight" (the bodys response to stress or danger)
|
ACTH is released by the hypothalmus which signals the adrenal glands to release the hormones cortisol, epinephrine, and norepinephrine.
|
|
|
What is the role of the hormones cortisol, epinephrine, and norepinephrine in readying the body to respond to a threat
|
increase blood pressure and heart rate, speed reaction time, divert blood to muscles, and release glucose for use by the muscles and brain
|
|
|
finally, cortisol completes the "fight or flight" feedback loop by
|
acting on the hypothalmus to stop hormonal production after the threat has passed
|
|
|
Which gland produces hormones that help maintain heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tone, digestion, and reproductive functions
|
The thyroid gland
|
|
|
the pancreas maintains glucose homeostasis by
|
secreting insulin and glucagon
|
|
|
What are the three gonadal steroids and what to they regulate
|
androgen (testosterone), estrogen, and progesterone relgualte the deelopment of the male and female reproductive organs
|
|
|
________ are chemical messengers
|
neurotransmitters
|
|
|
what is the most common neurotransmitter and what is its function
|
acetylcholine controls muscle contraction and heartbeat
|
|
|
what are the effects of epinephrine and noepinehprine on the cardiovascular and respitory systems
|
they can be used to increase the rate and stroke volume of the heart, this increasing the rate of oxygen delivery to the blood cells
|
|
|
what is the function of the muscular system and what are the three types of muscle tissue
|
to facilitate movement
skeletal, cardiac, smooth |
|
|
Which type of muscle is voluntary, attached to bones, and is responsible for movement
|
skeletal muscle
|
|
|
_____ muscle is found in the heart, and a person has no direct control over this muscle
|
cardiac muscle
|
|
|
Which type of muscle is involuntary, found in organs, and enables functions such as digestion and respiration
|
smooth muscle
|
|
|
unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is NOT
|
striated, does not generate as much tension
|
|
|
Bone is a connective tissue. The axial skeleton consists of bondes of the
|
skull and vertabrates
|
|
|
the appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the
|
legs, arms, and tail, and shoulder girdle
|
|
|
what is the protective covering on the outside of the bone
|
periosteum
|
|
|
which part of the bone gives strength
|
compact bone
|
|
|
Why are joints important
|
place where two bones meet. enable movement
|
|
|
What are the three types of joints and what is their function
|
ball and socket: rotational movement (arms and legs in many different ways)
hinge: movement is restricted to a single plane pivot:rotation of forearm and hands at the wrist |
|
|
what is the function of skin
|
serves as a protective barrier against infection and plays a role in thermoregulation
|
|
|
An antigen is
|
any foreign body that elicits an immune response
|
|
|
the two main repsonses made by the body after exposure to an antigen:
|
humoral and cell-mediated
|
|
|
What type of antigens activitate the humoral response to infection
|
free antigens
|
|
|
What is secreted by plasma cells in hte humoral response
|
antibodies and memory cells
|
|
|
How do the antibodies defend against extracellular pathogens
|
by binding to the antigen and making it an easy target for phagocytes to engulf and destroy
|
|
|
antibodies are in a class of proteins called
|
immunoglobulins (lg)
|
|
|
what are the 5 major classes of immunoglobins (lg)
|
lgG
lgA lgM lgE lgD |
|
|
What is each class of immunoglobin responsible for
|
lgG: Immune protection of newborns (only one that can cross placenta); secondary immune responses
lgA: not to destroy antigen but to prevent passage of foreign substances into the circulatory system (protect mucus membranes) lgM: Main antibody of primary immune responses, largest of the five lgE: Autoimmune responses that include allergies, arthritis, multiple sclerosis lgD: unknown function |
|
|
the ______ response responds to an antigen and provides and established protection for future exposure
|
humoral
|
|
|
explain the cell-mediated response to infection
|
infected cells activate T cells (lymphocytes from the thymus) which defend by binding to the infected cell and destroying them and the antigen.
|
|
|
compare cell-mediated and humoral responses to infection
|
cell-mediated immunity is more involved with T cells
humoral response is more involved with b cells (they release plasma cells that secrete the antibodies) Both B and T cells are used in both types of response |
|
|
How does vaccination work
|
Vaccines artifically induce immunity by priming the immune system to response to infection by specific pathogens
|
|
|
vaccines introduce
|
antigens, proteins, or polyssacharides derived from a specific pathogen.
|
|
|
Exposure to pathogen antigens prepares the body to respond to future infection by
|
stimullating the production of specific antibodies and memory immune cells
|
|
|
Name variables affect the success rate of vaccines
|
genetics, type of disease and vaccine, strength of individuals immune response to a vaccine, the timing, method, and delivery of the vaccine, and the health of the patient
|
|
|
scientists have had greater success generating vacines that elicit
|
antibody responses rather than T cell responses
|
|
|
many vaccines need to be delivered
|
two or more times to boost the immunity or a booster needs to be given every few years
|
|
|
immunodeficiency and an example
|
a deficiency in either the humoral or cell-mediated immune defenses
HIV |
|
|
predict the consquences of a compromised immune system
|
the inablility of the immune system to combat normally benign microbes can lead to CHRONIC ILLNESS and eventual DEATH
|

