![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
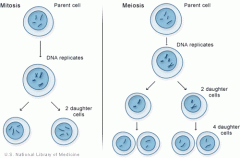
Cell Division- normal body cells have 4 chromosomes. stage 1 copy of each chromosomes is made cells divide in two to form two daughter cells .Each with a nucleus |
|
|
|
Gene-is a small packet of information that controls a characteristic , or part of a characteristic of your body. chromosome - carry genes and are made of DNA. |
cell cycle - process called mitosis where cell divide in a number of stages |
|
|
Differentiation is the process of cells becoming specialized. Most types of animal cells differentiate at an early stage. They become specialized for a particular function and cannot change into different types of cells. In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to replacement and repair. On the other hand, many plant cells keep the ability to differentiate. |
Stem cells can be made to differentiate to form different types of cell, such as nerve cells.Human stem cells can come from:Human embryos (embryonic stem cells)Adult bone marrow (adult stem cells)Stem cells can develop into any kind of human cell. |
|
|
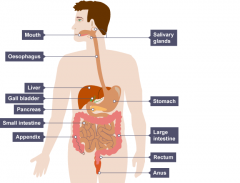
Alimentary canal-The digestive tract which runs from mouth to anus. An amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. |
Mouth-Where food enters the alimentary canal and digestion begins Salivary glands-Produce saliva containing amylase Oesophagus-Muscular tube which moves ingested food to the stomach Stomach-Muscular organ where digestion continues |
|
|
Pancreas-Produces digestive enzymes Liver-Produces bile Gall bladder-Stores bile before releasing it into the duodenum Small intestine - duodenum-Where food is mixed with digestive enzymes and bile |
Small intestine - ileum-Where digested food is absorbed into the blood and lymph Large intestine - colon -Where water is reabsorbed Large intestine - rectum-Where faeces are stored Large intestine - anus-Where faeces leave the alimentary canal |
|
|
ss |
|
|
The stomach has adapted to its purpose by the folded lining letting the stomach expand for more food.Another way is the 3 different tissues used.the glandular tissue create digestive juices that break down food .muscular tissue which covers the whole stomach letting the stomach to contract to churn the food |
ss |

