![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an igneous rock |
- The umbrella term for all rocks - split into two categories |
|
|
What are the two classifications of rocks |
Intrusive + extrusive |
|
|
What are the two other rock types |
Sedimentary + metamorphic |
|
|
What is a sedimentary rock |
A rock made of bits and pieces of other rocks |
|
|
How is a sedimentary rock formed |
1 weathering breaks rocks 2 erosion transports fragments 3 over time layers build up and compress the fragments 4 the water is squeezed out and cements the fragments 5 forces expose the rock 6 repeat |
|
|
What are the three classifications of sedimentary rocks |
Detrital + chemical + organic |
|
|
What is a detrital sedimentary rock |
- Made from broken fragments from other rocks - created and moved by weathering + erosion |
|
|
What is a chemical sedimentary rock |
- Made from dissolved minerals from solution - created by weathering + erosion |
|
|
What is an organic sedimentary rock |
- Made from remains of once a living organism - created by weathering + erosion |
|
|
Examples of sedimentary rocks |
Limestone - from shells + coral Sandstone - from sand Coal - from dead organisms |
|
|
What is Metamorphic rock |
Made from sedimentary or igneous rocks during a chemical reaction |
|
|
How are sedimentary rocks formed |
When the rock inside the earth crust get affected by extreme heat or pressure |
|
|
What is foliation |
When the rock is forming under pressure, the crystals often align in bands |
|
|
What must minerals have |
1 must be naturally made 2 have a consistent chemical composition 3 be a solid 4 be inorganic |
|
|
How do you identify minerals |
1 colour 2 luster 3 cleave 4 hardness 5 streak 6 density 7 lattice |
|
|
1. Mineral colour |
- often unreliable * chemical impurities * surface coation *grain size * weathering |
|
|
2. What is Luster |
* how minerals reflect light *metallic or nonmetallic *if nonmetallic must give description * vitreous is often used for glassy luster |
|
|
What is cleave |
* tendency to split along smooth planes of weakness * related to atomic structure * Related to crystal form * every cleave face is a possible crystal face |
|
|
What is hardness in relation to minerals |
* Resistance to scratching * Related to strength of atomic bonds * scratch test |
|
|
What is streak in relation to minerals |
* leaves a mark when pushed against an unglazed tile |
|
|
What is Density in relation to minerals |
* certain amount of volume - if two minerals are the same size but one is heavier then it is more dense |
|
|
How do you calculate a density
|
Density(g/cm3) =mass (g) ÷ volume (cm3) |
|
|
What is crystalline structure |
* each mineral has a characteristic crystal form which doesn't change |
|
|
What are the laws of relative rock dating |
1 law of superposition 2 law of crosscutting 3 law of inclusion |
|
|
What is law of superposition |
- in an undisturbed sequence of rocks, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the youngest are on the top |
|
|
What is the law of cross cutting |
- any feature that cuts across a sequence of rocks is younger than everything it cuts |
|
|
What is the law of inclusions |
- any rock or fragment that's included inside of another rock is older than the rock in which it's included |
|
|
What are fossils |
* an impression, cast of an original material or track of any organism that is preserved in rock after original organic material is transformed or removed |
|
|
What are the 2 forms of fossils |
* body fossils * trace fossils |
|
|
What is a body fossil |
The actual part of an organism, unaltered or altered bones, shells, leaves |
|
|
What is a trace fossils |
Evidence of life that is not a body fossil - tracks, burrows, casts |
|
|
What are the modes of fossil preservation for body fossils |
Unaltered + altered |
|
|
What is an unaltered body fossil |
Original material from the living from the living organisim |
|
|
What are the Forms of unaltered fossilisation |
Mummification - quickly dried Refrigeration - material trapped in ice and tissue is preserved |
|
|
What are the Forms of altered body fossils |
*Permineralization - pores in tissue filled with minerals *Replacement - replacement of tissue with minerals *Carbonization - tissue is decomposed or reduced to a film of carbon |
|
|
What promotes fossilisation |
Rapid burial and lack of oxygen |
|
|
Difference between weathering + erosion |
Weathering is the break down of the rocks and erosion is the deposition of the fragments |
|
|
Crystallization |
The longer it takes for the magma/ lava to cool the larger crystals it has and vice versa for a short cooling period |
|
|
What is the rock cycle |
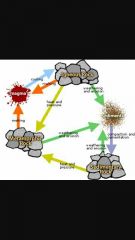
|

