![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does sound travel? |
It travels on compression and longitudinal waves. The particles move back and forth in the same direction. E.g. slinky. |
|
|
How does light travel? |
It travels on transverse waves. The medium vibrates up and down. E.g. visible light, gamma and x-rays. |
|
|
What is the medium? |
The material which the waves travel through. |
|
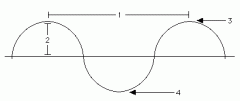
Name the parts of the wave. |
1. Wavelength 2. Amplitude 3. Crest 4. Trough |
|
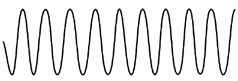
What does this mean? |
It has a short wavelength which means it has a lot waves, high frequency, high sound and high pitch. |
|
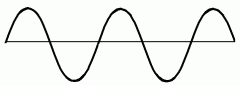
What does this mean? |
It has a long wavelength which means it has a small amount of waves, low frequency, low sound and low pitch. |
|
|
What is hertz? (Hz) |
It is how you measure the number of sound waves per second (frequency) |
|
|
What does the length of the amplitude mean? |
If the amplitude is short it means the sound is quiet, if the amplitude is long it means the sound is loud. |
|
|
What are the 3 main parts of the ear and what are their jobs? |
Outer Ear - where sound waves are collected. Middle Ear - where the sound is amplified. Inner Ear - where sound is changed into an electric signal and sent along the auditory nerve. |
|
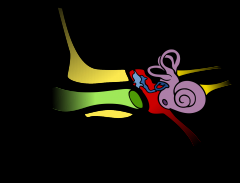
Name the parts of the ear |
Light green - Ear canal Dark green - Ear drum Red - Middle Ear Purple strips - Semicircular canals Purple swirl - Cochlea Yellow - Auditory Nerve |
|
|
What is absorption? |
When waves get absorbed by a substance and lose its energy. When an object absorbs light it gets hotter. Substances that absorb are opaque. E.g. blinds and wood. |
|
|
What is reflection? |
When a wave bounces off a substance. Light may be reflected from particles within a substance, scattering, because light bounces off in so many directions. This happens with dust or smoke. |
|
|
What is refraction? |
A wave can change speed when it passes from one material to another. Glass and water slow down light. |
|
|
What is diffraction? |
When waves spread out from the source or bend around an object. light waves diffract very little. Wide gap = small diffraction. Narrow gap = large diffraction. |
|
|
What is Myopia and Hyperopia? |
Myopia is nearsightedness and Hyperopia is farsightedness. |
|
|
What is conjunctivitis? |
An inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye. |
|
|
What is a cataract? |
A medical condition in which the lens of the eye becomes progressively opaque, resulting in blurred vision. |
|
|
What is a stye? |
A small, painful lump on the inside or outside of the eyelid. |
|
|
How do we see colours? |
Light shines onto on object and the object absorbs some of the light while the rest reflects off the object and into our eyes. White objects reflect all colours of the spectrum, black objects reflect no colours of the spectrum and red reflects red colours of the spectrum. |
|
|
What is colour blindness? |
Colour blindness is genetic. It is when the 3 types of cones in your eyes do not work properly or at all. E.g. If your blue cone doesn't work you can't see colours containing blue. |
|
|
What are the primary light colours? |
Blue. red and green. |
|
|
What does the stomach do? |
It breaks down food by churning it up and digesting protein. |
|
|
What does the pancreas do? |
It regulates blood sugar and produces enzymes. |
|
|
What does the small intestine do? |
Finishes breakdown and starts absorption. |
|
|
What does the large intestine do? |
Absorbs water and releases water. |
|
|
What does the liver do? |
It cleansyour blood, produces digestive liquid called bile, stores energy in the form ofsugar (glycogen). |
|
|
What is a peristalsis? |
It is contractions forcing food through the digestive system. |
|
|
What do the kidneys do? |
They remove waste and chemicals e.g. salts, water and urine from the body. Urine is madethen carried to the bladder by the ureters where it is then stored. |
|
|
What are kidney nephrons? |
They containsmillions of nephrons, each a tiny filtering unit, processing the blood andremoving unwanted substances. |
|
|
What does the respiratory system do? |
It suppliesoxygen to all parts of the body. When you breathe in (inhale) the lungs getbigger. When you breathe out (exhale)the lungs get smaller. We breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. |
|
|
What does the Bronchi do? |
They are smallertubes that bring air to and from the lungs. |
|
|
What does the alveoli do? |
It transfers oxygen into the capillaries and allows theexchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. |
|
|
What do arteries do? |
They carryblood away from the heart. Very thick. |
|
|
What do veins do? |
They carryblood to the heart. Not as thick. |
|
|
What do capillaries do? |
They allowfor exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Very thin. |
|
|
What is plasma? |
Plasma is ayellowish liquid that carries nutrients, hormones and proteins through thebody. |
|
|
What are white blood cells? |
Theyare a part of the immune system and they help fight infections. |
|
|
What are platelets? |
They are cellsthat stop you from bleeding when you get cut. |
|
|
What are red blood cells? |
They are cells that carryoxygen through the body. |
|
|
What is diffusion? |
Diffusion are moleculesmoving from high concentration to low concentration. |
|
|
Where do plants get their energy from? |
The sunlight. |
|
|
How do they make their own food? |
They use carbon dioxide and water. |
|
|
What do chloroplasts do? |
Theycontain chlorophyll and that is what makes the plants green. The chlorophyll trapsthe energy from the sunlight and converts it into food. |
|
|
What do leaves do? |
They absorbs sunlight and help manufacture food. They convert sunlight into energy. Then with the energy in the sunlight they turn water andcarbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen. |
|
|
What do stomata do? |
They are onthe outside of a plant, let water and gases pass in and out of plants. |
|
|
What do Xylem do? |
They are on the insidelayer of trees, carries water and minerals. |
|
|
What do Phloem do? |
They are onthe outside layer of trees, carries food made by leaves. |
|
|
What is the anther? |
This is where malecells are made. |
|
|
What is the filament? |
The stem that holds the anther above the flower. |
|
|
What is the ovary? |
It is atbase of flower with developing eggs inside. |
|
|
What is the style? |
stemthat leads to top of flower. |
|
|
What is the stigma? |
topof flower. |
|
|
What does the root system do? |
It stopsplants from falling, provides stem and leaves with water and dissolved minerals. |
|
|
What is the stem? |
mainbody of the plant, holds leaves and carries water through the plant. |
|
|
What does the flower do? |
Reproduce. |
|
|
What does the fruit/seed do? |
the fruit protects the seeds. The seeds are a part of thereproduction. |

