![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the independent variable? |
The variable that is changed or manipulated in the experiment |
|
|
What are constants on an experiment ? |
They are all the factors in an experiment that are kept the same in all the groups being tested |
|
|
The more _______ done of an experiment, the more reliable the results of that experiment are. |
trials |
|
|
What is the dependent variable |
It is the responding variable in an experiment. |
|
|
What part of the scientific method are you performing if you are listening to the sounds that whales are making? |
Observing |
|
|
What part of the scientific method are you performing if you are writing down an educated guess about how you think the experiment will turn out? |
Forming a hypothesis |
|
|
What part of the scientific method are you performing if you are making charts and graphs that show your data visually? |
Analyzing data |
|
|
After we perform an experiment, what is the next step in the scientific method? |
Analyze data |
|
|
A scientist wants to perform an experiment to study the effects of a new fertilizer on plants. What would he need to include in his experiment to be able to truly see how effective the fertilizer is? |
a control group that doesn’t receive fertilizer |
|
|
Sponge Bob loves to garden and wanted to grow lots of pink flowers for his pal Sandy. He bought a special Flower fertilizer to see if it would help produce more flowers. He planted two plants of the same size and variety in identical containers with the same amount and type of soil. The plants were both placed in his kitchen window. Using water from his sink, Sponge Bob watered one container (labeled A) with the special fertilizer mixture and the other container (labeled B) was watered with water that did not contain the fertilizer. He made sure to water each plant with the same amount of water. Each week, he measured the plants and counted how many pink flowers were on each the plants. At the end of four weeks, plant A was twice the size as plant B and it had three times as many pink flowers on it. a. What is the control? b. What is the independent variable? c. What is the dependent variable?
|
a. Plant B
b. Special fertilizer
c. number of pink flowers
|
|
|
Which of the following would be an acceptable hypothesis? a. Are double stuffed oreos actually filled twice as much as regular oreos? b. If oreos are double stuffed, they taste better than regular oreos.
|
c. If oreos are double stuffed, then they contain twice as much filling as regular oreos. |
|
|
A hypothesis must be _______ |
A hypothesis must be testable |
|
|
What is the name of the curve you see at the top of a liquid in a cylinder? |
meniscus |
|
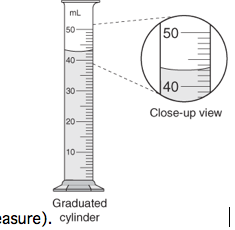
What is the volume of the liquid below? |
43 mL |
|

What is the mass shown below? |
135.7 g |
|
|
Which piece of lab equipment is best to use if you need to transfer 10 drops of a liquid from one test tube to another? |
Dropper |
|
|
Which piece of lab equipment would you use to measure the length of the windows? |
Meter stick |
|
|
Which of the following is the correct units of measurement if you are measuring the volume of a liquid in a beaker? |
Milliliters (mL) |
|
|
cells |
The basic unit of structure and function in living things |
|
|
organelles |
The small bodies in cells that have a specific function |
|
|
What scientist discovered and named cells after studying cork through a microscope? |
Hooke |
|
|
What scientist made his own microscopes and discovered small cells, which he called “animalcules”, swimming in pond water? |
Leeuwenhoek |
|
|
What was Schwann’s theory? |
All animals are made out of cells |
|
|
What was Schleiden’s theory? |
All plants are made out of cells
|
|
|
What was Virchow’s theory? |
All cells come existing cells |
|
|
Name the 3 parts of the Cell Theory:
|
1. All living things are made out of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function and structure in living things 3. Cells come from existing cells
|
|
|
Why do cells need to be small? |
because they need to get food in and waste out |
|
|
What is the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? |
Prokaryote cells have no nucleus and no membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. |
