![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name all of the organelles in a plant cell.
|
Cell wall, cell membrane, chloroplasts, cytoplasm and a nucleus.
|
|
|
Name of the organelles in a animal cell.
|
Cell membrane, mitochondria, ribosomes, cytoplasm and a nucleus
|
|
|
What is yeast?
|
Yeast is a single cell organism.
|
|
|
What do bacteria cells not contain?
|
Bacteria cells have no nucleus.
|
|
|
Name all of the organelles in a bacteria cell.
|
Slime capsule, Cell wall, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Plasmids, Genetic material and Flagella.
|
|
|
What is a Prokaryotic cell?
|
A prokaryote is a single cell organism which lacks a membrane bound nucleus, mitochondria or any other organelles.
|
|
|
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
|
A Eukaryote is any organism whose cells contains organelles which are enclosed within membranes.
|
|
|
Name the three types of pathogens.
|
Bacteria, Fungi and virus.
|
|
|
Name the method in which Bacteria reproduce.
|
Bacteria use the method of binary fission to reproduce asexually.
|
|
|
Name the the biproduct produced by yeast when producing energy anaerobically.
|
Ethanol
|
|
|
How are red blood cells adapted for their job of carrying oxygen around the body?
|
Red blood cells are adapted to have their concave shape to increase surface area to maximise the amount of oxygen they carry. They also have a thin membrane to allow easy diffusion of oxygen in and out of the cell.
|
|
|
What is photosynthesis?
|
The process in which green plants produce food (glucose).
|
|
|
Which layer of the leaf is adapted for photosynthesis?
|
The palisade layer.
|
|
|
Things that slow down photosynthesis.
|
Lack of water, Lack of carbon dioxide, Lack of sunlight or it is too hot.
|
|
|
Why do plants store glucose?
|
Because glucose is soluble in the water, plants store glucose as starch; as it is insoluble. Starch is stored in the seeds, tubers, leaves as well as in the produce - fruit and vegetables.
|
|
|
What is Hydroponics?
|
Hydroponics is where you grow plants without the use of soil, instead they grow plants in water which contains all the vitamins and minerals which the plants need.
|
|
|
What factors affect living organisms?
|
Sunlight, Space, Food and Water.
|
|
|
How to increase photosynthesis inside a greenhouse?
|
Have lights within the greenhouse so in the winter, the plants still have a constant source of light. Increase the volume of carbon dioxide inside using aspirator some. Have a constant source of water. And have heaters to retain a constant heat inside.
|
|
|
What are enzymes?
|
Enzymes are catalysts which help speed up chemical reactions but don't get used up themselves.
|
|
|
What can affect enzymes?
|
All enzymes have an optimum pH that they work best at. It's often neutral pH 7, however not always Pepsin an enzyme which breaks down proteins in the stomach works best at pH 2, which means it's well suited to acidic conditions. As well as this enzymes like any reaction, a higher temperature increases the rate at first. However if they get too hot, some of the bonds holding the enzyme together break - this destroys the enzymes special shape and so it won't work any more. It's said to be denatured.
|
|
|
Give an example of using an enzyme in the industry.
|
We can use protease to 'predigest' some of the protein in baby foods so that it is easier to digest for babies.
We also use the enzyme isomerase to convert glucose syrup into fructose syrup. We do this because fructose syrup is sweeter than normal syrup so you use less of it. We use fructose syrup in dieting foods. |
|
|
Where does aerobic respiration happen?
|
It happens within the mitochondria in cells.
|
|
|
What is mitosis?
|
A process which is used to create identical cells.
|
|
|
What are the four different bases that form DNA called?
|
Thymine & Adamine, Cytosine & Guanine
|
|
|
What do chromosomes contain?
|
Chromosomes contain genes which hold DNA.
|
|
|
How many pairs of chromosomes are in a normal human body cell?
|
23 pairs or 46 chromosomes.
|
|
|
What is a allele?
|
Alleles are different versions of the same gene.
|
|
|
What is speciation?
|
Speciation is the development of a new species.
|
|
|
What leads to speciation?
|
Isolation and Natural Selection.
Isolation is where populations of species are separated. This can happen due to a physical barrier. E.g. floods and earthquakes can cause barriers the geographically isolate some individuals from the main population. Because the environment is different on each side, the species will evolve of over hundreds of years to adapt to have a better chance of survival and so they are more likely to breed so the beneficial characteristics are passed on the next generation. This is natural selection. |
|
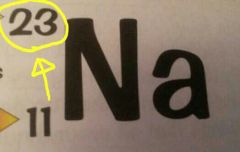
What is this number?
|
The mass number - the total number of protons and neutrons
|
|

What is this number?
|
The atomic number - number of protons
|
|
|
What is a isotope?
|
Isotopes are different atomic forms of the same element, which have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
|
|
|
What is ionic bonding?
|
Ionic bonding is the transference of electrons. In ionic bonding, atoms lose or gain electrons to form charged particles (called ions) which are then strongly attracted to one another (because of the attraction of opposite charges, + and - ).
|
|
|
Which groups do ionic bonds usually form between?
|
Groups 1 & 2, and 6 & 7. Ionic bonds only happen between metals and non metals.
|
|
|
What type of structure down a ionic compound have?
|
The ions form a closely packed regular lattice arrangement
|
|
|
What properties does a ionic compound have?
|
All ionic compounds have similar properties which consist of high melting and boiling points due to the strong attraction between the ions.
|
|
|
What is velocity? |
A speed of something in a given direction. |
|
|
What unit do we measure both speed and velocity in? |
m/s (or km/h or mph) |
|
|
What is the difference between speed and velocity? |
Speed is just how fast you are going (e.g. 30 mph) with no regard to the direction whereas volocity is speed with a direction. Speed is a scalar quantity - it is the magnitude of velocity. |
|
|
What does the gradient of a distance - time graph tell us? |
It tells us how fast a object is travelling. |
|
|
What do curves represent on a distance - time graph? |
Curves represent acceleration or deceleration. |
|
|
How to caculate speed on a distance - time graph? |
Soeed = Gradient = Vertical ÷ Horizontal |
|
|
What is acceleration? |
The rate of change in velocity per unit of time. |
|
|
What unit do we use for acceleration? |
m/s^2 ( metres per second squared) |
|
|
What do flat sections in a velocity time graph represent? |
They represent a steady speed. |
|
|
Whatvis gravitational force? |
Gravitational force is the force of attraction between ALL MASSES. |
|
|
What is the difference between weight and mass? |
Weight is caused by the pull of the gravitational force, whereas mass is just the amount of 'stuff' in an object. |
|
|
True or false, an object will have the same mass whether it's on Earth or on the Moon. |
True, but it's weight will be different. |
|
|
How do you work out weight? |
Weight = Mass × Gravitational field strength |
|
|
What unit do we measure weight in? |
Newtons (N) |
|
|
What is a resultant force? |
Resultant force is the overall force in a point or object. |
|
|
What thing does an object need to carry on at a steady speed? |
It needs zero resultant force. |
|
|
True or false, reaction forces are equal and opposite |
True |

