![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Microscopy + three types of scopsz |
The science of using microscopes to view samples Bright field/ bark field Transmission electron Scanning electron |
|
|
|
Cells: |
Smallest unit that can perform the functions of life. Discovered by Robert Hooke - looked like monk cells |
|
|
|
Cell theory |
All living organisms are made up of one or more cells The cell is the basic organizational unit of life All cells came from preexisting cells |
|
|
|
Parts of a cell |
Nucleus: the organelle that acts like the brains- holds all GENETIC DATA Organelles: specialized structure in cells |
|
|
|
Organelles (12) |

|

|
|
|
DNA: |
Material found in the center nucleus that contains genetic info; controls everything about that person |
|
|
|
Genes: |
Segment of DNA that controls protein production |
|
|
|
Cell cycle: |
Interphase: Performs; grows; DNA replication Cell division: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis |
|
|
|
Prophase: |
Chromatin condense & become visible (chromosomes). Spindle fibers to opp sides. Nuclear membrane disappears. Spindle fibers form at each pole from centrioles. |
|
|
|
Metaphase: |
Spindle fibers attach go chromosomes centromeres. Chromosomes all line up. |
|
|
|
Anaphase: |
Centromeres split (spindles pull chromatid apart). Chromosomes go to opp sides. |
|
|
|
Telophase: |
Sis chromosomes arrive at piles. Centrioles replicate. New nuclear membrane. Chromosomes turn back to chromatin. |
|
|
|
Cytokinesis: |
Cell membrane pinches=two sister cells |
|
|
|
Cell checkpoints: |
Makes sure that the cell is still healthy. Happens after+before division and after DNA rep |
|
|
|
If ... cell checkpoints will kill cells |
Not enough nutrients DNA was not replicated DNA was damaged |
|
|
|
Cancer: |
When cells continue to replicate even if they be damaged |
|
|
|
Cell specialization vs differentiation |
S: cells come from similar cells to perform specific task D: stage of development when specialized cells form |
|
|
|
Tissue: |
Group of similar cells that share same function and structure |
|
|
|
Organ: |
Combo of several types of tissue working together to perform |
|
|
|
Tissues in plants |
Tissue: dermal, ground, vascular (xylem/phloem) |
|
|
|
Tissues in animals |

|

|
|
|
All the human systems |

|
|
|
|
Digestive system: parts, how it works |
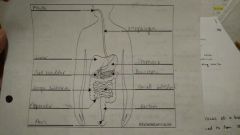
|
|
|
|
Respiratory: parts, how it works |

|
|
|
|
Circulatory: parts, how it works |
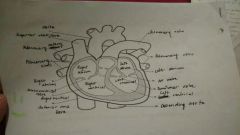
|
|