|
|
What two structures are only found in plant cells? |
Chloroplast and cell wall |
|
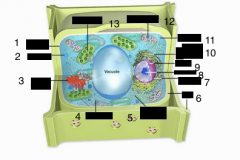
label 1,,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13 |
1. Plasma membrane 3. Golgi complex 4. Ribosomes 5. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 6. Cell wall 8. Nucleolus 9. Nucleus 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 11. Cytoplasm 12. Mitochondria 13. Chloroplast
|
|
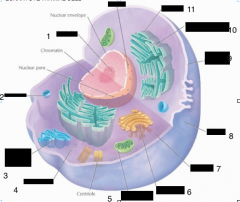
label 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12 |
1. Nucleolus 2. Lysosome 3. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 4. Free ribosome 5. Mitochondrion 6. Golgi complex 7. Cytoplasm 8. Cell coat 9. Plasma membrane 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 11. Ribosome 12. Nucleus
|
|
|
What is the surrounding of all cells that controls what enters and leaves the cell? |
Cell membrane |
|
|
This is the supportive outer covering of plant and bacteria cells. |
Cell wall |
|
|
An organelle that is used for storage in cells. |
Vacuoles |
|
|
The organelle that uses part of its' membrane to package things like proteins. |
Golgi complex |
|
|
A series of folded membranes that move materials around in a cell. It is also the place where proteins and lipids are made. |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
The part of the cell that contains the genetic material and controls the cells activities. |
Nucleus |
|
|
This organelle contains the RNA to make proteins. |
Nucleolus |
|
|
True or False: The chromosomes contain instructions for traits and characteristics. |
True |
|
|
Mitochondria |
the organelles where energy is created. |
|
|
Chloroplast |
the cell organelle that is the site of photosynthesis. |
|
|
The control center of the cell |
nucleus |
|
|
The organelles that contain digestive enzymes. |
Lysosomes |
|
|
Which organelle modifies, packages, and delivers protein, acting as the post office of the cell? |
Golgi complex |
|
|
Which organelle makes protein? |
Ribosome |
|
|
What are the two types of Endoplasmic Reticulum? |
Rough and Smooth |
|
|
Muscle cells need more energy than most types of cells. Therefore, which organelle would be more numerous in muscle cells?
|
mitochondria |
|
|
In plant cells, ________ is the way plants use energy from the sun to make food.
|
photosynthesis |
|
|
chlorophyll. |
The green pigment that captures sunlight energy for photosynthesis to take place |
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
This is the process where our cells use oxygen to make energy from food. |
|
|
Cellular respiration takes place in what cell organelle? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
After exercising, your muscles are sore and tired due to the build up of lactic acid. What cellular process causes this? |
Fermentation |
|
|
ATP |
The molecule of energy that is created during cellular respiration |
|
|
The cell membrane only allows certain molecules into and out of the cell, so it is called _______ |
semipermeable |
|
|
Which type of cell membrane transport does NOT require energy? |
Passive transport |
|
|
Which type of transport would occur when the cell membrane encloses around nutrients and brings them into the cell by forming a vesicle?
|
endocytosis |
|
|
Which type of transport occurs when glucose moves through a protein across the membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration? |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Which type of transport occurs when water moves through the cell membrane from high concentration to low concentration? |
osmosis |
|
|
List the phases of mitosis in order. |
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
cell cycle |
The life cycle of the cell |
|
|
The process of cell division, in eukaryotic cells, that forms two new nuclei is known as _______
|
mitosis |
|
|
What is the name of bacterial cell division called? |
Binary Bission |
|
|
During cytokinesis, a _________ forms between the new plant cells.
|
cell plate |
|
|
How do the two cells created through mitosis compare to the original cell? |
they are identical |
|
|
During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication, or copying, occur?
