![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the 6 elements that combine to make up most of the chemical compounds in living things
|
C-Carbon
H-Hydrogen O-Oxygen N-Nitrogen P-Phosphorus S-Sulfur |
|
|
What is the function of carbohydrates
|
macromolecules composed of
used to store energy in the form of sugars or starches AND used to form complex structures such as the cellulose polysaccharide that is used to form the cell walls of plants |
|
|
What three elements are carbohydrates are composed of?
Explain the structure of carbohydrates |
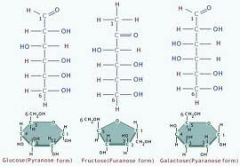
carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen
|
|
|
What is the funcion of lipids
|
used to store energy, help form membranes, chemical signals between cells
|
|
|
lipids do not interact well with other organic compounds because they are
|
hydrophobic
|
|
|
function of lipids
|
used for energy storage and make up the the lipid bi-layer of the plasma membrane of cells.
|
|
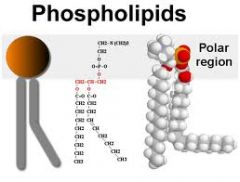
Describe the structure of a phospholipid
|
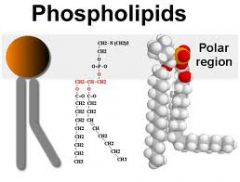
the long hydrocarbon chains at one end of the molecule is a non-polar, hydrophobic, hydrocarbon structure.
This part of the molecule is often referred to as the hydrophobic tail. At the opposite end of the molecule you will see carbons attached to oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus. These components make this end of the phospholipid hydrophilic and therefore water-soluble. This end of the phospholipid is called the hydrophilic head. The dual hydrophobic and hydrophilic nature of this phospholipid is essential to the structure of all cell membranes |
|
|
A lipid monomer is either
|
glycerol and fatty acids or a steroid core
|
|
|
cholesterol, testosterone, estrogene are examples of
|
steroids.
They form a group of four interlocking rings of carbon = steroid core |
|
|
What is the function of proteins
|
form structures, antibodies, hormones, enzymes
|
|
|
enzymes are the
|
chemical workers of the cell
|
|
|
monomers that make up proteins are
|
amino acids
|
|
|
proteins also known as polypeptide chains are macromolecules made up of
|
linked amino acids
|
|
|
proteins have several levels of structure. Name them:
|
primary, secondary, tertiary
|
|
|
What are the four basic parts of amino acids
|
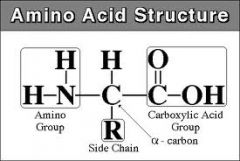
The central part is called the alpha carbon which has a hydrogen attached to it and then all the other side groups. This group over here is called the amino group and it’s made up of a nitrogen with a couple of hydrogens.
Over here we have the carboxyl group which gives the acidic quality to an amino acid because this C double bond OOH that’s a carboxylic acid Down here you see the R group. That instead is just a place holder used to represent the different side groups that give each amino acid its individual qualities |
|
|
long chains of monomers (nucleotides) that function as storage molecules in a cell are called
|
nucleic acids
|
|
|
Nucleotides are composed of
|
sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
|
|
|
examples of nucleic acids include
|
ATP, DNA, RNA
|
|
|
What is the function of nucleic acids
|
store genetic information, transfer energy
|
|
|
What are the monomers of nucleic acids
|
nucleotides
|
|
|
Explain the structure of a nucleotide (monomer of nucleic acid)
|
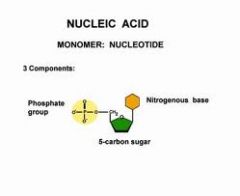
the basic structure of a nucleotide is that you'll have at the heart a five carbon sugar sometimes called a pentose sugar, -ose meaning carbohydrate, pent meaning five.
On one end of our pentose sugar we’ll have phosphate group and this gives a strong negative charge to molecules like DNA and RNA. On the other end you’ll have the one thing that makes one nucleotide different from the other and that’s a base that has the element nitrogen in it |
|
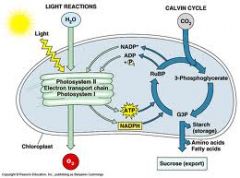
Describe the process of photosynthesis
|
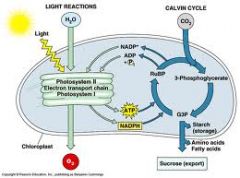
basically what happens is that the light reactions on the thylakoid membrane you've got special molecules that can absorb light. Using that energy they strip off electrons and put them onto a high energy electron carrier called NADPH they also use the energy of those electrons to make a molecule called ADP an energy molecule that's going to be needed later on in the Calvin cycle. Where do they get some of these electrons that they're putting on to NADPH? Ultimately they take these electrons from water molecules, so they rip apart the water taking the electrons that were holding the hydrogen's onto the oxygen and release the oxygen as oxygen gas. Now the ATP and NADPH are sent off to the Calvin cycle that is happening in the stroma. In the stroma you've got all these enzymes floating around, they grab carbon dioxide then using the energy of ATP and the high energy electrons of NADPH and hydrogens that are being carried on the NADPH. They build glucose or other sugars ultimately you recycle the building materials that you're using and you send the now used up NADPH which become NADP positive and you send the used up ATP it's now adenosine diphosphate and unattached phosphate ion and those go back to be recharged by the light dependent reactions to begin the cycle again.
