![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Problem |
A question you want to investigate |
|
|
Hypothesis |
A testable explanation for observations (an educated prediction
If IV, then DV |
|
|
Independent Variable (IV) |
The condition in the experiment that the experimenter (you) is changing. |
|
|
Dependent Variable (DV) |
The condition(s) that change(s) because of changing the IV. What you are measuring in the experiment |
|
|
Constants |
Conditions of the experiment that don't change. |
|
|
Control Group |
The condition/group in an experiment that doesn't receive experimental treatment. A source of comparison |
|
|
Reference point |
Object that appears to stay in place relative to the other objects that are moving around it |
|
|
Useful reference points |
Trees and buildings (anything non-moving) |
|
|
Speed |
Distance traveled by an obj divided by the taken to travel that that distance |
|
|
Formula for calculating for average speed |
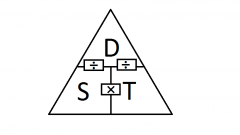
Speed= Distance/Time
|
|
|
Formula for calculating time |
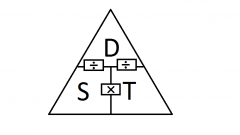
Time= Distance/speed |
|
|
Formula for calculating distance |
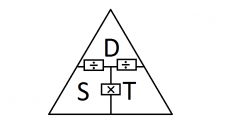
Distance= Speed x Time |
|
|
Velocity |
The speed of an object in a particular direction. (type of speed) Velocity is a vector quantity.
|
|
|
Force |
Push or pull that acts on an object. (Measured in Newtons) |
|
|
Net Force |
The total amount of force acted on an object. (Forces that act in the same direction is added. Forces that act in different directions are subtracted.) |
|
|
Balanced Forces |
When the forces acting on an object produce a net force of 0 N. Object will not move |
|
|
Unbalanced forces |
When objects don't produce a net force of 0 N, which produces a change in motion. |
|
|
Friction |
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact |
|
|
Two factors that determine the amount of friction that occurs between two objects |
1. The force pushing the surfaces together. If more force is applied, more friction is created. (Directly proportional) 2. The roughness of the surfaces. The more rough the surfaces are, the more friction is created. (Directly proportional) |
|
|
Kinetic friction |
Friction that occurs between moving surfaces, -sliding kinetic friction- obj.s slide past each other - rolling kinetic friction-obj.s roll past each other |
|
|
Static friction |
When a force is applied to an obj. but the obj. doesn't move. Can be overcome by applying a large enough force. Static friction will disappear and is replaced w/ kinetic friction once the obj. starts moving. |
|
|
Gravity |
The force of attraction between obj.s, that is exerted on each other because of their mass |
|
|
Two factors that determine the strength of gravitational attraction between two objects |
1. The mass of the obj.s- the more mass 2 obj.s have, the greater the force of gravity between them (directly proportional) 2. The distance between the obj.s- As the distance between the objects increases, the gravity decreases (Inversely proportional relationship) |
|
|
Difference between mass and weight |

|
|
|
Newton's First Law of Motion |
An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force |
|
|
Newton's Second Law of Motion |
The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. (Force=mass x acceleration) |
|
|
Newton's Third Law of Motion |
Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal (in size) and opposite (in direction) force on the first |
|
|
Energy |
Ability to do work or to cause a change |
|
|
Law of Conservation of Energy |
Energy can neither be created or destroyed. |
|
|
Energy Conversion |
Changes from one form of energy to another |
|
|
Difference between speed and velocity |
Velocity is a vector quantity, and is measured in speed and direction. It is a type of speed. **Difference between speed and velocity** |
|
|
On a graph depicting speed, a horizontal line means.... |
A horizontal line means that the object is not moving, on a graph depicting speed |
|
|
When is the potential energy greatest on rollercoasters? |
At the top of the rollercoaster |
|
|
When is the kinetic energy greatest on a rollercoaster? |
When the rollercoaster is moving the fastest |
|
|
Units of the metric system |
Mass Volume Density Solids- g cm3 g/cm3 liquids- g mL g/mL |
|
|
Why do some liquids in a graduated cylinder form different layers? |
The liquids in the cylinder have different densities. |
|
|
Where is the least dense liquid located in a graduated cylinder? |
At the top of the graduated cylinder |
|
|
Where is the most dense liquid located in a graduated cylinder |
At the bottom of the graduated cylinder |