|
interphase |
|
|
Division of the cytoplasm that separates the dividing cell into two cells is called _________ |
cytogenesis |
|
|
In animal cells, what structure pinches in to separate the dividing cell into two cells? |
Contractile ring |
|
|
After cell division has occurred, what phase of the cell cycle are the two new cells in? |
Interphase |
|
|
What disease occurs when cells divide uncontrollably? |
cancer |
|
|
Label a, b, c ,d , e, and f |
A=Telophase B=Interphase C= Prophase F=Metaphase E=Anaphase D= Cytokinesis |
|
|
When cells divide normally, a group of the same type of cells work together to form a(n) |
tissue |
|
|
A group of tissues that work together make up a(n) |
organ |
|
|
A group of organs that work together make up a(n) |
organ system |
|
|
Why does mitosis occur? |
Growth, repair, replacing dying cells |
|
|
What substance lines the digestive tract to help food move through and to protect organs from the acid? |
mucus |
|
|
The type of digestion in which food is mashed, crushed, and broken up is called |
mechanical digestion |
|
|
What is the wave-like muscle movements that move food through the digestive tract? |
peristalsis |
|
|
What type(s) of digestion occurs in the stomach? |
mechanical and chemical |
|
|
Partially digested food that is ready to leave the stomach is called _______ |
chyme |
|
|
Name 3 organs that are NOT part of the digestive system. |
Liver Gallbladder pancreas |
|
|
Which organ stores, compacts, and eliminates waste material? |
Large intestine |
|
|
What is the name of the organ that produces bile? |
Liver |
|
|
List the order that food goes through the digestive tract organs. |
Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus |
|
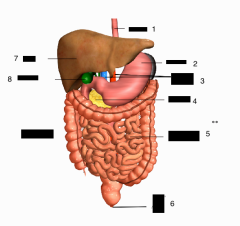
Label 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 |
1. Esophagus 2. Stomach 3. Blood Vessels 4. Pancreas 5. Small Intestines 6. Anus 7. Liver 8. Gall Bladder 9. Large intestine |
|
|
At the elbow, the radius and ulna of the lower arm meet the humerus of the upper arm. What type of connective tissue holds these bones together in the elbow joint? |
Ligaments |
|
|
What type of muscle is found in the bicep? |
Skeletal muscle |
|
|
What type of muscle is involved in peristalsis that occurs in the digestive tract? |
Smooth muscle |
|
|
What type of muscle action would your heart beating involve? |
involuntary muscle |
|
|
In your arm, your bicep muscle is attached to a bone in the shoulder and to a bone in the forearm. Which type of connective tissue connects the bicep muscle to those bones? |
Tendons |
|
|
The material within bones that makes blood cells is called |
Red Marrow |
|
|
The kind of exercise that helps strengthen your heart and increase your endurance is __________ |
Aerobic exercise |
|
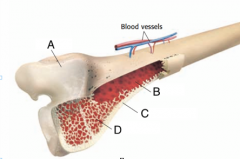
label a, b, c ,d |
A= cartilage B=Marrow C=compact bone D=spongy bone
|
|
|
The pharynx splits into 2 tubes. Which is the tube that air enters? |
Larynx |
|
|
What are the pair of elastic bands that stretch across the larynx and produce sound? |
Vocal chords |
|
|
The windpipe that sits below the larynx is called the _______ |
Trachea |
|
|
What is the dome-shaped muscle that sits below the lungs that assits with allowing inhaling and exhaling to occur? |
Diaphragm |
|
|
In order for you to inhale, what must your diaphragm do? |
Contract and Move down |
|
|
What two muscles in the respiratory system make it possible for breathing to take place? |
Rib muscles and diaphragm |
|
|
What two reactants do we need for cellular respiration to begin? |
Oxygen and glucose |
|
|
Along with energy (ATP), what other two products are created during cellular respiration? |
Carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
List the order of the structures of the respiratory system that air passes through starting with the nose and ending with the alveoli. |
Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli |
|
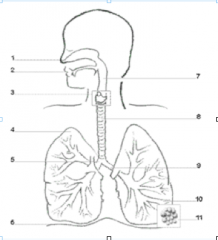
|
1- nose 2-mouth 3-larynx 4- lungs 5-bronchius 6- diaphragm 7-pharynx 8-trachea 9-bronchus (5 and 9 together are the bronchi) 10- bronchioles 11-alveoli
|
|
|
What type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart? |
Arteries |
|
|
What side of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs? |
Right side |
|
|
What type of circulation occurs between the heart and the lungs? |
Pulmonary circulation |
|
|
Which side of the heart pumps oxygen- rich blood to the body? |
Left side |
|
|
What type of blood cell contains the protein hemoglobin that allows them to transport oxygen?
|
Red blood cell |
|
|
This is the component of blood that forms clots at a cut or wound to prevent excessive blood loss. |
Platelets |
|
|
How many chambers are located in our heart?
|
4 chambers |
|
|
Which chamber of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs? |
Left atrium |
|
|
List the order of blood flow from the right atrium back to the right atrium.
|
Right atrium right ventricle, lungs left atrium left ventricle arteries capillaries, veins right atrium |
|
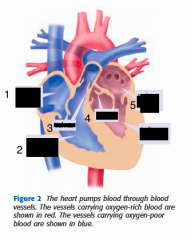
label 1,2,3,4,5,6 |
1. Right atrium 2. Right ventricle 3. valves 4. valves 5. Left atrium 6. Left ventricle
|
|
|
A joint that allows the knee enables you to flex and extend . |
hinge joint |