|
|
|
Photosynthesis is a process found in plant cells which converts ______ energy into _________ energy in the form of sugars that the plant can store and use at any time. Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts, an organelle only found in plant cells, and consists of two parts: the light dependent reaction, which converts light energy into ATP, and the Calvin cycle, which converts ATP into glucose
|
light
chemical |
|
|
What is anerobic respiration
|
breakdown of food without oxygen. It is the process of producing cellular energy without oxygen.
|
|
|
Explain anerobic respiration
|
Anaerobic respiration is a relatively fast reaction and produces 2 ATP, which is far fewer than aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration happens in the cytoplasm where glycolysis releases energy from glucose and fermentation recycles NADH back to NAD+.
|
|
|
What is aerobic respiration
|
the breakdown of food with the use of oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the process of producing cellular energy involving oxygen.
|
|
|
Where does aerobic respiration take place and how
|
Cells break down food in the mitochondria in a long, multistep process that produces roughly 36 ATP. The first step in is glycolysis, the second is the citric acid cycle and the third is the electron transport system
|
|
|
Describe the process of aerobic respiration
|
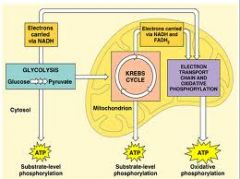
1. Glycolysis: break down of glucose which happens in the cytosol or the cytoplasm of the cell. Once it's done then the molecules enter the mitochondria where it undergoes the series of chemical reactions that are called the Krebs cycle
2. Krebs cycle 3. It ends with a process known as the electron transport system. Let's take a closer look at how this happens, so here we see glucose which is a 6 carbon molecule. And in going through the process known as glycolysis which means literally sugar splitting the glucose is split in half into a pair of 3 carbon molecules called pyruvate. This gives you some high energy electrons they were helping hold this together and those are sent off here to the electron transport system inside the mitochondria. You do get a little bit of ATP here but it's only 2 so not a big deal. The pyruvate eventually makes it's way into the inner portion of the mitochondria called the matrix where it undergoes the series of chemical reactions known as the Krebs cycle. Again we get a little bit of energy molecules in the form of ATP this is where we finally start releasing all of the carbon dioxides as they come flying out those carbons used to be in the glucose. We get a whole bunch more of these NADHs again they're high energy electron carriers and a couple of FADH 2 molecules. These are carrier molecules they literally carry electrons that have a lot of energy off to the molecules that make up something cleverly known as the electron transport system. The electron transport system uses the energy all of those high energy electrons to do something called proton pumping or hydrogen ion transport. And what they do is they shove the hydrogen ions across the membrane then as those hydrogen ions make their way back across the membrane just like water going from one side of a dam through the other can drive a hydro dynamic electric generator. Here we see the high energy electrons have shoved the hydrogen ions across then as they go back they make bucket loads of ATP. Now we need some place to dump those high energy electrons and that's what oxygen is for. We dump the high energy electrons onto the O2 molecules they pick up a couple of hydrogen ions and become water. |
|
|
Describe the process of aerobic respiration
|
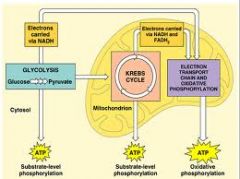
1. Glycolysis: break down of glucose which happens in the cytosol or the cytoplasm of the cell. Once it's done then the molecules enter the mitochondria where it undergoes the series of chemical reactions that are called the Krebs cycle
2. Krebs cycle 3. It ends with a process known as the electron transport system. Let's take a closer look at how this happens, so here we see glucose which is a 6 carbon molecule. And in going through the process known as glycolysis which means literally sugar splitting the glucose is split in half into a pair of 3 carbon molecules called pyruvate. This gives you some high energy electrons they were helping hold this together and those are sent off here to the electron transport system inside the mitochondria. You do get a little bit of ATP here but it's only 2 so not a big deal. The pyruvate eventually makes it's way into the inner portion of the mitochondria called the matrix where it undergoes the series of chemical reactions known as the Krebs cycle. Again we get a little bit of energy molecules in the form of ATP this is where we finally start releasing all of the carbon dioxides as they come flying out those carbons used to be in the glucose. We get a whole bunch more of these NADHs again they're high energy electron carriers and a couple of FADH 2 molecules. These are carrier molecules they literally carry electrons that have a lot of energy off to the molecules that make up something cleverly known as the electron transport system. The electron transport system uses the energy all of those high energy electrons to do something called proton pumping or hydrogen ion transport. And what they do is they shove the hydrogen ions across the membrane then as those hydrogen ions make their way back across the membrane just like water going from one side of a dam through the other can drive a hydro dynamic electric generator. Here we see the high energy electrons have shoved the hydrogen ions across then as they go back they make bucket loads of ATP. Now we need some place to dump those high energy electrons and that's what oxygen is for. We dump the high energy electrons onto the O2 molecules they pick up a couple of hydrogen ions and become water. |
|
|
Compare anerobic and aerobic respiration
|
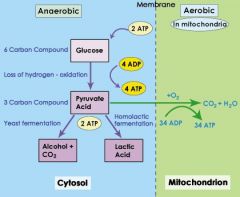
|

