![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Q
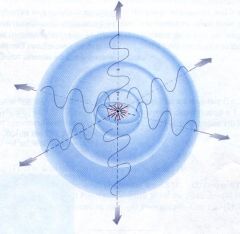
What is intensity |
A
The amount of energy a sound wave carries per second through a unit area. |
|
|
Q
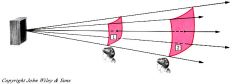
What unit iws used to measure intensity? |
A
watts per square meter (W/m²) |
|
|
Q
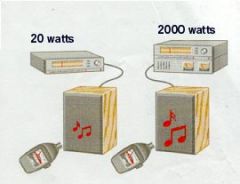
What is loudness? |
A
How strong (intense) a sound seems to the listener. |
|
|
Q
What is another way to say loudness? |
A
sound level |
|
|
Q
How are loudness and intensity related? |
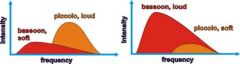
A
The greater the intensity of the sound wave - the louder it sounds. |
|
|
Q
What units are used to measure loudness? |
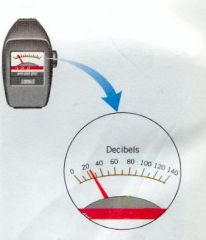
A
decibels (dB) |
|
Q
What happens to your hearing at 200 dB? |

A
immediate and irreversible hearing loss |
|
|
Q
For each increase of 10 dB, how much louder is the sound? |

A
The sound is ten times (10 x) louder. (example: 60 dB is ten times louder than 50 dB) |
|
|
Q
What is frequency? |
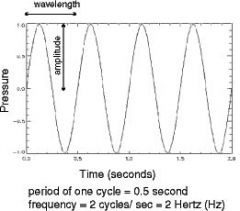
A
The number of vibrations that occur per second? |
|
|
Q
What unit is used to measure frequency? |
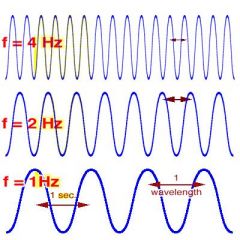
A
hertz (Hz) |
|
|
Q
What does Hz represent? |
A
the number of waves (vibrations) per second (#w/sec) |
|
|
Q
What is pitch? |
A
how low or high a sound seems to a person |
|
|
Q
What is the relationship between pitch and frequency? |
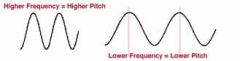
A
The pitch of a sound depends on the frequency of the sound wave. (high frequency - high pitch, low frequency - low pitch) |
|
|
Q
What frequencies can the average person hear? |
A
20 Hz to 20,000 Hz |
|
|
Q
What do you call a sound too high for normal hearing? |

A
ultrasound |
|
|
Q
What do you call a sound too low for humans to hear? |
A
infrasound |
|
|
A
higher than 20,000 Hz |

Q
What are the frequencies for ultrasound? |
|
|
Q
What are the frequencies of infrasounds? |
A
lower than 20 Hz |
|

Q
What is resonance? |
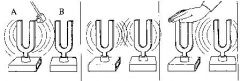
A
the increase in the amplitude of vibration af an object when external sound waves match the object's natural frequency. |
|
|
Q
For resonance to occur, what property of of both the object and the sound wave must be the same? |

A
The sound wave must have the same frequency as the natural frequency of the object. |
|
|
Q
What is the Doppler effect? |
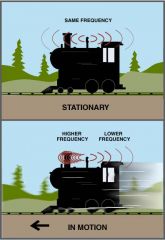
A
The apparent change in frequency when a wave source and listener are MOVING closer together or further apart. |
|
|
Q
What happens to a sound when the source is quickly moving towards the listener? |

A
The pitch appears to increase because of the Doppler effect. |
|
|
Q
What happens to a sound when the source is quickly moving away from the listener? |

A
The pitch appears to decrease because of the Doppler effect. |
|
|
Q
When does a sonic boom occur? |

A
When a plane goes faster than the speed of sound, the sound waves that were piled up in front of it are released as a shock wave and are heared as a loud noise. |

