![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Coriolis Effect
|
The Earth's rotation imparts an acceleration known as the Coriolis effect. This acceleration causes cyclonic systems to turn towards the poles in the absence of strong steering currents.
|
|
|
latent heat
|
latent heat is the amount of energy in the form of heat released or absorbed by a substance during a change of phase
|
|
|
specific heat
|
is the measure of the heat energy required to increase the temperature of a unit quantity of a substance by a certain temperature interval.
|
|
|
troposphere
|
the troposphere is about 15 kilometer. We live in the troposphere. It contains 75% of all ATM gases dust ice and liquid. where smog and clouds form. 70c- -60c
|
|
|
exosphere
|
uppermost part of the ATM. beyond it is space. -30c and above
|
|
|
ozone
|
has O3 three oxygen. filters cancer causing U.V. rays.
|
|
|
stratosphere
|
-5c to -60c has a layer of ozone. weather instruments like weather balloons are released here. 20-50km from the earth
|
|
|
mesosphere
|
most radio waves are found here. -5c - -90c about 50-90km away from the earth
|
|
|
Thermosphere
|
-40c - -90c the thermosphere is the beginning of radio waves. you can find meteor trails and auroras. satellites are found here
90 through 350 Kilometers above the earth. |
|
|
leeward
|
with the wind
the point or quarter toward which the wind blows. |
|
|
windward
|
into the wind
|
|
|
global warming
|
The theory that the earth is beng heated by the greenhouse gases that we produce. The gasses deflect the suns energy inside the atmosphere traping the energy. It can't escape so it heats up the earth.
|
|
|
melanoma
|
skin cancer can be cause by over exposure to U.V. rays
|
|
|
ultraviolet radiation
|
Ultraviolet radiation is a type of radiation emitted from the sun. Skin cancer can be caused by over exposure to U.V. rays
|
|
|
climate
|
is the temperature, atmospheric pressure, wind, rain, and humidity of a certain area.
|
|
|
phase change
|
The change of a matter's state by gaining or losing energy.
|
|
|
cold front
|
A cold front is a cooler and drier mass of air. The front with the greater density wedges under the less dense warmer air, lifting it, which can cause the formation of a narrow line of showers and thunderstorms when enough moisture is present. This upward motion causes lowered pressure along the cold front.
|
|
|
warm front
|
A warm front is the leading edge of an advancing mass of warm air originating from a high pressure system.
|
|
|
arid
|
dry, lack of water, low humidity
|
|
|
melting
|
the phase change of a solid to liquid
|
|
|
precipitation
|
When cloud particles become too heavy to remain suspended in the air, they fall to the earth as precipitation
|
|
|
evaporation
|
the phase change of water going from liquid to a gas
|
|
|
condensation
|
the phase change of water changing from a gas to a liquid
|
|
|
Barometer
|
a tool used to measure ATM presure
|
|
|
saturation
|
"thoroughly full"
|
|
|
photosynthesis
|
the process that plants use to convert h2o and co2 into a sugar that plants use to feed its cells. it supports all living creatures
|
|
|
absolute humidity
|
Absolute humidity is the quantity of water in a particular volume of air. The most common units are grams per cubic meter
|
|
|
sulfur dioxide
|
SO2 is produced by volcanoes and in various industrial processes
Cause of Acid Rain. |
|
|
evapotranspiration
|
is a term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the earth's land surface to atmosphere. The water that evaporates off the vegetative canopy. it is part of the water cycle
|
|
|
Ionosphere
|
A part of the Thermosphere. A layer of electrically charged particles that interfere with certain radio waves.
90-350km away -30 to -90c it is an electrically charged particles called ions and free electrons which interfere with radio waves. |
|
|
tropical
|
defines it as a non-arid climate in which all twelve months have mean temperatures above 64.4 °F (18.0 °C).
|
|
|
isobar
|
lines of equal pressure shown on a map.
|
|
|
isotherm
|
a graph used to show temperature changes. this is used with the isobar to find cold and warm fronts.
|
|
|
tropical climate
|
bound on the north and south 18c isotherm. no true winter
|
|
|
temperate climate
|
bounded on the poleward side by the 10c isotherm and on the equatorward side by the 18c isotherm. has winter and summer
|
|
|
polar climate
|
bounded on the equatorward side by the 10c isotherm. no true summer
|
|
|
precipitation factors
|
1. latitude of 0 degree and 60N have heavy precipitation due to belts of low pressure.
30N and 30S has belts of high pressure, which produce dry climates. 2. Nearness to center of large land mass. Centers are usually more dry. 3. Nearness to large bodies of water. Near ocean have high precipitation, especially areas on leeward side. 4. Location relative to large mountain ranges. Windward sides get higher average Precipitation, leeward get less. 5. Wind direction, which determines the leeward sides of mountain ranges and large bodies of water. |
|
|
temperature factors
|
1. Latitude. As latitude increases, average Temps get lower.
2. Nearness to center of large land masses. These have large ranges between and night, and seasonally. 3. Nearness to large bodies of water. Low ranges between day and night and seasonally. 4. location relative to mountains. Windward sides are cooled, leeward are warmed. 5. Altitude. Higher is cooler. 6. Ocean Currents. Eastern coast is warmed by ocean currents, western coast is cooled. ocean current: eastern coast gets warmer temperature. |
|
|
What is the difference between climate and weather.
|
Weather is the hour-to-hour/day-to-day conditions.
Climate is the average of weather changes over many years. |
|
|
What major worldwide climate types are classified by which atmospheric property?
|
Temperature and Precipitation.
|
|
|
What factors would cause a location to have a colder yearly climate than others?
|
Near the center of land mass, or on west coast, higher altitude, higher latitude, on windward side of large mountain range
|
|
|
What three factors would cause a location to have more precipitation?
|
being on the windward side of mountains, or the leeward side of water, or being in a low pressure belt
|
|
|
Where is the low pressure belts?
|
latitudes 0, 60N, 60S
|
|
|
Where are High pressure belts?
|
latitudes 30N, 30S
|
|
|
How can two areas have same average temperature but different climate ratios?
|
One has more rain than the other.
|
|
|
How can two regions with the same precipitation have different climate ratios?
|
Their average temperatures can be different.
|
|
|
Are low pressure belts more arid or humid than high pressure belts?
|
Low pressure belts are more humid and have more rainfall.
|
|
|
Pollutant
|
harmful material that can harm an ecosystem.
|
|
|
relative humidity
|
Actual Vapor Density divided by the Saturation Vapor Density * 100%
|
|
|
Physical Change
|
physical change is any change not involving a change in the substance's chemical identity. It only changes its look.
|
|
|
Hydrologic Cycle
|
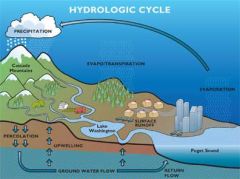
|
|
|
Global Winds
|
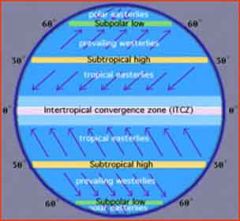
|
|
|
What is a climate ratio.
|
p/e precipitation/ potential evapotranspiration
|
|
|
Smog
|
mixture of compounds including sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen.
|
|
|
Solids in the atmosphere
|
smoke, dust and ice
|
|
|
Liquids in the atmosphere
|
water vapor
|
|
|
Atmosphere
|
A mixture of different substances, gases, solids, liquids.
|
|
|
What is a mixture
|
A mixture is a substance made by combining two or more different materials
|

