![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Steps of the scientific method? ex) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. |
1.state the problem 2.gather information 3.form a hypothesis 4.test hypothesis 5.analyze data 6.draw conclusions |
|
|
what exactly is the scientific method? (not the steps) |
series of steps in which a question or problem is investigated by observing and experimenting |
|
|
observation: |
bits of information gathered with the senses |
|
|
inference: |
conclusion draw from an observation |
|
|
hypothesis: |
statement that can be tested
|
|
|
independent variable: |
single factor in an experiment that the experimenter changes |
|
|
dependent variable: |
factor that will be measured in an experiment |
|
|
constant: |
factor that stays the same through all phases of an experiment |
|
|
control: |
standard use for comparison in an experiment |
|
|
physical property: |
characteristics that can be observed using the five senses, without changing or trying to change the composition of the substance |
|
|
chemical property: |
characteristics that cannot be observe without changing the substance |
|
|
physical change: |
change in which the form or appearance of matter changes, but not its composition |
|
|
vaporization: |
liquid to gas |
|
|
condensation: |
gas to liquid |
|
|
sublimation: |
solid to gas |
|
|
deposition: |
gas to solid |
|
|
chemical change: |
change in which the composition of a substances changes |
|
|
Law of Conservation: |
states that mass is neither created nor destroyed-and as a result the mass of the substance before a physical or chemical change is equal to the mass of the substance present after the change |
|
|
list five signs of a physical change ex) example, example, example, example, example |
changes color, energy, odor, gases or solids, not easily reversed |
|
|
list 3 signs of a physical change: ex) example, example, example |
shape, state, dissolves |
|
|
list physical properties: ex) example, example, example, example |
density, mass, volume, melting/boiling point, solubility, ability to attract a magnet, state of matter, color |
|
|
substance: |
matter that has the same fixed composition |
|
|
heterogeneous mixture: |
not evenly mixed |
|
|
homogeneous mixture: |
mixed evenly |
|
|
solution |
another name for homogeneous mixture |
|
|
solute |
substance that dissolves |
|
|
solvent |
dissolves the solute |
|
|
precipitate |
result of a chemical change |
|
|
aqueous |
solution where water is the solvent |
|
|
acid |
substance that release positively charged ions |
|
|
base |
substance that accepts hydrogen ions |
|
|
pH |
measurement of how acidic or basic things are |
|
|
neutralization |
reaction of acid plus base |
|
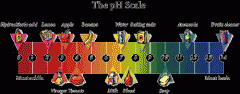
what is this and what does it mean? |
ph scale, measures how acidic or basic things are. |
|
|
what is most likely the ph of water? a) ph 2 b) ph 7 c) ph 14 d) ph 8 |
ph 7 |
|
|
what is most likely the ph of hand soap? a) ph 3 b) ph 9 c) ph 14 d) ph 10 |
ph 10 |
|
|
what is 7 on the ph scale? |
neutral |
|
|
list 5 homogeneous mixtures |
shampoo, sugar and water, frozen pop, koolaid, soap and water. |
|
|
list 5 heterogeneous mixtures |
salad, watermelon, backpack, strawberry, tomato |
|
|
displacement? |
distance and direction between starting and ending point |
|
|
speed? |
distance divided by time |
|
|
velocity? |
displacement divided by time |
|
|
acceleration? |
change in velocity divided by the time it took |
|
|
formula for speed? |
d/t |
|
|
force? |
push or pull |
|
|
Newton's first law of motion? |
object will stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. |
|

what does this represent?
|
balanced forces |
|
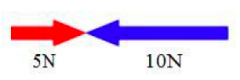
what does this represent?
|
unbalanced forces |
|
|
Newtons second law |
if you push something with force then that thing will go in the direction of that force |
|
|
friction |
force that resists sliding |
|
|
newtons 3rd law |
forces act in equal but opposite pairs |

