![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Six examples of physical change |
Melting, dissolving, bending, coding, freezing |
My dad bent cold fruit |
|
|
Compare mass and weight (gravitational force put on an object) |
The more mass an object has results in greater gravitational pull on the object and a greater gravitational pull means a larger weight. |
Mass....gravitational pull...weight |
|
|
What happens to matter during physical change? |
Physical changes don't change the identity of the matter involved |
Nothing |
|
|
Six examples of physical properties (think: 20 Questions game...is it orange? Does it smell, etc) |
Color Oder mass volume magnetism strength flexibility and conduct of electrical current |
Cole ordered massive volumes (of) magnets, straws, fidget spinner's, condoms |
|
|
How is density used to identify substances? (density is a physical property used to describe relationship between mass and volume, or the amount of matter (AKA:mass) in a given space (AKA:volume) D=m/v (units: g/cm cube3 or kg/m cube3, but typically g/cm cube3 is used. |
The cool things about density are: 1. no 2 substances have the same density and 2. pressure and temperature (or location in the universe) don't affect density |
Volume is the amount of space matter takes up |
|
|
What are the units for measuring volume |
For liquids: Liter (L) and milliliter (ml)
For regular solids (think: cube): L x w x h Length times width times height
For your regular solids (think 12 sides shape): Measure the amount of liquid for example in graduated beaker then dropped object in the beaker then record the difference.
Units are typically centimeters cubed3 (cm3) for a solid and milliliters (ml) for a liquid |
|
|
|
Describe the two properties of all matter. |
1. Has mass 2. And takes up space (volume) |
|
|
|
Units for measuring mass (amount of matter in a given object) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What happens during a chemical change? |
During a chemical change something might change into new matter that has different chemical properties. For example wood is flammable but ashes are inflammable. |
|
|
|
What are some examples of chemical changes |

1. Flammability 2. Reactivity 3. Oxidation 4. Toxicity 5. Radioactive 6. Corrosion 7. Heat of combustion 8. Reactivity with acid
|
|
|

Front (Term) See pic |

See pic |
|
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Explain the difference between the states of matter |
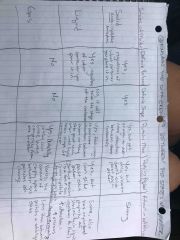
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Describe how energy is involved in changes of state |

|
|

